Summary Presentation, Topic 9.2 File
... The potential is therefore a measure of the amount of work that has to be done to move particles between points in a gravitational field and its units are J kg –1 The work done is independent of the path taken between the two points in the field, as it is the difference between the initial and final ...
... The potential is therefore a measure of the amount of work that has to be done to move particles between points in a gravitational field and its units are J kg –1 The work done is independent of the path taken between the two points in the field, as it is the difference between the initial and final ...
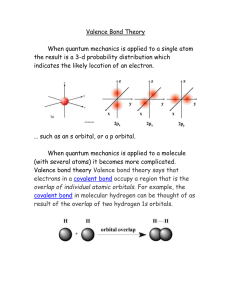
Valence Bond Theory
... electrons in a covalent bond occupy a region that is the overlap of individual atomic orbitals. For example, the covalent bond in molecular hydrogen can be thought of as result of the overlap of two hydrogen 1s orbitals. ...
... electrons in a covalent bond occupy a region that is the overlap of individual atomic orbitals. For example, the covalent bond in molecular hydrogen can be thought of as result of the overlap of two hydrogen 1s orbitals. ...
The Earth`s Magnetic Field
... Do this by rotating the dip needle so that it is horizontal and can act as a compass. The coil of the tangent galvanometer should be in line with the "compass" needle which points north-south. 3. Measure three different values for the angle өby varying the current input. Record the angle and the c ...
... Do this by rotating the dip needle so that it is horizontal and can act as a compass. The coil of the tangent galvanometer should be in line with the "compass" needle which points north-south. 3. Measure three different values for the angle өby varying the current input. Record the angle and the c ...
Do now! - MrSimonPorter
... current is not parallel to the field). This is called the motor effect. Can you copy this sentence into your books please. ...
... current is not parallel to the field). This is called the motor effect. Can you copy this sentence into your books please. ...
Logic, Geometry And Probability Theory - Philsci
... von Neumann to the development of geometry. But what is the meaning of Logic and Geometry in this context? In this short article, we will explore a possible answer to this question and relate it to a generalized probability theory [11]. Later on, the quantum logical approach of Birkhoff and von Neum ...
... von Neumann to the development of geometry. But what is the meaning of Logic and Geometry in this context? In this short article, we will explore a possible answer to this question and relate it to a generalized probability theory [11]. Later on, the quantum logical approach of Birkhoff and von Neum ...
Particle Physics
... This lecture is about particle physics, the study of the fundamental building blocks of Nature and the forces between them. We call our best theory of particle physics the Standard Model (in capital letters). This pompous name reflects our confidence in the theory. Recently, the Large Hadron Collide ...
... This lecture is about particle physics, the study of the fundamental building blocks of Nature and the forces between them. We call our best theory of particle physics the Standard Model (in capital letters). This pompous name reflects our confidence in the theory. Recently, the Large Hadron Collide ...
Quantum Discord: A Measure of the Quantumness of Correlations
... interrogate just one part of a composite system and discover its state while leaving the overall density matrix (as perceived by observers that do not have access to the measurement outcome) unaltered. A general separable rS ,A does not allow for such insensitivity to measurements: Information can b ...
... interrogate just one part of a composite system and discover its state while leaving the overall density matrix (as perceived by observers that do not have access to the measurement outcome) unaltered. A general separable rS ,A does not allow for such insensitivity to measurements: Information can b ...
PHY492: Nuclear & Particle Physics Lecture 22 Way Beyond the Standard Model
... • GUT scale was 1015 GeV (Did not include gravity) • Quantum Gravity – exchange spin 2, massless gravitons, gives an attractive force – scattering cross sections give infinities – gravitino (spin 3/2) helps to cancel these out – still lots of problems that are not solved April 4, 2007 ...
... • GUT scale was 1015 GeV (Did not include gravity) • Quantum Gravity – exchange spin 2, massless gravitons, gives an attractive force – scattering cross sections give infinities – gravitino (spin 3/2) helps to cancel these out – still lots of problems that are not solved April 4, 2007 ...
1 - the David R. Cheriton School of Computer Science
... [Shor ’94]: polynomial-time algorithm for factoring integers on a quantum computer This could be used to break most of the existing public-key cryptosystems, including RSA, and elliptic curve crypto [Bennett, Brassard ’84]: provably secure codes with short keys ...
... [Shor ’94]: polynomial-time algorithm for factoring integers on a quantum computer This could be used to break most of the existing public-key cryptosystems, including RSA, and elliptic curve crypto [Bennett, Brassard ’84]: provably secure codes with short keys ...
How are quantum numbers used to describe electrons
... Each energy level can have n2 orbitals and 2n2 electrons. For instance, for the second energy level, n = 2 so it has 22 orbitals (4 orbitals—1 s orbital and 3 p orbitals). It can hold 8 electrons. How many orbitals in the 4th energy level? How many electrons can be in the 4th energy level? For the k ...
... Each energy level can have n2 orbitals and 2n2 electrons. For instance, for the second energy level, n = 2 so it has 22 orbitals (4 orbitals—1 s orbital and 3 p orbitals). It can hold 8 electrons. How many orbitals in the 4th energy level? How many electrons can be in the 4th energy level? For the k ...
Experimental Test of Local Hidden
... show that any hidden-variable theory satisfying only the natural assumption of "locality" also leads to predictions ("Bell's inequality" ) in conflict with quantum mechanics. ' Bell's proof was extended to realizable systems by Clauser, Horne, Shimony, and Holt, ' who also pointed out that their gen ...
... show that any hidden-variable theory satisfying only the natural assumption of "locality" also leads to predictions ("Bell's inequality" ) in conflict with quantum mechanics. ' Bell's proof was extended to realizable systems by Clauser, Horne, Shimony, and Holt, ' who also pointed out that their gen ...
Motion in a magnetic field
... a) Calculate the force acting on the proton inside the magnetic field. b) Calculate the radius of curvature of the proton path in the magnetic field. c) Describe and draw a sketch to show the path of the proton in and beyond the magnetic field. d) A uniform electric field is applied and adjusted so ...
... a) Calculate the force acting on the proton inside the magnetic field. b) Calculate the radius of curvature of the proton path in the magnetic field. c) Describe and draw a sketch to show the path of the proton in and beyond the magnetic field. d) A uniform electric field is applied and adjusted so ...
MODERN QUANTUM KINETIC THEORY AND SPECTRAL LINE SHAPES
... ones with the walls, and occasional interactions with externally imposed fields . Consequently, the state, particularly the velocity, of an individual radiating molecule is not known exactly, but it is distributed according to some probability rule, usually taken to be the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribu ...
... ones with the walls, and occasional interactions with externally imposed fields . Consequently, the state, particularly the velocity, of an individual radiating molecule is not known exactly, but it is distributed according to some probability rule, usually taken to be the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribu ...
another essay - u.arizona.edu
... Attempts to further unify these interactions into a so-called grand unified theory (GUT) have so far not proved experimentally successful. Many physicists believe that superstring theory (or its generalization, M-theory) hold the best prospects for a successful unified theory, of not only strong and ...
... Attempts to further unify these interactions into a so-called grand unified theory (GUT) have so far not proved experimentally successful. Many physicists believe that superstring theory (or its generalization, M-theory) hold the best prospects for a successful unified theory, of not only strong and ...
Lecture 8: Nonclassical light • Squeezing • Photon anti
... in Eq. (8.4) with the variance of the electric-field strength, [ΔEk (r� α� α∗)]2 , which itself is a non-negative function. Hence, for the inequality (8.3) to hold, the probability distribution associated with this variance must take negative values somewhere in phase space which violates our assumpt ...
... in Eq. (8.4) with the variance of the electric-field strength, [ΔEk (r� α� α∗)]2 , which itself is a non-negative function. Hence, for the inequality (8.3) to hold, the probability distribution associated with this variance must take negative values somewhere in phase space which violates our assumpt ...