Metal Complexes Containing Natural and Artificial Radioactive
... In contrast to lanthanides, the actinides have a variety of oxidation states in aqueous solution. The stable oxidation states go from +3 for Ac to +6 for U and Np and then successively decrease to +3 for Am and succeeding elements except No(+2). The maximum and stable oxidation states coincide for A ...
... In contrast to lanthanides, the actinides have a variety of oxidation states in aqueous solution. The stable oxidation states go from +3 for Ac to +6 for U and Np and then successively decrease to +3 for Am and succeeding elements except No(+2). The maximum and stable oxidation states coincide for A ...
technical report 91 -32
... adsorbed radionuclides directly and/or they are dissolved and reduce the radionuclides in solution. For this reason, the redox conditions can be simulated best by letting the minerals/rocks equilibrate with the water at the desired pH, carbon dioxide concentration and water chemistry. This is what h ...
... adsorbed radionuclides directly and/or they are dissolved and reduce the radionuclides in solution. For this reason, the redox conditions can be simulated best by letting the minerals/rocks equilibrate with the water at the desired pH, carbon dioxide concentration and water chemistry. This is what h ...
Reading 2.1 A Return to Isotopes
... mass number, however, is A = 6 for the isotope with 3 neutrons, and A = 7 for the isotope with 4 neutrons. In nature, only certain isotopes exist. For instance, stable lithium exists as an isotope with 3 neutrons and as an isotope with 4 neutrons, but there are no stable lithium isotopes with 2 neut ...
... mass number, however, is A = 6 for the isotope with 3 neutrons, and A = 7 for the isotope with 4 neutrons. In nature, only certain isotopes exist. For instance, stable lithium exists as an isotope with 3 neutrons and as an isotope with 4 neutrons, but there are no stable lithium isotopes with 2 neut ...
Help us improve Wikipedia by supporting it financially
... The naming of elements precedes the atomic theory of matter, although at the time it was not known which chemicals were elements and which compounds. When it was learned, existing names (e.g., gold, mercury, iron) were kept in most countries, and national differences emerged over the names of elemen ...
... The naming of elements precedes the atomic theory of matter, although at the time it was not known which chemicals were elements and which compounds. When it was learned, existing names (e.g., gold, mercury, iron) were kept in most countries, and national differences emerged over the names of elemen ...
Modern Physics
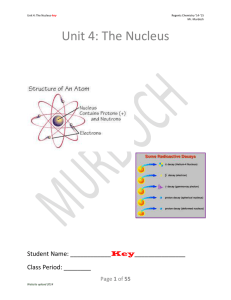
... • An atom is stable (not radioactive) if it is in the belt of stability • An atom is unstable (radioactive) if it is outside the belt of stability • All elements beyond number 83, Bismuth are unstable - WHY? ...
... • An atom is stable (not radioactive) if it is in the belt of stability • An atom is unstable (radioactive) if it is outside the belt of stability • All elements beyond number 83, Bismuth are unstable - WHY? ...
Mendelevium
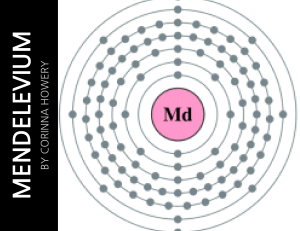
... table so its atomic number is 101. There are 101 protons/electrons in the nucleus and 157 neutrons. It also has 2 valence electrons. Mendelevium has 7 shells. On the periodic table, mendelevium is in the group actinide and it is radioactive. Mendeleviums state of matter is radioactive. ...
... table so its atomic number is 101. There are 101 protons/electrons in the nucleus and 157 neutrons. It also has 2 valence electrons. Mendelevium has 7 shells. On the periodic table, mendelevium is in the group actinide and it is radioactive. Mendeleviums state of matter is radioactive. ...
Trends in the Periodic Table
... Name: _________________________________ Period: ____ Date: ___ / ___ / ___ ...
... Name: _________________________________ Period: ____ Date: ___ / ___ / ___ ...
Unit Nuclear Chemistry
... › Emission of subatomic particles or high-energy electromagnetic radiation by nuclei › Such atoms/isotopes said to be radioactive › All nuclides of elements beyond Bismuth (#83) in the periodic table are radioactive with only Polonium (84), Radon (86), Actinium ((89), Thorium (90), Uranium (92) and ...
... › Emission of subatomic particles or high-energy electromagnetic radiation by nuclei › Such atoms/isotopes said to be radioactive › All nuclides of elements beyond Bismuth (#83) in the periodic table are radioactive with only Polonium (84), Radon (86), Actinium ((89), Thorium (90), Uranium (92) and ...
element connections
... • The Latin name for this element is natrium. (sodium) • The average weight of an atom of this element is about 190. (osmium) • This is the lightest member of the true metals. (aluminum) • This heavy transition metal is a liquid at room temperature. (mercury) • This precious metal is current worth m ...
... • The Latin name for this element is natrium. (sodium) • The average weight of an atom of this element is about 190. (osmium) • This is the lightest member of the true metals. (aluminum) • This heavy transition metal is a liquid at room temperature. (mercury) • This precious metal is current worth m ...
Discussion Notes (cont.)
... How are the smallest bits of matter described? • All matter is made up of extremely small particles called atoms. These particles are too small to be seen directly, even under a microscope. • The atom is composed of even smaller particles called protons, neutrons, and electrons. The protons and neut ...
... How are the smallest bits of matter described? • All matter is made up of extremely small particles called atoms. These particles are too small to be seen directly, even under a microscope. • The atom is composed of even smaller particles called protons, neutrons, and electrons. The protons and neut ...
LBC1_Sec3_Unit01_Alchemy
... How are the smallest bits of matter described? • All matter is made up of extremely small particles called atoms. These particles are too small to be seen directly, even under a microscope. • The atom is composed of even smaller particles called protons, neutrons, and electrons. The protons and neut ...
... How are the smallest bits of matter described? • All matter is made up of extremely small particles called atoms. These particles are too small to be seen directly, even under a microscope. • The atom is composed of even smaller particles called protons, neutrons, and electrons. The protons and neut ...
Getting to Know: Periodic Table
... Like a data table used for an experiment, this table had rows and columns. Not every part of the table was filled in. There were holes. Mendeleev predicted that there would be additional elements to “fill” those holes. He was right. Many more elements have been discovered. ...
... Like a data table used for an experiment, this table had rows and columns. Not every part of the table was filled in. There were holes. Mendeleev predicted that there would be additional elements to “fill” those holes. He was right. Many more elements have been discovered. ...
ISOTOPES
... Why are relative atomic masses decimals, and not simple whole numbers? Dalton’s original model of an atom assumed that all atoms of each element were the same. According to the model of atomic structure we have been developing, this would mean that each atom of an element would have the same number ...
... Why are relative atomic masses decimals, and not simple whole numbers? Dalton’s original model of an atom assumed that all atoms of each element were the same. According to the model of atomic structure we have been developing, this would mean that each atom of an element would have the same number ...
Chemical Element
... carbon-13 are stable atoms, but carbon-14 is unstable; it is slightly radioactive, decaying over time into other elements. Like carbon, some isotopes of various elements are radioactive and decay into other elements upon radiating an alpha or beta particle. For certain elements, all their isotopes a ...
... carbon-13 are stable atoms, but carbon-14 is unstable; it is slightly radioactive, decaying over time into other elements. Like carbon, some isotopes of various elements are radioactive and decay into other elements upon radiating an alpha or beta particle. For certain elements, all their isotopes a ...
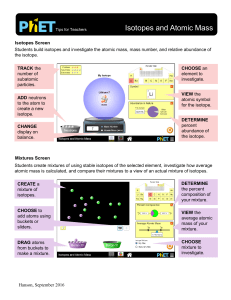
Isotopes and Atomic Mass
... Insights into Student Use • In college interviews, students wanted to select other common elements such as gold; investigation into other elements could be incorporated as part of an activity. • On the Mixtures screen, students attempted to match Nature’s Mix using My Mix view. This is not possible ...
... Insights into Student Use • In college interviews, students wanted to select other common elements such as gold; investigation into other elements could be incorporated as part of an activity. • On the Mixtures screen, students attempted to match Nature’s Mix using My Mix view. This is not possible ...
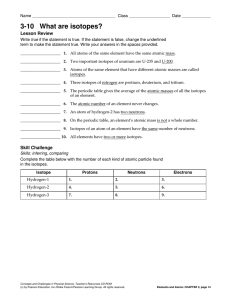
3-10 What are isotopes?
... reason for this? ____________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ 5. According to the table, how are isotopes named? ______________________________________________ 6. What is true a ...
... reason for this? ____________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ 5. According to the table, how are isotopes named? ______________________________________________ 6. What is true a ...
isotopes
... Can we write isotopes in a different way? • You can also use the mass number and the name of the element to designate the atom or isotope – This is called hyphen notation • For example, two isotopes of carbon are carbon-12 and carbon-13 – The nuclear symbols for these two isotopes would be: ...
... Can we write isotopes in a different way? • You can also use the mass number and the name of the element to designate the atom or isotope – This is called hyphen notation • For example, two isotopes of carbon are carbon-12 and carbon-13 – The nuclear symbols for these two isotopes would be: ...
elements and isotopes - vocabulary
... A species of atom; each atom of a particular isotope has a specific number of protons and a specific number of neutrons in the nucleus which are the same for all atoms of the isotope, but are not necessarily equal to each other. atomic number The number of protons in the nucleus of one atom; the ato ...
... A species of atom; each atom of a particular isotope has a specific number of protons and a specific number of neutrons in the nucleus which are the same for all atoms of the isotope, but are not necessarily equal to each other. atomic number The number of protons in the nucleus of one atom; the ato ...
Isotopes
... occur in nature as mixtures of isotopes. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that differ in the number of neutrons. ...
... occur in nature as mixtures of isotopes. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that differ in the number of neutrons. ...
Chapter 12 –Radioactivity
... identical atomic numbers but different mass numbers • Nuclide – each unique atom ...
... identical atomic numbers but different mass numbers • Nuclide – each unique atom ...
Periodic Table Review Key
... 9. Which elements have one valence electron? F,E 10. Which elements have a full outer cloud (octet)? B, H 11. Which element has 2 valence electrons? C 12. Which elements have 8 valence electrons? H 13. Which element is more reactive F or B? F 14. Which elements are considered noble gases? B, H 15. W ...
... 9. Which elements have one valence electron? F,E 10. Which elements have a full outer cloud (octet)? B, H 11. Which element has 2 valence electrons? C 12. Which elements have 8 valence electrons? H 13. Which element is more reactive F or B? F 14. Which elements are considered noble gases? B, H 15. W ...
10B Atoms and Isotopes
... You have learned that atoms contain three smaller particles called protons, neutrons, and electrons, and that the number of protons determines the type of atom. How can you figure out how many neutrons an atom contains, and whether it is neutral or has a charge? Once you know how many protons and ne ...
... You have learned that atoms contain three smaller particles called protons, neutrons, and electrons, and that the number of protons determines the type of atom. How can you figure out how many neutrons an atom contains, and whether it is neutral or has a charge? Once you know how many protons and ne ...
and View
... atom. * Number never changes* b. Isotopes—atoms of same element that have different numbers of neutrons. Ex: carbon-12, carbon-13, carbon-14 c. Mass number—number of neutrons plus protons in an atom. i. Neutron number is found by--Mass number - Atomic number _______________ Number of neutrons ...
... atom. * Number never changes* b. Isotopes—atoms of same element that have different numbers of neutrons. Ex: carbon-12, carbon-13, carbon-14 c. Mass number—number of neutrons plus protons in an atom. i. Neutron number is found by--Mass number - Atomic number _______________ Number of neutrons ...