PHYS-2020: General Physics II Course Lecture Notes Section I
... along the x axis. Calculate the electric flux through a rectangular plane 0.350 m wide and 0.700 m long if (a) the plane is parallel to the yz plane; (b) the plane is parallel to the xy plane; and (c) the plane contains the y axis and its normal makes an angle of 40.0◦ with the x axis. Solution (a): ...
... along the x axis. Calculate the electric flux through a rectangular plane 0.350 m wide and 0.700 m long if (a) the plane is parallel to the yz plane; (b) the plane is parallel to the xy plane; and (c) the plane contains the y axis and its normal makes an angle of 40.0◦ with the x axis. Solution (a): ...
Do relations require underlying intrinsic properties? A physical
... a kind of magic building material out of which everything in the physical world is made: (1) slow curvature in one region of space describes a gravitational field; (2) a rippled geometry with a different type of curvature somewhere else describes an electromagnetic field; (3) a knotted-up region of ...
... a kind of magic building material out of which everything in the physical world is made: (1) slow curvature in one region of space describes a gravitational field; (2) a rippled geometry with a different type of curvature somewhere else describes an electromagnetic field; (3) a knotted-up region of ...
ppt - damtp
... Higher loops (higher powers of small ) are smaller, because the magnetic theory is IR free. ...
... Higher loops (higher powers of small ) are smaller, because the magnetic theory is IR free. ...
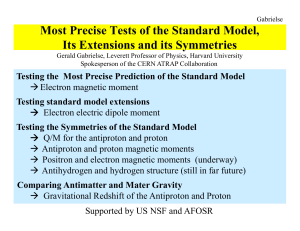
Most Precise Tests of the Standard Model, Its - Indico
... this latest triumph. Thank you for sending the two papers. Your statement, that QED is tested far more stringently than its inventors could ever have envisioned, is correct. As one of the inventors, I remember that we thought of QED in 1949 as a temporary and jerry-built structure, with mathematical ...
... this latest triumph. Thank you for sending the two papers. Your statement, that QED is tested far more stringently than its inventors could ever have envisioned, is correct. As one of the inventors, I remember that we thought of QED in 1949 as a temporary and jerry-built structure, with mathematical ...
QUANTUM SUPERPOSITION PRINCIPLE
... • What is this "wave function" and what can it tell you? After all, a particle, by its nature, is localized at a point, whereas the wave function is spread out in space (it's a function of x, for any given time t). How can such an object (which is the wave function) be said to describe the state of ...
... • What is this "wave function" and what can it tell you? After all, a particle, by its nature, is localized at a point, whereas the wave function is spread out in space (it's a function of x, for any given time t). How can such an object (which is the wave function) be said to describe the state of ...
Stark Effect - Physics
... perturbation theory by diagonalizing the perturbation term in the N 2 -fold degenerate multiplet of states with principal quantum number N . We exploit the symmetries of this problem to simplify the numerical computations. In particular, after assuming the N 0 -N matrix elements of the hamiltonian h ...
... perturbation theory by diagonalizing the perturbation term in the N 2 -fold degenerate multiplet of states with principal quantum number N . We exploit the symmetries of this problem to simplify the numerical computations. In particular, after assuming the N 0 -N matrix elements of the hamiltonian h ...
Entangled State Quantum Cryptography
... Since its discovery, quantum cryptography has been demonstrated by a number of groups using weak coherent states, both in fiber-based systems [7] and in free space arrangements [8,9]. These experiments are provably secure against all eavesdropping attacks based on presently available technology; how ...
... Since its discovery, quantum cryptography has been demonstrated by a number of groups using weak coherent states, both in fiber-based systems [7] and in free space arrangements [8,9]. These experiments are provably secure against all eavesdropping attacks based on presently available technology; how ...
A class of quantum many-body states that can be efficiently simulated
... product states (MPS) [6] for 1D systems, tree tensor networks (TTN) [3] for systems with tree shape, and projected entangled-pair states (PEPS) [2] for 2D systems and beyond, the three structures differing in the graph that defines how the tensors are interconnected into a network: the graphs for MP ...
... product states (MPS) [6] for 1D systems, tree tensor networks (TTN) [3] for systems with tree shape, and projected entangled-pair states (PEPS) [2] for 2D systems and beyond, the three structures differing in the graph that defines how the tensors are interconnected into a network: the graphs for MP ...
Quantum Computing
... that no type of computing machine could o er this large a speed-up over a classical digital computer. In retrospect, several results [7, 30] should have led them to question this; however, not much attention was paid to these results until they led to the development of the factoring algorithm, A qu ...
... that no type of computing machine could o er this large a speed-up over a classical digital computer. In retrospect, several results [7, 30] should have led them to question this; however, not much attention was paid to these results until they led to the development of the factoring algorithm, A qu ...
Quintet pairing and non-Abelian vortex string in spin-3/2 cold atomic... Congjun Wu, Jiangping Hu, and Shou-Cheng Zhang
... playground to study high symmetries which do not appear in usual condensed matter systems. Three of us have shown that spin-3/2 fermionic systems with contact interactions, which can be realized by atoms such as 132 Cs, ...
... playground to study high symmetries which do not appear in usual condensed matter systems. Three of us have shown that spin-3/2 fermionic systems with contact interactions, which can be realized by atoms such as 132 Cs, ...
Lec. 42 notes
... Jimmy sees two lightning flashes and determines that one happens 10 ns before the other. Which statement is true: A. Another inertial observer must find the order of events, the location of events, and the time difference to be the same. B. Another inertial observer must find the order of events to ...
... Jimmy sees two lightning flashes and determines that one happens 10 ns before the other. Which statement is true: A. Another inertial observer must find the order of events, the location of events, and the time difference to be the same. B. Another inertial observer must find the order of events to ...
Quantum Entanglement, Nonlocality, and Back-In
... in the physics literature from the 1940s by Wheeler and Feynman (advanced waves) to the 1990s by Kip Thorne and his colleagues (timelike wormholes). The consensus of such discussions is that Nature will forbid inconsistent timelike loops and will instead require a consistent set of conditions. Thorn ...
... in the physics literature from the 1940s by Wheeler and Feynman (advanced waves) to the 1990s by Kip Thorne and his colleagues (timelike wormholes). The consensus of such discussions is that Nature will forbid inconsistent timelike loops and will instead require a consistent set of conditions. Thorn ...
How “Quantum” is the D-Wave Machine?
... in the introduction, this schedule is different from the one reported in [7], which was based on an error by D-Wave [24], although this did not change their conclusions. Our paper is based entirely on the new corrected schedule [8]. We note that our conclusions also hold equally well for both schedu ...
... in the introduction, this schedule is different from the one reported in [7], which was based on an error by D-Wave [24], although this did not change their conclusions. Our paper is based entirely on the new corrected schedule [8]. We note that our conclusions also hold equally well for both schedu ...
Quantum Stabilizer Codes Embedding Qubits Into Qudits
... a qudit with complex Hilbert space Hd 6= H2⊗n . We refer to this kind of encoding as embedding or qudit-encoding H2 3 |qlogical i 7−→ |qphysical i ∈ Hd 6= H2⊗n , where d 6= 2n . For block-coding schemes a powerful formalism, named stabilizer formalism [3], has been developed describing one of the mo ...
... a qudit with complex Hilbert space Hd 6= H2⊗n . We refer to this kind of encoding as embedding or qudit-encoding H2 3 |qlogical i 7−→ |qphysical i ∈ Hd 6= H2⊗n , where d 6= 2n . For block-coding schemes a powerful formalism, named stabilizer formalism [3], has been developed describing one of the mo ...