Quantum Theory
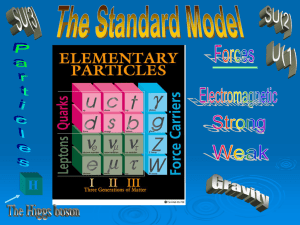
... Many new subatomic particles have been discovered. There are three families of particles. Each family contains two of the quarks, an electron (or one of its cousins), and one of the neutrinos. These are the building blocks of all matter. ...
... Many new subatomic particles have been discovered. There are three families of particles. Each family contains two of the quarks, an electron (or one of its cousins), and one of the neutrinos. These are the building blocks of all matter. ...
Matrix Models - Harvard Department of Mathematics
... Our understanding of string theory is still in its infancy. In most cases, we only know how to expand physical quantities in a power series in the string coupling constant, ~. Each term in the power series is given by a sum over Riemann surfaces (the string worldsheet) of a given genus. Different sp ...
... Our understanding of string theory is still in its infancy. In most cases, we only know how to expand physical quantities in a power series in the string coupling constant, ~. Each term in the power series is given by a sum over Riemann surfaces (the string worldsheet) of a given genus. Different sp ...
Quantum Numbers
... 7. Answer the following questions as a summary quiz on the chapter. [Check answer in book #78] a) The quantum number n describes the _______ of an atomic orbital. b) The shape of an atomic orbital is given by the quantum number ____. c) A photon of orange light has _____ (less or more) energy than ...
... 7. Answer the following questions as a summary quiz on the chapter. [Check answer in book #78] a) The quantum number n describes the _______ of an atomic orbital. b) The shape of an atomic orbital is given by the quantum number ____. c) A photon of orange light has _____ (less or more) energy than ...
6 Compact quantum spaces: “fuzzy spaces”
... • all other interactions: electroweak and strong interactions ...
... • all other interactions: electroweak and strong interactions ...
Quantum Numbers
... • Excited state: Higher potential energy than ground state. • Photon: A particle of electromagnetic radiation having zero mass and carrying a quantum of energy (i.e., packet of light) • Only certain wavelengths of light are emitted by hydrogen atoms when electric current is passed through—Why? Mulli ...
... • Excited state: Higher potential energy than ground state. • Photon: A particle of electromagnetic radiation having zero mass and carrying a quantum of energy (i.e., packet of light) • Only certain wavelengths of light are emitted by hydrogen atoms when electric current is passed through—Why? Mulli ...
The Quantum Mechanical Model
... 16. _____ The spin quantum number can have up to four values. 17. _____ The s orbital has a spherical shape. 18. _____ The principal quantum number designates the principal energy level occupied by the electron. 19. _____ The term for the discrete energy levels of an electron is quantal. 20. _____ T ...
... 16. _____ The spin quantum number can have up to four values. 17. _____ The s orbital has a spherical shape. 18. _____ The principal quantum number designates the principal energy level occupied by the electron. 19. _____ The term for the discrete energy levels of an electron is quantal. 20. _____ T ...
The Higgs Boson and Fermion Masses
... Antiparticles are created at accelerators in ensemble with particles but the visible Universe does not contain antimatter ...
... Antiparticles are created at accelerators in ensemble with particles but the visible Universe does not contain antimatter ...
Constructive Interference
... exist in stable configurations around nuclei Wavefunctions and energies for these configurations determine most properties of matter ...
... exist in stable configurations around nuclei Wavefunctions and energies for these configurations determine most properties of matter ...
Homework Set 1
... atom. (This formula foreshadows the fact that, in general, the ground state of any system is the most in need of a quantum description.) c. Taking λ/r ≤ 0.1 as the (arbitrary) cut-off when classical mechanics begins to be valid as Bohr’s quantum number n increases, calculate the lowest (smallest n) ...
... atom. (This formula foreshadows the fact that, in general, the ground state of any system is the most in need of a quantum description.) c. Taking λ/r ≤ 0.1 as the (arbitrary) cut-off when classical mechanics begins to be valid as Bohr’s quantum number n increases, calculate the lowest (smallest n) ...
What is the quantum state?
... What now? • A quantum state is not “experimenter’s information about the objective physical state of a system”. ...
... What now? • A quantum state is not “experimenter’s information about the objective physical state of a system”. ...
Lorentz violating field theories and nonperturbative physics
... In the last fifteen years, there has been growing interest in the possibility that Lorentz symmetry may not be exact. ...
... In the last fifteen years, there has been growing interest in the possibility that Lorentz symmetry may not be exact. ...