• a single seller wants to sell a single indivisible unit of some object
... extracts the full surplus exists if and only if there is no type for any buyer whose beliefs about the other buyers’ types can be written as a positive linear combination of his own beliefs when he has other types. • intuition (due to Zvika Neeman) - start with a second price auction in which the hi ...
... extracts the full surplus exists if and only if there is no type for any buyer whose beliefs about the other buyers’ types can be written as a positive linear combination of his own beliefs when he has other types. • intuition (due to Zvika Neeman) - start with a second price auction in which the hi ...
CHT. 5 DATABASE MANAGEMENT
... For column strategies X and Y: if X has a better (smaller) payoff than Y for any row strategy, then Y is dominated by X. A dominated decision can be removed from the payoff table to simplify the problem. ...
... For column strategies X and Y: if X has a better (smaller) payoff than Y for any row strategy, then Y is dominated by X. A dominated decision can be removed from the payoff table to simplify the problem. ...
mixed strategy: p ^ i - Computer and Information Science
... improve our ability to predict (and design) the overall behavior of multi-agent systems. • Question of which strategy is “best” is often not the most appropriate, a mix of strategies can be an equilibrium. • The tournament approach has the shortcoming of being one trajectory through an infinite spac ...
... improve our ability to predict (and design) the overall behavior of multi-agent systems. • Question of which strategy is “best” is often not the most appropriate, a mix of strategies can be an equilibrium. • The tournament approach has the shortcoming of being one trajectory through an infinite spac ...
M - Sebastien Rouillon
... A player i’s message is an element mi = (pi, y) in IR2 For n ≥ 2, r is defined by: r(m) = ((wi – pi(m) y(m) – fi(m)2/2)i, y(m)), where: pi(m) = 1 – Sji pj, y(m) = Si yi/n, fi(m) = 1 – Si pi + Si yji/(n – 1) – yj. ...
... A player i’s message is an element mi = (pi, y) in IR2 For n ≥ 2, r is defined by: r(m) = ((wi – pi(m) y(m) – fi(m)2/2)i, y(m)), where: pi(m) = 1 – Sji pj, y(m) = Si yi/n, fi(m) = 1 – Si pi + Si yji/(n – 1) – yj. ...
Game Theory Zero
... This is just A's payoff matrix. What about B's? Because the total payoff for both A and B is always 100%, so B's payoff matrix can be constructed by deducting each of the payoff by 100. However, there is no urgency to construct B's payoff. We can simply analyze the game by assuming that: 1. A aims t ...
... This is just A's payoff matrix. What about B's? Because the total payoff for both A and B is always 100%, so B's payoff matrix can be constructed by deducting each of the payoff by 100. However, there is no urgency to construct B's payoff. We can simply analyze the game by assuming that: 1. A aims t ...
a > -r
... – Typically, transform such games into games of imperfect information and different ‘types’, modeled as a simultaneous game – Helpful to make a normal form (given beliefs about nature) and solve ...
... – Typically, transform such games into games of imperfect information and different ‘types’, modeled as a simultaneous game – Helpful to make a normal form (given beliefs about nature) and solve ...
Comparative Statics - Oregon State University
... Comparative statics or sensitivity analysis investigates how the endogenous variables of a model are affected by a change in a parameter or exogenous variable. The “comparative” term refers to a before and after comparison of an optimum or equilibrium value that results from a very small change in a ...
... Comparative statics or sensitivity analysis investigates how the endogenous variables of a model are affected by a change in a parameter or exogenous variable. The “comparative” term refers to a before and after comparison of an optimum or equilibrium value that results from a very small change in a ...
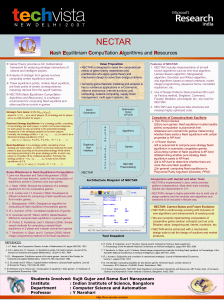
NECTAR: Nash Equilibrium Computation Algorithms
... Strategic Form Game: G=(N,(Si)iЄN,(ui)iЄN), where N = {1,2,…,n} is set of players, Si is strategy set for player i and ui is utility function for player i. Dominant Strategy Equilibrium: It is a strategy profile, consisting of one strategy per each player, in which it is the best response for each p ...
... Strategic Form Game: G=(N,(Si)iЄN,(ui)iЄN), where N = {1,2,…,n} is set of players, Si is strategy set for player i and ui is utility function for player i. Dominant Strategy Equilibrium: It is a strategy profile, consisting of one strategy per each player, in which it is the best response for each p ...
Towards a Constructive Theory of Networked Interactions
... Theorem [Daskalakis, Papadimitriou ’09] In every network of competitors: - a Nash equilibrium can be found efficiently with linear-programming; - the Nash equilibria comprise a convex set; - if every node uses a no-regret learning algorithm, the players’ behavior converges to a Nash equilibrium. str ...
... Theorem [Daskalakis, Papadimitriou ’09] In every network of competitors: - a Nash equilibrium can be found efficiently with linear-programming; - the Nash equilibria comprise a convex set; - if every node uses a no-regret learning algorithm, the players’ behavior converges to a Nash equilibrium. str ...
Existence and computation of equilibria of first
... monotonicity of the strategies. A pure strategy is said to be monotonic if for all vj < vi , β(vj ) ≤ β(vi ), i.e., bj ≤ bi . Theorem 3. A symmetric PSNE for a p.i.i.d auction with Vickrey tie-breaking is monotonic. ...
... monotonicity of the strategies. A pure strategy is said to be monotonic if for all vj < vi , β(vj ) ≤ β(vi ), i.e., bj ≤ bi . Theorem 3. A symmetric PSNE for a p.i.i.d auction with Vickrey tie-breaking is monotonic. ...
S - Webcourse
... Consider the following modification: the highest bidder wins, but pays half of his bid. The new (strange?) protocol implements the same function (the same allocation and payments for every tuple of agents’ valuations), and truth-revealing is in equilibrium there. ...
... Consider the following modification: the highest bidder wins, but pays half of his bid. The new (strange?) protocol implements the same function (the same allocation and payments for every tuple of agents’ valuations), and truth-revealing is in equilibrium there. ...
Learning and Belief Based Trade - David Levine`s Economic and
... Dekel at al showed that this is the case when players observe one another’s actions and there are independent private values. In the trading games that we consider here, it is not plausible that all agents observe one another’s actions. Never-the-less the equivalence of Nash and self-confirming equi ...
... Dekel at al showed that this is the case when players observe one another’s actions and there are independent private values. In the trading games that we consider here, it is not plausible that all agents observe one another’s actions. Never-the-less the equivalence of Nash and self-confirming equi ...
Static Games
... σ is a Nash equilibrium profile if for each i ∈1,! N ui (σ ) = max σ ’i ui (σ’i , σ − i ) ...
... σ is a Nash equilibrium profile if for each i ∈1,! N ui (σ ) = max σ ’i ui (σ’i , σ − i ) ...
Information Aggregation and Large Auctions
... • In private values markets, price reflect the aggregate demand and supply conditions, and measures the equilibrium level of scarcity. • With common values, price also reflects aggregate information on the true value of goods for sale. Financial markets are a prime example. • In general equilibrium ...
... • In private values markets, price reflect the aggregate demand and supply conditions, and measures the equilibrium level of scarcity. • With common values, price also reflects aggregate information on the true value of goods for sale. Financial markets are a prime example. • In general equilibrium ...
GEK1544 The Mathematics of Games Suggested Solutions to
... 1. Consider a zero sum game between players A and B, with the payoffs for A shown in the following diagram . ...
... 1. Consider a zero sum game between players A and B, with the payoffs for A shown in the following diagram . ...
mechanism design
... surplus, (iii) where all bidders are risk neutral, and (iv) drawn from a strictly increasing and atomless distribution, will lead to the same expected revenue for the seller (and each type of agent can expect the same surplus across auction types). Although we will not present a formal proof here, t ...
... surplus, (iii) where all bidders are risk neutral, and (iv) drawn from a strictly increasing and atomless distribution, will lead to the same expected revenue for the seller (and each type of agent can expect the same surplus across auction types). Although we will not present a formal proof here, t ...
Kin selection and Evolution of Sympathy
... • Selection is for utility and sympathy, not strategies (as in Alger-Weibull theory). • Individuals cannot determine sympathies of others, can only observe actions. • Mutants act as if probability that their opponent is like them is r. • Normals almost never see mutants. They act as if opponent is s ...
... • Selection is for utility and sympathy, not strategies (as in Alger-Weibull theory). • Individuals cannot determine sympathies of others, can only observe actions. • Mutants act as if probability that their opponent is like them is r. • Normals almost never see mutants. They act as if opponent is s ...
Rational expectation can preclude trades
... trade of the amounts of state-contingent commodities and they know their expectations. Common-knowledge about these conditions among all traders can preclude trade if the initial endowments allocation is a rational expectations equilibrium, even when the traders have the non-partition structure of i ...
... trade of the amounts of state-contingent commodities and they know their expectations. Common-knowledge about these conditions among all traders can preclude trade if the initial endowments allocation is a rational expectations equilibrium, even when the traders have the non-partition structure of i ...
How to rationalise auction sales
... At the level of establishing standards, the consequences have been even more important. Within the framework of the assumptions of the theory of auctions thus constructed, one could prove a rather fascinating theorem: the revenue equivalence theorem. Without going into the details, this theorem show ...
... At the level of establishing standards, the consequences have been even more important. Within the framework of the assumptions of the theory of auctions thus constructed, one could prove a rather fascinating theorem: the revenue equivalence theorem. Without going into the details, this theorem show ...
Paul Milgrom

Paul Robert Milgrom (born April 20, 1948 in Detroit, Michigan) is an American economist. He is the Shirley and Leonard Ely Professor of Humanities and Sciences at Stanford University, a position he has held since 1987. Professor Milgrom is an expert in game theory, specifically auction theory and pricing strategies. He is the co-creator of the no-trade theorem with Nancy Stokey. He is the co-founder of several companies, the most recent of which, Auctionomics, provides software and services that create efficient markets for complex commercial auctions and exchanges.