OBJECTIVE WORKSHEET Quantum Theory 1. How did
... 3. How many energy levels for electrons does the chapter discuss? 4. Who discovered the QUANTUM MECHANICAL MODEL? 5. What shape does the s and p orbitals have? 6. What does "n" stand for when we discuss atomic orbitals? 7. What is the maximum number of electrons allowed in when n=4? 8. What is "neon ...
... 3. How many energy levels for electrons does the chapter discuss? 4. Who discovered the QUANTUM MECHANICAL MODEL? 5. What shape does the s and p orbitals have? 6. What does "n" stand for when we discuss atomic orbitals? 7. What is the maximum number of electrons allowed in when n=4? 8. What is "neon ...
The Zeeman Effect
... The same expressions, but with ml and ms replaced by ML and MS, apply to the combined magnetic moments of several coupled electrons. When an atom has L≠0 and S≠0, these net magnetic moments are simply additive. Spin-orbit coupling (itself a magnetic effect) is usually large enough that the total ele ...
... The same expressions, but with ml and ms replaced by ML and MS, apply to the combined magnetic moments of several coupled electrons. When an atom has L≠0 and S≠0, these net magnetic moments are simply additive. Spin-orbit coupling (itself a magnetic effect) is usually large enough that the total ele ...
Dark Matter and Dark Energy - Hitoshi Murayama Home Page
... • “Anti-matter attraction” cancels “Likecharge repulsion” • It does not cost too much energy to tightly pack the electric charge inside the electron • Needed anti-matter: double #particles • Theory of electromagnetism now works at very short distances (12 digits accuracy!) ...
... • “Anti-matter attraction” cancels “Likecharge repulsion” • It does not cost too much energy to tightly pack the electric charge inside the electron • Needed anti-matter: double #particles • Theory of electromagnetism now works at very short distances (12 digits accuracy!) ...
Quantum simulators of lattice gauge theories
... are too big). Exceptions from this rule are possible for quantum simulators that exhibit novel, only theoretically predicted and not yet observed phenomena (simulating ≠ simulating and observing). IV. Quantum simulator should allow for broad control of the parameters of the simulated model, and for ...
... are too big). Exceptions from this rule are possible for quantum simulators that exhibit novel, only theoretically predicted and not yet observed phenomena (simulating ≠ simulating and observing). IV. Quantum simulator should allow for broad control of the parameters of the simulated model, and for ...
Ch. 6 notes
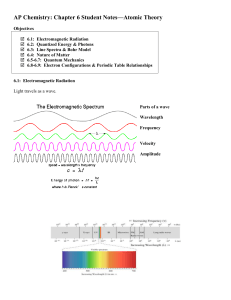
... 6.5-6.7: Quantum Mechanics Developed by Werner Heisenberg (1901-1976), Louis De Broglie (1892-1987), Erwin Schrodinger (1887-1961) This answers the question: Where is the _____________ in the atom? The answer is complex. We can’t say exactly where the atom is. We can only say where we think it _____ ...
... 6.5-6.7: Quantum Mechanics Developed by Werner Heisenberg (1901-1976), Louis De Broglie (1892-1987), Erwin Schrodinger (1887-1961) This answers the question: Where is the _____________ in the atom? The answer is complex. We can’t say exactly where the atom is. We can only say where we think it _____ ...
Abstracts
... effects of interactions on the condensation of a dilute trapped atomic gas. First, we experimentally scrutinised the concept of purely statistical saturation of the thermal component as the driving mechanism for condensation [1]. We show that under usual experimental conditions ultracold atomic gase ...
... effects of interactions on the condensation of a dilute trapped atomic gas. First, we experimentally scrutinised the concept of purely statistical saturation of the thermal component as the driving mechanism for condensation [1]. We show that under usual experimental conditions ultracold atomic gase ...
CH7 handout is here.
... o Line Spectra and the Rydberg Equation o Bohr Model of the Hydrogen Atom o Energy Levels of the Hydrogen Atom 7.3The Wave-Particle Duality of Matter and Energy o Wave Nature of Electrons and Particle Nature of Photons o Heisenberg's Uncertainty Principle 7.4The Quantum-Mechanical Model of the Atom ...
... o Line Spectra and the Rydberg Equation o Bohr Model of the Hydrogen Atom o Energy Levels of the Hydrogen Atom 7.3The Wave-Particle Duality of Matter and Energy o Wave Nature of Electrons and Particle Nature of Photons o Heisenberg's Uncertainty Principle 7.4The Quantum-Mechanical Model of the Atom ...
1. Crystal Properties and Growth of Semiconductors
... Shortest Course in Quantum Mechanics, Cont. Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle (Nobel prize 1932 for the creation of quantum mechanics) The more precise you know the position of a particle , the less precise you know the momentum of the ...
... Shortest Course in Quantum Mechanics, Cont. Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle (Nobel prize 1932 for the creation of quantum mechanics) The more precise you know the position of a particle , the less precise you know the momentum of the ...
Quantum mechanics in electronics
... Q-Computers use Q-bits which occupies the value 0, 1 or both simultaneously • Concepts used : entanglement , superposition ...
... Q-Computers use Q-bits which occupies the value 0, 1 or both simultaneously • Concepts used : entanglement , superposition ...
PHYS6520 Quantum Mechanics II Spring 2013 HW #5
... that your results for T (k) and R(k) have bound state poles at the expected positions when k is treated as a complex variable. (2) Modern Quantum Mechanics, Problem 6.3 (3) Modern Quantum Mechanics, Problem 6.4. I recommend Chapter 10 of the NIST Digital Library of Mathematical Functions at http://d ...
... that your results for T (k) and R(k) have bound state poles at the expected positions when k is treated as a complex variable. (2) Modern Quantum Mechanics, Problem 6.3 (3) Modern Quantum Mechanics, Problem 6.4. I recommend Chapter 10 of the NIST Digital Library of Mathematical Functions at http://d ...
Great Debates in IR theory
... • Believe there is not such thing as absolute certainty • But we can still falsify wrong conjectures • Theoretical and methodological diversity • Key strengths in social sciences ...
... • Believe there is not such thing as absolute certainty • But we can still falsify wrong conjectures • Theoretical and methodological diversity • Key strengths in social sciences ...