Chapter 5 Practice Test
... g sinq cosq where a is the length (in feet) of the base and g Ô 32 feet per second per second is the acceleration of gravity. How long does it take a block to slide down an inclined plane with base a = 8 when q = 45e? Round the final answer to the nearest tenth of a second. ...
... g sinq cosq where a is the length (in feet) of the base and g Ô 32 feet per second per second is the acceleration of gravity. How long does it take a block to slide down an inclined plane with base a = 8 when q = 45e? Round the final answer to the nearest tenth of a second. ...
Unit 1-5
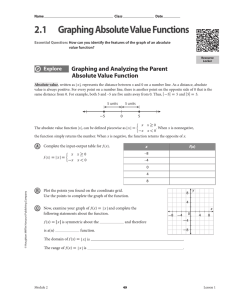
... Evaluate the expression |2x + y| if x = 1.5 and y = 4. Evaluate the expression 5|xy – w| if w = –2, x = 1.5, and y = 4. Solve the equation |b + 20| = 21. Solve the equation –4|a + 5| = –8. What is the solution to the equation 2|3x – 1| – 1 = –5? ...
... Evaluate the expression |2x + y| if x = 1.5 and y = 4. Evaluate the expression 5|xy – w| if w = –2, x = 1.5, and y = 4. Solve the equation |b + 20| = 21. Solve the equation –4|a + 5| = –8. What is the solution to the equation 2|3x – 1| – 1 = –5? ...