Record - cloudfront.net
... river basins - as well as their internal structure. Y.A. Mescherikov, 196~. Branch of geomorphology studying the tectonic influences of large elements of relief, elucidating the connection between surficial features and underlying ...
... river basins - as well as their internal structure. Y.A. Mescherikov, 196~. Branch of geomorphology studying the tectonic influences of large elements of relief, elucidating the connection between surficial features and underlying ...
Structure
... layer as it intersects with a horizontal surface • Dip – is measured at right angles to strike and is the amount of tilting of the formation (angle at which the bed is inclined from the horizontal) ...
... layer as it intersects with a horizontal surface • Dip – is measured at right angles to strike and is the amount of tilting of the formation (angle at which the bed is inclined from the horizontal) ...
Field Guide to Tectonic Evolution of Utah`s Central Wasatch
... took decades for the geological community to rediscover. For example, his discovery of ancient shorelines of Lake Bonneville led him to theories about climate change and isostatic rebound. His mapping scarps along the Wasatch Fault led to ideas about elastic rebound on faults as the cause of earthqu ...
... took decades for the geological community to rediscover. For example, his discovery of ancient shorelines of Lake Bonneville led him to theories about climate change and isostatic rebound. His mapping scarps along the Wasatch Fault led to ideas about elastic rebound on faults as the cause of earthqu ...
Word format
... Folds consist of two sides that have the beds dipping in opposite directions to each other (away from each other in an anticline, and towards each other in a syncline). Each side of the fold is called a _________________. Every fold has 2 fold limbs with one always being shared with the fold right n ...
... Folds consist of two sides that have the beds dipping in opposite directions to each other (away from each other in an anticline, and towards each other in a syncline). Each side of the fold is called a _________________. Every fold has 2 fold limbs with one always being shared with the fold right n ...
DATING ROCK LAYERS RELATIVE DATING
... Oblique-slip faulting suggests both dip-slip faulting and strike-slip faulting. It is caused by a combination of shearing and tension or compressional forces. Nearly all faults will have some component of both dip-slip (normal or reverse) and strike-slip, so defining a fault as oblique requires both ...
... Oblique-slip faulting suggests both dip-slip faulting and strike-slip faulting. It is caused by a combination of shearing and tension or compressional forces. Nearly all faults will have some component of both dip-slip (normal or reverse) and strike-slip, so defining a fault as oblique requires both ...
Geologic Structures and Deformation
... • imaginary line constructed on the down slope surface of a sedimentary bed or fault--dip has 2 attributes: 1)bearing of dip is perpendicular to strike direction; 2)angle of dip measured from horizontal plane to top of bed or fault-dip cannot exceed 90 degrees • In a series of dipping sedimentary ro ...
... • imaginary line constructed on the down slope surface of a sedimentary bed or fault--dip has 2 attributes: 1)bearing of dip is perpendicular to strike direction; 2)angle of dip measured from horizontal plane to top of bed or fault-dip cannot exceed 90 degrees • In a series of dipping sedimentary ro ...
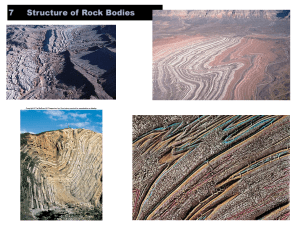
7 Structure of Rock Bodies
... deform by changing shape or position. Geologists call the change in shape strain. In other words, differential stress causes strain. Although strain proceeds by several complex phenomena, two end-member styles of deformation are recognized, with all gradations between them being possible. Under some ...
... deform by changing shape or position. Geologists call the change in shape strain. In other words, differential stress causes strain. Although strain proceeds by several complex phenomena, two end-member styles of deformation are recognized, with all gradations between them being possible. Under some ...
Chapter 11 Section 1
... • The amount of stress that rock can withstand without permanently changing shape is limited. • If a stress exceeds the rock’s limit, the rock’s shape ...
... • The amount of stress that rock can withstand without permanently changing shape is limited. • If a stress exceeds the rock’s limit, the rock’s shape ...
Structures, Mountains and Continents
... • The axial plane divides a fold into its two limbs – The surface trace of an axial plane is called the hinge line (or axis) of the fold ...
... • The axial plane divides a fold into its two limbs – The surface trace of an axial plane is called the hinge line (or axis) of the fold ...
Structures ppt - Jan Rasmussen.com
... inclined plane with a horizontal plane Dip is the direction in which and the angle downward from horizontal at which a plane is oriented ...
... inclined plane with a horizontal plane Dip is the direction in which and the angle downward from horizontal at which a plane is oriented ...
File - Varsity Field
... A. The limbs dip at different angles from one another. B. The limbs both dip in the same direction. C. The axial plane is not vertical. D. The fold axis is not horizontal. ...
... A. The limbs dip at different angles from one another. B. The limbs both dip in the same direction. C. The axial plane is not vertical. D. The fold axis is not horizontal. ...
90 Tectonic and Structural Geomorphology I. Introduction To Plate
... Generally: as stress is applied to rocks at low temp, and low press, rocks will first deform elastically (with ability to return to original size and shape once stress is removed), once the level of stress exceeds the elastic limit of a given type of rock (i.e. the point or strength of a rock, with ...
... Generally: as stress is applied to rocks at low temp, and low press, rocks will first deform elastically (with ability to return to original size and shape once stress is removed), once the level of stress exceeds the elastic limit of a given type of rock (i.e. the point or strength of a rock, with ...
Earth,Notes,RevQs,Ch10
... farther out on the limbs; thus after erosion, older strata are exposed along the axial part of the fold. Synclines are folds with two, well-defined limbs that dip inward toward a long, linear, fold axis. Strata are lowered or buckled down in the axial region; thus after erosion, younger strata are e ...
... farther out on the limbs; thus after erosion, older strata are exposed along the axial part of the fold. Synclines are folds with two, well-defined limbs that dip inward toward a long, linear, fold axis. Strata are lowered or buckled down in the axial region; thus after erosion, younger strata are e ...
The evolution of the southern Cordilleran foreland thrust and fold
... crystalline basement that are associated with the margins of former sedimentary basins. These structures, which are of crustal dimensions (3 to >10 km of throw), include the northeastern margin of the Mesoproterozoic Belt-Purcell basin, the boundary between the Cordilleran miogeocline and the craton ...
... crystalline basement that are associated with the margins of former sedimentary basins. These structures, which are of crustal dimensions (3 to >10 km of throw), include the northeastern margin of the Mesoproterozoic Belt-Purcell basin, the boundary between the Cordilleran miogeocline and the craton ...
Overheads shown in Lab on Geologic Maps
... • Determine the structure of rocks from the pattern created by the intersection of dipping layers with the (level) land surface. • Use strike, dip, and other map symbols to determine structure. • Formation: discrete mappable rock unit • Map notation of a formation: – Ex.: formation name age notation ...
... • Determine the structure of rocks from the pattern created by the intersection of dipping layers with the (level) land surface. • Use strike, dip, and other map symbols to determine structure. • Formation: discrete mappable rock unit • Map notation of a formation: – Ex.: formation name age notation ...
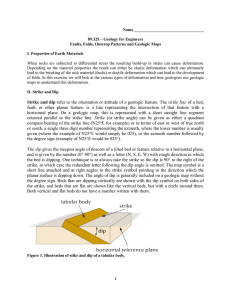
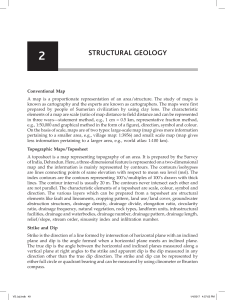
Strike and dip refer to the orientation or attitude of a geologic feature
... horizontal plane. On a geologic map, this is represented with a short straight line segment oriented parallel to the strike line. Strike (or strike angle) can be given as either a quadrant compass bearing of the strike line (N25°E for example) or in terms of east or west of true north or south, a si ...
... horizontal plane. On a geologic map, this is represented with a short straight line segment oriented parallel to the strike line. Strike (or strike angle) can be given as either a quadrant compass bearing of the strike line (N25°E for example) or in terms of east or west of true north or south, a si ...
Part B KEY
... During the ice age the enormous weight of the glaciers pushed the lithosphere down. But when the glaciers melted the weight was removed and the lithosphere has ...
... During the ice age the enormous weight of the glaciers pushed the lithosphere down. But when the glaciers melted the weight was removed and the lithosphere has ...
The Sevier Orogeny The Sevier orogeny took place at about the
... and uplift. The Laramide orogeny in its various manifestations involves deeply penetrating, steeply dipping reverse faults that deform and fault crystalline basement rocks. The Sevier orogeny was a more ‘thin-skinned’ deformation event. It is characterized by shallow thrust faults affecting only Pal ...
... and uplift. The Laramide orogeny in its various manifestations involves deeply penetrating, steeply dipping reverse faults that deform and fault crystalline basement rocks. The Sevier orogeny was a more ‘thin-skinned’ deformation event. It is characterized by shallow thrust faults affecting only Pal ...
Structures - MSU Billings
... • The axial plane divides a fold into its two limbs – The surface trace of an axial plane is called the hinge line (or axis) of the fold ...
... • The axial plane divides a fold into its two limbs – The surface trace of an axial plane is called the hinge line (or axis) of the fold ...
Overview of Geologic Structures
... Generally: as stress is applied to rocks at low temp, and low press, rocks will first deform elastically (with ability to return to original size and shape once stress is removed), once the level of stress exceeds the elastic limit of a given type of rock (i.e. the point or strength of a rock, with ...
... Generally: as stress is applied to rocks at low temp, and low press, rocks will first deform elastically (with ability to return to original size and shape once stress is removed), once the level of stress exceeds the elastic limit of a given type of rock (i.e. the point or strength of a rock, with ...
Deformation - Bakersfield College
... Folds • Common types of folds • Monoclines – large, step-like folds in otherwise horizontal ...
... Folds • Common types of folds • Monoclines – large, step-like folds in otherwise horizontal ...
STRUCTURAL GEOLOGY
... Folds are wavy undulations or flexures which are developed in country rocks whenever areas are subjected to several pressures of stress and are secondary structures. The two idealized folds are cylindrical and conical. A synform is a fold that concaves upwards and the limbs dip towards each other and ...
... Folds are wavy undulations or flexures which are developed in country rocks whenever areas are subjected to several pressures of stress and are secondary structures. The two idealized folds are cylindrical and conical. A synform is a fold that concaves upwards and the limbs dip towards each other and ...
File
... A special compass is used by geologists for the purpose of recording the orientation and dip of planar rock structures like folds, beds, faults, and metamorphic laminations. These measurements are reported on 2-D geological maps to help geologists see how the structure is are oriented relative to th ...
... A special compass is used by geologists for the purpose of recording the orientation and dip of planar rock structures like folds, beds, faults, and metamorphic laminations. These measurements are reported on 2-D geological maps to help geologists see how the structure is are oriented relative to th ...
Chapter 9 of Earth
... • Parts of a fold (limbs, axial plane, axis) Note: Anticlines and synclines are structures in rocks, not surface landforms ...
... • Parts of a fold (limbs, axial plane, axis) Note: Anticlines and synclines are structures in rocks, not surface landforms ...