CHAPTER 4: Structure of the Atom
... electrons by a positive nucleus is discussed in relation to Planck’s theory. It will be shown that it is possible from the point of view taken to account in a simple way for the law of the line spectrum of hydrogen. - Niels Bohr, 1913 ...
... electrons by a positive nucleus is discussed in relation to Planck’s theory. It will be shown that it is possible from the point of view taken to account in a simple way for the law of the line spectrum of hydrogen. - Niels Bohr, 1913 ...
CHAPTER 4: Structure of the Atom
... electrons by a positive nucleus is discussed in relation to Planck’s theory. It will be shown that it is possible from the point of view taken to account in a simple way for the law of the line spectrum of hydrogen. - Niels Bohr, 1913 ...
... electrons by a positive nucleus is discussed in relation to Planck’s theory. It will be shown that it is possible from the point of view taken to account in a simple way for the law of the line spectrum of hydrogen. - Niels Bohr, 1913 ...
Serge Haroche
... The Nobel Laureates have opened the door to a new era of experimentation with quantum physics by demonstrating the direct observation of individual quantum particles without destroying them. For single particles of light or matter the laws of classical physics cease to apply and quantum physics take ...
... The Nobel Laureates have opened the door to a new era of experimentation with quantum physics by demonstrating the direct observation of individual quantum particles without destroying them. For single particles of light or matter the laws of classical physics cease to apply and quantum physics take ...
量子力學發展史
... Oscillate at the apparent frequency of the radiation since the oscillating electric field should set the electrons in motion ...
... Oscillate at the apparent frequency of the radiation since the oscillating electric field should set the electrons in motion ...
Lecture 8 1 Planck-Einstein Relation E = hν 2 Time evolution of real
... where h̄ = h/2π. ν is linear frequency and ω is angular frequency. The fundamental constant h is called Planck’s constant and is equal to 6.62608 ×10−34 Js (h̄ = 1.05457 × 10−34 Js, or 1.05457 × 10−27 erg s). This relation was first proposed by Planck in 1900 to explain the properties of black body ...
... where h̄ = h/2π. ν is linear frequency and ω is angular frequency. The fundamental constant h is called Planck’s constant and is equal to 6.62608 ×10−34 Js (h̄ = 1.05457 × 10−34 Js, or 1.05457 × 10−27 erg s). This relation was first proposed by Planck in 1900 to explain the properties of black body ...
lecture 10
... It is clear from the above equation that particle can have only desecrated values of energies. The lowest energy that particle can have corresponds to n=o , and is called zero-point energy. It is given by ...
... It is clear from the above equation that particle can have only desecrated values of energies. The lowest energy that particle can have corresponds to n=o , and is called zero-point energy. It is given by ...
PHYS 1111 Mechanics, Waves, & Thermodynamics
... - teach you the fundamental principles/laws of physics - teach you how to apply these principles to practical problem solving (useful in other fields) ...
... - teach you the fundamental principles/laws of physics - teach you how to apply these principles to practical problem solving (useful in other fields) ...
This `practice exam`
... capacities of zinc and water are 0.388 J/g·K and 4.184 J/g·K, respectively. 72.1 °C 27. What is the wavelength of radiation that has a frequency of 2.10 × 1014 s −1? 1.43 × 10−6 m 28. The ________ of a photon of light is ________ proportional to its frequency and ________ proportional to its wavelen ...
... capacities of zinc and water are 0.388 J/g·K and 4.184 J/g·K, respectively. 72.1 °C 27. What is the wavelength of radiation that has a frequency of 2.10 × 1014 s −1? 1.43 × 10−6 m 28. The ________ of a photon of light is ________ proportional to its frequency and ________ proportional to its wavelen ...
Particle in a box (PPT - 6.9MB)
... The Munich physics professor Jolly advised Planck against going into physics, saying, “in this field, almost everything is already discovered, and all that remains is to fill a few holes.” In 1877 he went to Berlin for a year of study with physicists Helmholtz and Kirchhoff. He wrote that Kirchhoff ...
... The Munich physics professor Jolly advised Planck against going into physics, saying, “in this field, almost everything is already discovered, and all that remains is to fill a few holes.” In 1877 he went to Berlin for a year of study with physicists Helmholtz and Kirchhoff. He wrote that Kirchhoff ...
Characteristic Functions and the Uncertainty Principle
... Characteristic Functions and the Uncertainty Relationship There is an inverse relationship between the dispersion of a function and the range of the frequencies which are present in its transform. Thus one finds that, the shorter is the duration of a transient signal, the wider is the spread of the ...
... Characteristic Functions and the Uncertainty Relationship There is an inverse relationship between the dispersion of a function and the range of the frequencies which are present in its transform. Thus one finds that, the shorter is the duration of a transient signal, the wider is the spread of the ...
Example Midterm Solutions
... which the electrons are leaving and the negative plate is the plate to which they are heading. As you know, this will slow the electrons down, and if he turns the voltage up high enough, it will slow them to a complete stop and we won’t have emitted electrons. In such a case, we have KE = e · ∆V . D ...
... which the electrons are leaving and the negative plate is the plate to which they are heading. As you know, this will slow the electrons down, and if he turns the voltage up high enough, it will slow them to a complete stop and we won’t have emitted electrons. In such a case, we have KE = e · ∆V . D ...
Solutions to the 2017 Sample Exam Paper
... Young interpreted the bright and dark lines as evidence of interference due to light travelling by paths of different distances from the two vertical openings to a point on the screen. Interference is a phenomenon unique to waves. This experiment showed that light could behave as a wave. (1) 18b In ...
... Young interpreted the bright and dark lines as evidence of interference due to light travelling by paths of different distances from the two vertical openings to a point on the screen. Interference is a phenomenon unique to waves. This experiment showed that light could behave as a wave. (1) 18b In ...
REVIEW OF WAVE MECHANICS
... Thus in quantum mechanics we typically calculate the probabilities of results of measurements. You are already familiar with this idea through the interpretation of the wave function, where * gives the probability of finding the particle at a given position. This restriction to probability rather ...
... Thus in quantum mechanics we typically calculate the probabilities of results of measurements. You are already familiar with this idea through the interpretation of the wave function, where * gives the probability of finding the particle at a given position. This restriction to probability rather ...
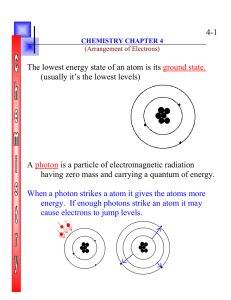
4-1 The lowest energy state of an atom is its ground state. (usually
... A photon is a particle of electromagnetic radiation having zero mass and carrying a quantum of energy. When a photon strikes a atom it gives the atoms more energy. If enough photons strike an atom it may cause electrons to jump levels. ...
... A photon is a particle of electromagnetic radiation having zero mass and carrying a quantum of energy. When a photon strikes a atom it gives the atoms more energy. If enough photons strike an atom it may cause electrons to jump levels. ...
FREE WILL - science.uu.nl project csg
... At the Planck scale, Quantum Mechanics is not wrong, but its interpretation may have to be revised, not only for philosophical reasons, but also to enable us to construct more concise theories, recovering e.g. locality (which appears to have been lost in string theory). The “random numbers”, inheren ...
... At the Planck scale, Quantum Mechanics is not wrong, but its interpretation may have to be revised, not only for philosophical reasons, but also to enable us to construct more concise theories, recovering e.g. locality (which appears to have been lost in string theory). The “random numbers”, inheren ...
Nanoscience
... and valleys that move around and reflect off walls much like water waves. You can see the electron waves in the left image of Fig. 1.1. When a peak meets a valley there is destructive interference and when a peak meets a peak there is constructive interference. While an electron is moving, don't thi ...
... and valleys that move around and reflect off walls much like water waves. You can see the electron waves in the left image of Fig. 1.1. When a peak meets a valley there is destructive interference and when a peak meets a peak there is constructive interference. While an electron is moving, don't thi ...
Unit 3: Atomic Theory & Quantum Mechanics Section A.3
... at a given temperature (blackbody radiation) Doesn’t explain why some metals emit electrons when light of a specific frequency shines on them (photoelectric effect) ...
... at a given temperature (blackbody radiation) Doesn’t explain why some metals emit electrons when light of a specific frequency shines on them (photoelectric effect) ...
Ex3710: Electron in Hall Geometry - Double Well
... A two dimensional rectangle is given. In the x direction (0 < x < L) there are periodic boundary conditions. In the y direction there is a slowly varying electric potential. V (y) ≈ 0. This potential ...
... A two dimensional rectangle is given. In the x direction (0 < x < L) there are periodic boundary conditions. In the y direction there is a slowly varying electric potential. V (y) ≈ 0. This potential ...
Discrete emission spectra
... instance go from the 3rd vibration mode to the 2nd, from the 4th to the 2nd or from the 5th to the 2nd. During such a transition the electrons gives away an energy ΔE which is radiated in the form of a vibration of the electromagnetic field: an electromagnetic wave (i.e. light). The more energy is r ...
... instance go from the 3rd vibration mode to the 2nd, from the 4th to the 2nd or from the 5th to the 2nd. During such a transition the electrons gives away an energy ΔE which is radiated in the form of a vibration of the electromagnetic field: an electromagnetic wave (i.e. light). The more energy is r ...
Introduction, Introduction to lasers, Properties of light
... The Fraunhofer limit - the distance after which the light starts to spread, a = s D = a2/l light starts to behave like a wave For a 1 mm wide slit, l = 500 nm D = ? At this D light behaves like a wave ...
... The Fraunhofer limit - the distance after which the light starts to spread, a = s D = a2/l light starts to behave like a wave For a 1 mm wide slit, l = 500 nm D = ? At this D light behaves like a wave ...