Chapter 17 Applications of Molecular Genetics
... Key Points Valuable proteins that could be isolated from eukaryotes only in small amounts and at great expense can now be produced in large quantities in genetically engineered bacteria. Proteins such as human insulin and human growth hormone are valuable pharmaceuticals used to treat diabetes an ...
... Key Points Valuable proteins that could be isolated from eukaryotes only in small amounts and at great expense can now be produced in large quantities in genetically engineered bacteria. Proteins such as human insulin and human growth hormone are valuable pharmaceuticals used to treat diabetes an ...
The Hormones of the Endocrine Glands Activity
... The Hormones of the Endocrine Glands The endocrine system is responsible for many different functions in the body. Hormones are in use in the body all the time! The different hormones, their target cells and their function in that cell are sometimes difficult to understand, and students need to unde ...
... The Hormones of the Endocrine Glands The endocrine system is responsible for many different functions in the body. Hormones are in use in the body all the time! The different hormones, their target cells and their function in that cell are sometimes difficult to understand, and students need to unde ...
Document
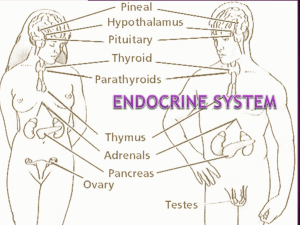
... Hypothalamus and Pituitary GlandThyroid and ParathyroidAdrenal GlandsPancreasPineal, Thymus, & Reproductive- ...
... Hypothalamus and Pituitary GlandThyroid and ParathyroidAdrenal GlandsPancreasPineal, Thymus, & Reproductive- ...
2011-02-17 Study on Dwarfs Brings Us Closer to Understanding
... mutation that is blocking a key growth hormone, and this mutation seems to offer lifelong protection against cancer and diabetes. Specifically, this is a mutation in the gene that makes the receptor for growth hormone, making it unable to react to growth hormone. In children without this gene mutati ...
... mutation that is blocking a key growth hormone, and this mutation seems to offer lifelong protection against cancer and diabetes. Specifically, this is a mutation in the gene that makes the receptor for growth hormone, making it unable to react to growth hormone. In children without this gene mutati ...
techniques of investigation and current concepts in the physiology
... the reproductive potential of the organism. Experiments conducted during the past 10 years, using the techniques of ablation or localized hormone implantation clearly demonstrate that many regulatory functions exerted by hormones occur via interactions at the level of the central nervous system. Dir ...
... the reproductive potential of the organism. Experiments conducted during the past 10 years, using the techniques of ablation or localized hormone implantation clearly demonstrate that many regulatory functions exerted by hormones occur via interactions at the level of the central nervous system. Dir ...
performanceenhancers
... causes the body to produce more HEMOGLOBIN. Why would this be a huge benefit to athletes? - Problems with this – higher RBC count makes the heart work much harder = risk of cardiac fatigue /even failure - Why do you think this is tough to test for? __________________________________________ I.O.C. b ...
... causes the body to produce more HEMOGLOBIN. Why would this be a huge benefit to athletes? - Problems with this – higher RBC count makes the heart work much harder = risk of cardiac fatigue /even failure - Why do you think this is tough to test for? __________________________________________ I.O.C. b ...
Peptide Hormones, Growth and Related Substances
... cell absorption of glucose and amino acids. Insulin increases the synthesis of glycogen in the liver, stimulates the production of fats from glucose and inhabits the conversion of proteins to glucose. Insulin triggers a number of anabolic (building up) processes in metabolism, including synthesis of ...
... cell absorption of glucose and amino acids. Insulin increases the synthesis of glycogen in the liver, stimulates the production of fats from glucose and inhabits the conversion of proteins to glucose. Insulin triggers a number of anabolic (building up) processes in metabolism, including synthesis of ...
Endocrine System—secrete hormones into body fluids
... Negative Feedback systems-gland secretes hormone until concentration is high enough, then the gland is inhibited (STOPPED). When concentration falls, inhibition ceases and secretion begins again. Gland secretion is controlled by: 1. Hypothalamus controls anterior pituitary, which stimulates other gl ...
... Negative Feedback systems-gland secretes hormone until concentration is high enough, then the gland is inhibited (STOPPED). When concentration falls, inhibition ceases and secretion begins again. Gland secretion is controlled by: 1. Hypothalamus controls anterior pituitary, which stimulates other gl ...
Growth Hormone
... Growth Hormone AKA: Somatotropic hormone Classification: Anterior pituitary hormone ACTIONS AND USES: Regulates growth of the individual until somewhere around early adulthood or the time when the person no longer gains height. Recombinant DNA origin and are identical to human GH and produce skeleta ...
... Growth Hormone AKA: Somatotropic hormone Classification: Anterior pituitary hormone ACTIONS AND USES: Regulates growth of the individual until somewhere around early adulthood or the time when the person no longer gains height. Recombinant DNA origin and are identical to human GH and produce skeleta ...
Growth hormone
Growth hormone (GH or HGH), also known as somatotropin or somatropin, is a peptide hormone that stimulates growth, cell reproduction and regeneration in humans and other animals. It is a type of mitogen which is specific only to certain kinds of cells. Growth hormone is a 191-amino acid, single-chain polypeptide that is synthesized, stored, and secreted by somatotropic cells within the lateral wings of the anterior pituitary gland.GH is a stress hormone that raises the concentration of glucose and free fatty acids. It also stimulates production of IGF-1.GH is used as a prescription drug in medicine to treat children's growth disorders and adult growth hormone deficiency. In the United States, it is only available legally from pharmacies, by prescription from a doctor. In recent years in the United States, some doctors have started to prescribe growth hormone in GH-deficient older patients (but not on healthy people) to increase vitality. While legal, the efficacy and safety of this use for HGH has not been tested in a clinical trial. At this time, HGH is still considered a very complex hormone, and many of its functions are still unknown.In its role as an anabolic agent, HGH has been used by competitors in sports since at least 1982, and has been banned by the IOC and NCAA. Traditional urine analysis does not detect doping with HGH, so the ban was unenforceable until the early 2000s, when blood tests that could distinguish between natural and artificial HGH were starting to be developed. Blood tests conducted by WADA at the 2004 Olympic Games in Athens, Greece targeted primarily HGH. The use for the drug for performance enhancement is not currently approved by the FDA.GH has been studied for use in raising livestock more efficiently in industrial agriculture and several efforts have been made to obtain governmental approval to use GH in livestock production. These uses have been controversial. In the United States, the only FDA-approved use of GH for livestock is the use of a cow-specific form of GH called bovine somatotropin for increasing milk production in dairy cows. Retailers are permitted to label containers of milk as produced with or without bovine somatotropin.