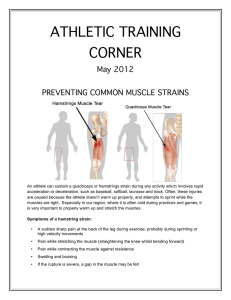
athletic training corner
... Tiredness and fitness: When fatigued, a player can lose coordination between muscle groups. The hamstrings and quadriceps muscle groups are innervated by multiple nerves. A lack of synchronization due to fatigue could result in more load being placed on one muscle. thereby causing injury. ...
... Tiredness and fitness: When fatigued, a player can lose coordination between muscle groups. The hamstrings and quadriceps muscle groups are innervated by multiple nerves. A lack of synchronization due to fatigue could result in more load being placed on one muscle. thereby causing injury. ...
CHAPTER 9 MUSCULAR SYSTEM: HISTOLOGY
... the microfilaments. Have them draw these structures in their notes or as a homework assignment. Membrane Potentials, Ion Channels, Action Potentials Stress the fact that muscles are excitable tissue and have resting membrane potentials that can be altered. Students must understand the resting membra ...
... the microfilaments. Have them draw these structures in their notes or as a homework assignment. Membrane Potentials, Ion Channels, Action Potentials Stress the fact that muscles are excitable tissue and have resting membrane potentials that can be altered. Students must understand the resting membra ...
Muscle and NerveKD13
... • Has features of both skeletal and smooth muscle - Like skeletal muscle, it has strong contractions and striated appearance - Like smooth muscle, it is under involuntary control and has rhythmic contraction ...
... • Has features of both skeletal and smooth muscle - Like skeletal muscle, it has strong contractions and striated appearance - Like smooth muscle, it is under involuntary control and has rhythmic contraction ...
File
... • Has features of both skeletal and smooth muscle - Like skeletal muscle, it has strong contractions and striated appearance - Like smooth muscle, it is under involuntary control and has rhythmic contraction ...
... • Has features of both skeletal and smooth muscle - Like skeletal muscle, it has strong contractions and striated appearance - Like smooth muscle, it is under involuntary control and has rhythmic contraction ...
Quadriceps Contusions(cork thigh)
... muscle contusion injuries. Moderate to severe may require crutches to ensure complete rest and particularly if full weight bearing on the affected leg is painful. In severe contusions, or poor management of treatment, there’s a greater t risk of Myositis Ossificans, which in this condition, calci ...
... muscle contusion injuries. Moderate to severe may require crutches to ensure complete rest and particularly if full weight bearing on the affected leg is painful. In severe contusions, or poor management of treatment, there’s a greater t risk of Myositis Ossificans, which in this condition, calci ...
of the smooth muscles
... and by the fact that it shows continuous, irregular contractions that are independent of its nerve supply. This maintained state of partial contraction is called tonus or tone. There is no true "resting" value for the membrane potential, but it averages about -50 mV, when the muscle active it become ...
... and by the fact that it shows continuous, irregular contractions that are independent of its nerve supply. This maintained state of partial contraction is called tonus or tone. There is no true "resting" value for the membrane potential, but it averages about -50 mV, when the muscle active it become ...
of the smooth muscles
... and by the fact that it shows continuous, irregular contractions that are independent of its nerve supply. This maintained state of partial contraction is called tonus or tone. There is no true "resting" value for the membrane potential, but it averages about -50 mV, when the muscle active it become ...
... and by the fact that it shows continuous, irregular contractions that are independent of its nerve supply. This maintained state of partial contraction is called tonus or tone. There is no true "resting" value for the membrane potential, but it averages about -50 mV, when the muscle active it become ...
muscles
... Cardiac Muscle • Same mechanism as skeletal • Less calcium stored but longer T-tubules & more released with a single impulse • Impulses travel rapidly from cell to cell so it is self-stimulating ...
... Cardiac Muscle • Same mechanism as skeletal • Less calcium stored but longer T-tubules & more released with a single impulse • Impulses travel rapidly from cell to cell so it is self-stimulating ...
Muscles - Solutions - VCC Library
... Have a transmembrane potential Sarcolemma and T tubules can generate action potentials(can be excited or depolarized) ...
... Have a transmembrane potential Sarcolemma and T tubules can generate action potentials(can be excited or depolarized) ...
08. Invol.muscle
... neuromuscular junctions (like motor endplates) in most smooth muscle, but some multiunit fibers have direct contact with nerve fibers (like motor units in skeletal muscle) - most junctions are diffuse junctions involving varicosities along the axon distributed over the surface of the smooth muscle - ...
... neuromuscular junctions (like motor endplates) in most smooth muscle, but some multiunit fibers have direct contact with nerve fibers (like motor units in skeletal muscle) - most junctions are diffuse junctions involving varicosities along the axon distributed over the surface of the smooth muscle - ...
Muscle contraction

Muscle contraction is the activation of tension-generating sites within muscle fibers. In physiology, muscle contraction does not mean muscle shortening because muscle tension can be produced without changes in muscle length such as holding a heavy book or a dumbbell at the same position. The termination of muscle contraction is followed by muscle relaxation, which is a return of the muscle fibers to their low tension-generating state.Muscle contractions can be described based on two variables: length and tension. A muscle contraction is described as isometric if the muscle tension changes but the muscle length remains the same. In contrast, a muscle contraction is isotonic if muscle length changes but the muscle tension remains the same. Furthermore, if the muscle length shortens, the contraction is concentric. But if the muscle length lengthens, then the contraction is eccentric. In natural movements that underlie locomotor activity, muscle contractions are multifaceted as they are able to produce changes in length and tension in a time-varying manner. Thus, length and tension are unlikely to remain the same in muscles that contract during locomotor activity.In vertebrates, skeletal muscle contractions are neurogenic as they require synaptic input from motor neurons to produce muscle contractions. A single motor neuron is able to innervate multiple muscle fibers, thereby causing the fibers to contract at the same time. Once innervated, the protein filaments within each skeletal muscle fiber slide past each other to produce a contraction, which is explained by the sliding filament theory. The contractions that is produced can be described as a twitch, summation, or tetanus, depending on the frequency of action potentials. In skeletal muscles, muscle tension is at its greatest when the muscle is stretched to an intermediate length as described by the length-tension relationship.Smooth and cardiac muscle contractions are myogenic and can be modulated by the autonomic nervous system. The mechanisms of contraction in these muscle tissues are similar to skeletal muscle tissues.