Asteroids, Meteoroids and Comets
... inner (rocky) planets of the solar system. They can sometimes be seen as fast moving objects against the background of star. Some have been studied by passing satellites. ...
... inner (rocky) planets of the solar system. They can sometimes be seen as fast moving objects against the background of star. Some have been studied by passing satellites. ...
Comets
... Occasionally, Oort Cloud or Kuiper Belt comets may have their orbits ‘perturbed’ by the gravity of a nearby passing star, an outer planet, or one of the larger Kuiper Belt Objects. (A typical comet is only about one trillionth of the mass of the Earth, so they are easily tweaked!) The object’s new o ...
... Occasionally, Oort Cloud or Kuiper Belt comets may have their orbits ‘perturbed’ by the gravity of a nearby passing star, an outer planet, or one of the larger Kuiper Belt Objects. (A typical comet is only about one trillionth of the mass of the Earth, so they are easily tweaked!) The object’s new o ...
Theme 10 – Leftovers: Comets
... After formation in the original Solar System nebula, a cometary nucleus may spend billions of years in the Oort Cloud or the Kuiper Belt Some small gravitational perturbation directs it inward The gravity of an inner planet (most likely Jupiter) changes its orbit, and it is captured into an orbit of ...
... After formation in the original Solar System nebula, a cometary nucleus may spend billions of years in the Oort Cloud or the Kuiper Belt Some small gravitational perturbation directs it inward The gravity of an inner planet (most likely Jupiter) changes its orbit, and it is captured into an orbit of ...
Meteorite
... Which explanation for the asteroid belt seems the most plausible? • The belt is where all the asteroids happened to form. • The belt is the remnant of a large terrestrial planet that used to be between Mars and Jupiter. • The belt is where all the asteroids happened to survive. But WHY didn’t they f ...
... Which explanation for the asteroid belt seems the most plausible? • The belt is where all the asteroids happened to form. • The belt is the remnant of a large terrestrial planet that used to be between Mars and Jupiter. • The belt is where all the asteroids happened to survive. But WHY didn’t they f ...
Worksheet
... 11. When was Comet Halley was first recorded? c. 240 B.C. A 12. Sent an impactor to collide with Comet Tempel 1. C 13. Took pictures of the Comet Tempel 1, photo graphing the crater. B 14. Studied Comet Hartley 2. 15. What will we find at the outermost edge of the Solar System? c. The Oort Cloud. 16 ...
... 11. When was Comet Halley was first recorded? c. 240 B.C. A 12. Sent an impactor to collide with Comet Tempel 1. C 13. Took pictures of the Comet Tempel 1, photo graphing the crater. B 14. Studied Comet Hartley 2. 15. What will we find at the outermost edge of the Solar System? c. The Oort Cloud. 16 ...
12_LectureOutlines
... Thought Question How come there are very few asteroids beyond Jupiter’s orbit? A. There was no rocky material beyond Jupiter’s orbit. B. The heaviest rocks sank towards the center of the solar system. C. Ice could form in the outer solar system. D. A passing star probably stripped away all of those ...
... Thought Question How come there are very few asteroids beyond Jupiter’s orbit? A. There was no rocky material beyond Jupiter’s orbit. B. The heaviest rocks sank towards the center of the solar system. C. Ice could form in the outer solar system. D. A passing star probably stripped away all of those ...
10 Comets, Dwarf Planets, Asteroids and Meteoroids
... packed bodies of homogeneously mixed ices and dust (a dirty snowball). The comet develops its tails when the Sun begins to sublimate the ices into gas and simultaneously releases the dust (~5 AU). He predicted the solar wind to drive off the ion tail and suggested radiation pressure to energize the ...
... packed bodies of homogeneously mixed ices and dust (a dirty snowball). The comet develops its tails when the Sun begins to sublimate the ices into gas and simultaneously releases the dust (~5 AU). He predicted the solar wind to drive off the ion tail and suggested radiation pressure to energize the ...
Kleopatra - OSIRIS
... Journey with us through the alphabet as we learn about Earth’s rocky neighbors – the asteroids! There are interesting asteroid characters in our solar system, including an asteroid that has its own moon and even one that is shaped like a dog bone! For each letter of the alphabet, we will showcase an ...
... Journey with us through the alphabet as we learn about Earth’s rocky neighbors – the asteroids! There are interesting asteroid characters in our solar system, including an asteroid that has its own moon and even one that is shaped like a dog bone! For each letter of the alphabet, we will showcase an ...
Ch 12 slides - UNLV Physics
... Why are there very few asteroids beyond Jupiter’s orbit? A.! There was no rocky material beyond Jupiter’s orbit. B.! The heaviest rocks sank towards the center of the solar system. C.! Ice could form in the outer solar system. D.! A passing star probably stripped away all of those asteroids, even if ...
... Why are there very few asteroids beyond Jupiter’s orbit? A.! There was no rocky material beyond Jupiter’s orbit. B.! The heaviest rocks sank towards the center of the solar system. C.! Ice could form in the outer solar system. D.! A passing star probably stripped away all of those asteroids, even if ...
chapter12AsterioidsC..
... Thought Question Which explanation for the belt seems the most plausible? A. The belt is where all the asteroids happened to form. B. The belt is the remnant of a large terrestrial planet that used to be between Mars and Jupiter. C. The belt is where all the asteroids happened to survive. But How d ...
... Thought Question Which explanation for the belt seems the most plausible? A. The belt is where all the asteroids happened to form. B. The belt is the remnant of a large terrestrial planet that used to be between Mars and Jupiter. C. The belt is where all the asteroids happened to survive. But How d ...
ppt
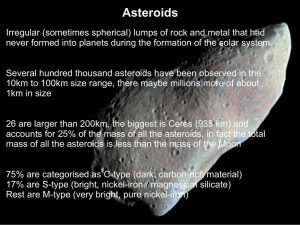
... Irregular (sometimes spherical) lumps of rock and metal that had never formed into planets during the formation of the solar system Several hundred thousand asteroids have been observed in the 10km to 100km size range, there maybe millions more of about 1km in size 26 are larger than 200km, the bigg ...
... Irregular (sometimes spherical) lumps of rock and metal that had never formed into planets during the formation of the solar system Several hundred thousand asteroids have been observed in the 10km to 100km size range, there maybe millions more of about 1km in size 26 are larger than 200km, the bigg ...
what is a comet? - Fireballs in the sky
... As the comet comes closer to the Sun the solar winds become stronger and blow away the coma to form a distinctive comet tail. A comet’s tail will always point away from the Sun because the solar wind exerts a force on the dust and gas particles. The tail itself is often split into two; a bright dust ...
... As the comet comes closer to the Sun the solar winds become stronger and blow away the coma to form a distinctive comet tail. A comet’s tail will always point away from the Sun because the solar wind exerts a force on the dust and gas particles. The tail itself is often split into two; a bright dust ...
here
... Why are there very few asteroids beyond Jupiter’s orbit? A. There was no rocky material beyond Jupiter’s orbit. B. The heaviest rocks sank towards the center of the solar system. C. Ice could form in the outer solar system. D. A passing star probably stripped away all of those asteroids, even if the ...
... Why are there very few asteroids beyond Jupiter’s orbit? A. There was no rocky material beyond Jupiter’s orbit. B. The heaviest rocks sank towards the center of the solar system. C. Ice could form in the outer solar system. D. A passing star probably stripped away all of those asteroids, even if the ...
Chapter 23 Section 4 Minor Members of the Solar System
... (2) Material from the asteroid belt (3) The solid remains of comets that once traveled near Earth’s orbit. A few meteoroids are believed to be fragments of the moon, or possibly Mars, that were ejected when an asteroid impacted these bodies. Some meteoroids are as large as asteroids. Most, however, ...
... (2) Material from the asteroid belt (3) The solid remains of comets that once traveled near Earth’s orbit. A few meteoroids are believed to be fragments of the moon, or possibly Mars, that were ejected when an asteroid impacted these bodies. Some meteoroids are as large as asteroids. Most, however, ...
The Asteroid Belt - peterboroughastronomy.com
... The first thing we should establish is the difference between an asteroid and a comet. In the very simplest terms an asteroid is a chunk of rock that orbits the Sun and is within our solar system. A comet is a giant dirty snowball that is pulled in from a very distant area called the Oort Cloud. Thi ...
... The first thing we should establish is the difference between an asteroid and a comet. In the very simplest terms an asteroid is a chunk of rock that orbits the Sun and is within our solar system. A comet is a giant dirty snowball that is pulled in from a very distant area called the Oort Cloud. Thi ...
CI513 Instruction and Technology Lesson Planning Guide
... Students will know that gravity is the force that pulls a meteroid towards a planet. Key Concept(s): What concepts (related to content and/or process) will students encounter as a result of this lesson? Aestroids are tiny planets, and most are concentrated in an area between the orbits of Mars and ...
... Students will know that gravity is the force that pulls a meteroid towards a planet. Key Concept(s): What concepts (related to content and/or process) will students encounter as a result of this lesson? Aestroids are tiny planets, and most are concentrated in an area between the orbits of Mars and ...
Presenters - Chemical Processing
... Q: Please expand on methods of detection to trigger the abort gate. A: Abort gate is a generic term usually applied to an explosion isolation flap valve. A typical explosion isolation flap valve is a passive device; the air flow from the process provides the force that opens the value under normal o ...
... Q: Please expand on methods of detection to trigger the abort gate. A: Abort gate is a generic term usually applied to an explosion isolation flap valve. A typical explosion isolation flap valve is a passive device; the air flow from the process provides the force that opens the value under normal o ...
Comet ISON - Lone Star Science with Mr. Zuber
... Comet C/2012 S1 (ISON) • ISON started its journey towards the Sun (out of the Oort Cloud) a few million years ago • Discovered by Russian astronomers, part of the ISON Project (International Scientific Optical Network) in September 2012. • Comet ISON is a sungrazer, a comet that travels close to th ...
... Comet C/2012 S1 (ISON) • ISON started its journey towards the Sun (out of the Oort Cloud) a few million years ago • Discovered by Russian astronomers, part of the ISON Project (International Scientific Optical Network) in September 2012. • Comet ISON is a sungrazer, a comet that travels close to th ...
Asteroids and Meteorites
... • Most probably are fragments of larger asteroids • A 100 km radius asteroid can produce 106 1 km fragments ...
... • Most probably are fragments of larger asteroids • A 100 km radius asteroid can produce 106 1 km fragments ...
A Comet Nucleus
... Beyond Neptune, there are at least 70,000 ice/rock bodies with diameters larger than 100 km and orbits of radius 30 to more than 50 AU. This ring of bodies (cf. the Asteroid belt) is called the Kuiper belt. Astronomers believe that it is the source of short-period comets. Plutinos are a special subs ...
... Beyond Neptune, there are at least 70,000 ice/rock bodies with diameters larger than 100 km and orbits of radius 30 to more than 50 AU. This ring of bodies (cf. the Asteroid belt) is called the Kuiper belt. Astronomers believe that it is the source of short-period comets. Plutinos are a special subs ...
DTU_9e_ch09 - University of San Diego Home Pages
... (a) This composite image of Comet Tempel 1 has higher resolution at ...
... (a) This composite image of Comet Tempel 1 has higher resolution at ...
Chapter 12 Asteroids, Comets, and Dwarf Planets What are
... Why are there very few asteroids beyond Jupiter’s orbit? A. There was no rocky material beyond Jupiter’s orbit. B. The heaviest rocks sank towards the center of the solar system. C. Ice could form in the outer solar system. D. A passing star probably stripped away all of those asteroids, even if the ...
... Why are there very few asteroids beyond Jupiter’s orbit? A. There was no rocky material beyond Jupiter’s orbit. B. The heaviest rocks sank towards the center of the solar system. C. Ice could form in the outer solar system. D. A passing star probably stripped away all of those asteroids, even if the ...
Space Rocks! - California Academy of Sciences
... erosion. Erosion can break a crater down to virtually nothing. The second process is tectonics. Because of tectonics, the surface of Earth is recycled many times throughout its long history. As a result, very few rocks on Earth are as old as the rocks on the Moon. The third thing is volcanism. Volca ...
... erosion. Erosion can break a crater down to virtually nothing. The second process is tectonics. Because of tectonics, the surface of Earth is recycled many times throughout its long history. As a result, very few rocks on Earth are as old as the rocks on the Moon. The third thing is volcanism. Volca ...
Lecture14: Solar System Debris
... Its orbit is highly eccentric; at times it is closer to the Sun than Neptune. Its orbit inclination is also much larger than other planets. Pluto rotates in the opposite direction from most other planets. Pluto is smaller than 7 satellites in the solar system. It has an average density of about 1900 ...
... Its orbit is highly eccentric; at times it is closer to the Sun than Neptune. Its orbit inclination is also much larger than other planets. Pluto rotates in the opposite direction from most other planets. Pluto is smaller than 7 satellites in the solar system. It has an average density of about 1900 ...
Tunguska event

The Tunguska event was a large explosion that occurred near the Stony Tunguska River, in what is now Krasnoyarsk Krai, Russia, on the morning of June 30, 1908 (N.S.). The explosion over the sparsely populated Eastern Siberian Taiga flattened 2,000 km2 (770 sq mi) of forest and caused no known casualties. The cause of the explosion is generally thought to have been a meteor. It is classified as an impact event, even though no impact crater has been found; the meteor is thought to have burst in mid-air at an altitude of 5 to 10 kilometres (3 to 6 miles) rather than hit the surface of the Earth. Different studies have yielded varying estimates of the superbolide's size, on the order of 60 to 190 metres (197 to 623 feet), depending on whether the meteor was a comet or a denser asteroid. It is considered the largest impact event on Earth in recorded history.Since the 1908 event, there have been an estimated 1,000 scholarly papers (mainly in Russian) published on the Tunguska explosion. Many scientists have participated in Tunguska studies: the best known are Leonid Kulik, Yevgeny Krinov, Kirill Florensky, Nikolai Vladimirovich Vasiliev, and Wilhelm Fast. In 2013, a team of researchers led by Victor Kvasnytsya of the National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine published analysis results of micro-samples from a peat bog near the center of the affected area showing fragments that may be of meteoritic origin.Estimates of the energy of the air burst range from 30 megatons of TNT (130 PJ) to 10 and 15 megatons of TNT (42 and 63 PJ), depending on the exact height of burst estimated when the scaling-laws from the effects of nuclear weapons are employed. While more modern supercomputer calculations that include the effect of the object's momentum estimate that the airburst had an energy range from 3 to 5 megatons of TNT (13 to 21 PJ), and that simply more of this energy was focused downward than would be the case from a nuclear explosion.Using the 15 megaton nuclear explosion derived estimate is an energy about 1,000 times greater than that of the atomic bomb dropped on Hiroshima, Japan; roughly equal to that of the United States' Castle Bravo ground-based thermonuclear test detonation on March 1, 1954; and about two-fifths that of the Soviet Union's later Tsar Bomba (the largest nuclear weapon ever detonated).It is estimated that the Tunguska explosion knocked down some 80 million trees over an area of 2,150 square kilometres (830 sq mi), and that the shock wave from the blast would have measured 5.0 on the Richter scale. An explosion of this magnitude would be capable of destroying a large metropolitan area, but due to the remoteness of the location, no fatalities were documented. This event has helped to spark discussion of asteroid impact avoidance.