Deutsch-Jozsa Paper
... which are not diagonal in the basis (1). This is called the method of computation by quantum parallelism and is possible only with computers whose computations are coherent quantum processes. For examples see Deutsch (1985) and Jozsa (1991). To date, all known computational tasks which can be perfor ...
... which are not diagonal in the basis (1). This is called the method of computation by quantum parallelism and is possible only with computers whose computations are coherent quantum processes. For examples see Deutsch (1985) and Jozsa (1991). To date, all known computational tasks which can be perfor ...
inflation
... • horizon problem – CMBR photons emitted from opposite sides of the sky seem to be in thermal equilibrium, which is not expected by the standard model since these photons did not have time to make contact (one is out of the other’s horizon) ...
... • horizon problem – CMBR photons emitted from opposite sides of the sky seem to be in thermal equilibrium, which is not expected by the standard model since these photons did not have time to make contact (one is out of the other’s horizon) ...
Ross.pdf
... gauge principle applied to a relativistic field theory that led to Quantum Electrodynamics (QED), the quantum version of Maxwell’s theory of electromagnetism. The underlying ingredient is the recognition of a symmetry relating the states of the theory. Such a symmetry is based on patterns and the pat ...
... gauge principle applied to a relativistic field theory that led to Quantum Electrodynamics (QED), the quantum version of Maxwell’s theory of electromagnetism. The underlying ingredient is the recognition of a symmetry relating the states of the theory. Such a symmetry is based on patterns and the pat ...
6 Theory of the topological Anderson insulator
... have repeated the calculations of the conductance including a coupling Hamiltonian between the spin blocks of the form ±iκσy , with κ = 1.6 meV, representative of bulk inversion asymmetry in a HgTe quantum well. The effect on the phase diagram was negliglibly small. ...
... have repeated the calculations of the conductance including a coupling Hamiltonian between the spin blocks of the form ±iκσy , with κ = 1.6 meV, representative of bulk inversion asymmetry in a HgTe quantum well. The effect on the phase diagram was negliglibly small. ...
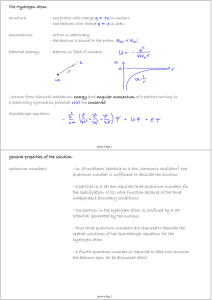
general properties of the solution: quantum numbers:
... Angular Momentum and the Uncertainty Principle: - the angular momentum is only quantized in one spatial direction - If L was aligned with the quantization axis the electron would be certain to move in the x-y plane. The uncertainty principle would require the momentum uncertainty Δpz to be infinite. ...
... Angular Momentum and the Uncertainty Principle: - the angular momentum is only quantized in one spatial direction - If L was aligned with the quantization axis the electron would be certain to move in the x-y plane. The uncertainty principle would require the momentum uncertainty Δpz to be infinite. ...
PDF
... such as red, blue, green, yellow, black, grey, or clear Legos. But, once decided, the laser obeys a conservation law that means that the color of the Lego blocks won’t change in time. The constancy of the color represents the invariance. Once the invariance is in place, one can make any state of a l ...
... such as red, blue, green, yellow, black, grey, or clear Legos. But, once decided, the laser obeys a conservation law that means that the color of the Lego blocks won’t change in time. The constancy of the color represents the invariance. Once the invariance is in place, one can make any state of a l ...
Alternative Approach to Time Evaluation of Schrödinger Wave
... from those pictures, ontological and epistemological approaches to the subject forwards that “a quantum particle must exist at a specific point at a particular time” therefore the position of the particle could, somehow, be definable. Additionally, the very existence of any quantum particle in space ...
... from those pictures, ontological and epistemological approaches to the subject forwards that “a quantum particle must exist at a specific point at a particular time” therefore the position of the particle could, somehow, be definable. Additionally, the very existence of any quantum particle in space ...
Document
... Belief: Attractive force between the positively charged nucleus and an electron orbiting around is equal to the centrifugal exerted on the electron. This balance determines the electron’s radius. Challenge: A force is exerted on the electron, then, the electron should accelerate continuously accordi ...
... Belief: Attractive force between the positively charged nucleus and an electron orbiting around is equal to the centrifugal exerted on the electron. This balance determines the electron’s radius. Challenge: A force is exerted on the electron, then, the electron should accelerate continuously accordi ...
QIPC 2011
... ψ = a | 000〉 + b | 001〉 + c | 010〉 + ... • “entangled” state—not a × of single qubits • 23=8 terms total, all states must be accessible (superselection restrictions not desired) • Qubits must have “resting” state in which state is unchanging: Hamiltonian H = 0 ...
... ψ = a | 000〉 + b | 001〉 + c | 010〉 + ... • “entangled” state—not a × of single qubits • 23=8 terms total, all states must be accessible (superselection restrictions not desired) • Qubits must have “resting” state in which state is unchanging: Hamiltonian H = 0 ...
analyses
... of the foil and along the width w. Because the foil is highly conductive, polarization charges will move to create two line charges +q and –q of length L at opposite sides of the width dimension. The dipole-like field from these two line charges an electric field when superimposed upon the ori ...
... of the foil and along the width w. Because the foil is highly conductive, polarization charges will move to create two line charges +q and –q of length L at opposite sides of the width dimension. The dipole-like field from these two line charges an electric field when superimposed upon the ori ...
Measurement Problem - The Information Philosopher
... But Bohr and Heisenberg also insisted that a measuring apparatus must be a regarded as a purely classical system. They can’t have it both ways. Can the macroscopic apparatus also be treated by quantum physics or not? Can it be described by the Schrödinger equation? Can it be regarded as in a superpo ...
... But Bohr and Heisenberg also insisted that a measuring apparatus must be a regarded as a purely classical system. They can’t have it both ways. Can the macroscopic apparatus also be treated by quantum physics or not? Can it be described by the Schrödinger equation? Can it be regarded as in a superpo ...
Quantum Mechanics and Common Sense
... simulation of quantum phenomena. Actually are these bra or ket waves or corpuscles is the detail of secondary importance. It is crucial only that two quantum entities are necessary to get an observable quantity in our Classical World. Note also that two independent quantities of Quantum World (i.e. ...
... simulation of quantum phenomena. Actually are these bra or ket waves or corpuscles is the detail of secondary importance. It is crucial only that two quantum entities are necessary to get an observable quantity in our Classical World. Note also that two independent quantities of Quantum World (i.e. ...
Philosophy and Religion Studies / Physics • Courses
... waves; effective range theory; integral equation approach; resonances; bound states; variational and R-Matrix methods. Emphasis on applications. Prerequisite(s): PHYS 5510. 6161. Introduction to Scattering Theory II. 3 hours. Time-dependent potential scattering, the general theory of collisions, ele ...
... waves; effective range theory; integral equation approach; resonances; bound states; variational and R-Matrix methods. Emphasis on applications. Prerequisite(s): PHYS 5510. 6161. Introduction to Scattering Theory II. 3 hours. Time-dependent potential scattering, the general theory of collisions, ele ...