VDD Stacking with Different Adder Topologies
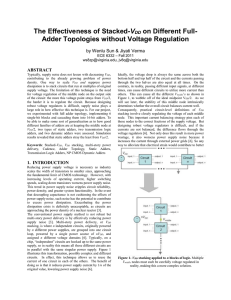
... times, can cause different circuits to utilize more current than others. This can cause all the different Vmiddle’s as shown in Figure 1, to wobble off of the ideal midpoint V DD/2. As we will see later, the stability of this middle node intrinsically determines whether the overall circuit balances ...
... times, can cause different circuits to utilize more current than others. This can cause all the different Vmiddle’s as shown in Figure 1, to wobble off of the ideal midpoint V DD/2. As we will see later, the stability of this middle node intrinsically determines whether the overall circuit balances ...
Lecture Notes for Algorithm Analysis and Design
... Clearly it grows exponentially with n. You can also prove that Fn = 1 + ...
... Clearly it grows exponentially with n. You can also prove that Fn = 1 + ...