LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034 PART-A
... stereochemistry of the major product. b) What is Alder’s endo rule? How does it control the stereochemistry of cycloaddition product? Explain with an example. 25. a) There are two rearrangements involved in the following reaction. Identify them and write the mechanism. OH ...
... stereochemistry of the major product. b) What is Alder’s endo rule? How does it control the stereochemistry of cycloaddition product? Explain with an example. 25. a) There are two rearrangements involved in the following reaction. Identify them and write the mechanism. OH ...
U. of Kentucky Chemistry 535 Synthetic Organic Chemistry Spring
... retrosynthetic analysis that leaves no doubt for the reader that you can make the molecule. You may start with molecules containing no less than eight carbon atoms. ...
... retrosynthetic analysis that leaves no doubt for the reader that you can make the molecule. You may start with molecules containing no less than eight carbon atoms. ...
Chem 30B Spring 2004 QUIZ #1 KEY Weds April 14th / 30
... 7. What is the product of the pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC) oxidation shown below? OH ...
... 7. What is the product of the pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC) oxidation shown below? OH ...
Chap Thirteen: Alcohols
... its mechanism of formation. Predict the acidity of alcohols relative to one another and relative to other functional groups Recognize structural features of a molecule that are key to its stability and reactivity. Predict the reagents needed to produce a given product from an alcohol in one or ...
... its mechanism of formation. Predict the acidity of alcohols relative to one another and relative to other functional groups Recognize structural features of a molecule that are key to its stability and reactivity. Predict the reagents needed to produce a given product from an alcohol in one or ...
Outline_CH13_Klein
... its mechanism of formation. Predict the acidity of alcohols relative to one another and relative to other functional groups Recognize structural features of a molecule that are key to its stability and reactivity. Predict the reagents needed to produce a given product from an alcohol in one or ...
... its mechanism of formation. Predict the acidity of alcohols relative to one another and relative to other functional groups Recognize structural features of a molecule that are key to its stability and reactivity. Predict the reagents needed to produce a given product from an alcohol in one or ...
Document
... In this rearrangement, an electron is donated through space; the other electron to form the bond comes from a bond to this atom. The initial cleavage does not cause fragmentation, only rearrangement and transfer of the radical site. This new radical site then initiates an alpha cleavage, resulting i ...
... In this rearrangement, an electron is donated through space; the other electron to form the bond comes from a bond to this atom. The initial cleavage does not cause fragmentation, only rearrangement and transfer of the radical site. This new radical site then initiates an alpha cleavage, resulting i ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 19. Explain the mechanism of Aldol condensation and Wittig reaction. 20. Discuss the mechanism of Baeyer Villiger reaction with suitable example. 21. Discuss on the electroorganic synthesis by reduction with suitable examples. 22. Explain the synthetic applications of oxidation reactions using lead ...
... 19. Explain the mechanism of Aldol condensation and Wittig reaction. 20. Discuss the mechanism of Baeyer Villiger reaction with suitable example. 21. Discuss on the electroorganic synthesis by reduction with suitable examples. 22. Explain the synthetic applications of oxidation reactions using lead ...
J. Indian. Chem. Soc. 1999, 76, 631-639
... J. Indian. Chem. Soc. 1999, 76, 631-639. N-protected amino acid allylic esters can easily be deprotonated by LDA at -78 °C and transmetallated by addition of metal salts. Chelated metal enolates, which undergo Claisen rearrangements upon warming up to room temperature, giving rise to unsaturated ami ...
... J. Indian. Chem. Soc. 1999, 76, 631-639. N-protected amino acid allylic esters can easily be deprotonated by LDA at -78 °C and transmetallated by addition of metal salts. Chelated metal enolates, which undergo Claisen rearrangements upon warming up to room temperature, giving rise to unsaturated ami ...
How to study organic chemistry?
... Funda is conjugate acid or conjugate base as the case may be if stable then that base or acid is strong. Solvent and its role in reaction mechanism. Inductive effect,Hyperconjugation,Resonance. Aromaticity. Tautomerism(keto-enol) Keto-Enol Ratio – Various factors like relief of angle strain. Solvent ...
... Funda is conjugate acid or conjugate base as the case may be if stable then that base or acid is strong. Solvent and its role in reaction mechanism. Inductive effect,Hyperconjugation,Resonance. Aromaticity. Tautomerism(keto-enol) Keto-Enol Ratio – Various factors like relief of angle strain. Solvent ...
oigchem
... Funda is conjugate acid or conjugate base as the case may be if stable then that base or acid is strong. Solvent and its role in reaction mechanism. Inductive effect,Hyperconjugation,Resonance. Aromaticity. Tautomerism(keto-enol) Keto-Enol Ratio – Various factors like relief of angle strain. Solvent ...
... Funda is conjugate acid or conjugate base as the case may be if stable then that base or acid is strong. Solvent and its role in reaction mechanism. Inductive effect,Hyperconjugation,Resonance. Aromaticity. Tautomerism(keto-enol) Keto-Enol Ratio – Various factors like relief of angle strain. Solvent ...
Chapter Nine: Alcohols, Ethers and Epoxides
... common reagents. Predict the likelihood of carbon skeleton rearrangement under a given set of conditions. Predict the relative acidity of alcohols within a functional group class and compared to other functional groups. ...
... common reagents. Predict the likelihood of carbon skeleton rearrangement under a given set of conditions. Predict the relative acidity of alcohols within a functional group class and compared to other functional groups. ...
suman_organic
... Funda is conjugate acid or conjugate base as the case may be if stable then that base or acid is strong. Solvent and its role in reaction mechanism. Inductive effect, Hyperconjugation, Resonance. Aromaticity. Tautomerism (keto-enol) Keto-Enol Ratio – Various factors like relief of angle strain. Solv ...
... Funda is conjugate acid or conjugate base as the case may be if stable then that base or acid is strong. Solvent and its role in reaction mechanism. Inductive effect, Hyperconjugation, Resonance. Aromaticity. Tautomerism (keto-enol) Keto-Enol Ratio – Various factors like relief of angle strain. Solv ...
Fundamentals Of Organic Chemistry
... 3, 3-dimethyl-2-bromo butane (neopentyl type) undergoes SN1 hydrolysis with rearrangement due to stability factor. ...
... 3, 3-dimethyl-2-bromo butane (neopentyl type) undergoes SN1 hydrolysis with rearrangement due to stability factor. ...
Here is the Original File - University of New Hampshire
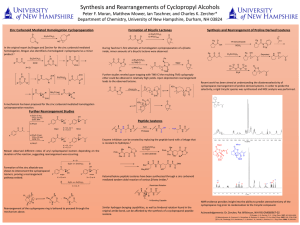
... Enzyme inhibitors can be created by replacing the peptide bond with a linkage that is resistant to hydrolysis.2 Mower observed different ratios of aryl cyclopropanol isomers depending on the duration of the reaction, suggesting rearrangement was occurring. ...
... Enzyme inhibitors can be created by replacing the peptide bond with a linkage that is resistant to hydrolysis.2 Mower observed different ratios of aryl cyclopropanol isomers depending on the duration of the reaction, suggesting rearrangement was occurring. ...