Abstract
... research where the confounding effects due to unknown infectious agents are a serious concern. Research areas such as aging, cancer, immunity, infection, and toxicology often require that the zebrafish be maintained for a much greater portion of their life span and that the histopathologic changes i ...
... research where the confounding effects due to unknown infectious agents are a serious concern. Research areas such as aging, cancer, immunity, infection, and toxicology often require that the zebrafish be maintained for a much greater portion of their life span and that the histopathologic changes i ...
Viral Diseases in Zebrafish: What Is Known and Unknown
... The potential effects of unrecognized viral infections may, in some cases, be similar to the confounding effects documented for parasitic and bacterial infections in zebrafish and other laboratory fishes. Mycobacterium spp. are the most important bacterial pathogens of laboratory zebrafish and cause ...
... The potential effects of unrecognized viral infections may, in some cases, be similar to the confounding effects documented for parasitic and bacterial infections in zebrafish and other laboratory fishes. Mycobacterium spp. are the most important bacterial pathogens of laboratory zebrafish and cause ...
Recommendations for Prevention and Control of Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) Chronic Disease
... exposures associated with transmission of HCV, blood transfusion and injecting-drug use, has changed over time (Figure 1) (2,5 ). Blood transfusion, which accounted for a substantial proportion of HCV infections acquired >10 years ago, rarely accounts for recently acquired infections. Since 1994, ri ...
... exposures associated with transmission of HCV, blood transfusion and injecting-drug use, has changed over time (Figure 1) (2,5 ). Blood transfusion, which accounted for a substantial proportion of HCV infections acquired >10 years ago, rarely accounts for recently acquired infections. Since 1994, ri ...
The Polio Vaccine
... Polio (poliomyelitis) is a potentially dangerous viral ailment. To combat this disease, researchers developed two polio vaccines (inactivated and live) grown in cultures made from monkey kidneys. Beginning in the 1950s, these vaccines were administered to millions of people in the United States and ...
... Polio (poliomyelitis) is a potentially dangerous viral ailment. To combat this disease, researchers developed two polio vaccines (inactivated and live) grown in cultures made from monkey kidneys. Beginning in the 1950s, these vaccines were administered to millions of people in the United States and ...
Syphilis: A Reemerging Infection
... attention to the diagnosis and treatment of this disease. Men who have sex with men are particularly affected; however, increases in infection rates have also been noted in women, as well as in all age groups and ethnicities. Physicians need to vigilantly screen high-risk patients. The concurrent ri ...
... attention to the diagnosis and treatment of this disease. Men who have sex with men are particularly affected; however, increases in infection rates have also been noted in women, as well as in all age groups and ethnicities. Physicians need to vigilantly screen high-risk patients. The concurrent ri ...
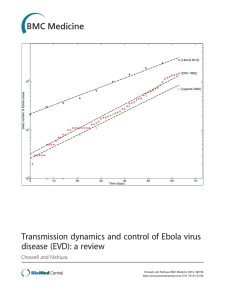
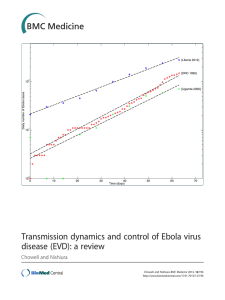
Transmission dynamics and control of Ebola virus disease (EVD): a review
... with fruit bats considered as the most likely reservoir host [15]. The great majority of past Ebola outbreaks in humans have been linked to three Ebola strains: EBOV, SUDV and BDBV [16]. The Ebola virus, EBOV, (formerly designated Zaire ebolavirus), the deadliest of the five Ebolavirus strains, was ...
... with fruit bats considered as the most likely reservoir host [15]. The great majority of past Ebola outbreaks in humans have been linked to three Ebola strains: EBOV, SUDV and BDBV [16]. The Ebola virus, EBOV, (formerly designated Zaire ebolavirus), the deadliest of the five Ebolavirus strains, was ...
Transmission dynamics and control of Ebola virus
... with fruit bats considered as the most likely reservoir host [15]. The great majority of past Ebola outbreaks in humans have been linked to three Ebola strains: EBOV, SUDV and BDBV [16]. The Ebola virus, EBOV, (formerly designated Zaire ebolavirus), the deadliest of the five Ebolavirus strains, was ...
... with fruit bats considered as the most likely reservoir host [15]. The great majority of past Ebola outbreaks in humans have been linked to three Ebola strains: EBOV, SUDV and BDBV [16]. The Ebola virus, EBOV, (formerly designated Zaire ebolavirus), the deadliest of the five Ebolavirus strains, was ...
Flu Home Care Guide
... You have probably heard of the flu, and you may have even had it before. The flu, also called seasonal flu or influenza, is one of the most common human infectious diseases. Infectious diseases are caused by germs (microorganisms). The germ that causes the flu is the influenza virus. The flu affects ...
... You have probably heard of the flu, and you may have even had it before. The flu, also called seasonal flu or influenza, is one of the most common human infectious diseases. Infectious diseases are caused by germs (microorganisms). The germ that causes the flu is the influenza virus. The flu affects ...
File - Mary Jacobs RN
... information for the management of MRSA. The chase study looks at new drug regimens to help combat against MRSA. Four hundred eighty-nine MRSA blood isolates were tested over four time periods spanning eleven years with the last one done in December 2006 (Chase, et al., 2009). Chase reveled an emergi ...
... information for the management of MRSA. The chase study looks at new drug regimens to help combat against MRSA. Four hundred eighty-nine MRSA blood isolates were tested over four time periods spanning eleven years with the last one done in December 2006 (Chase, et al., 2009). Chase reveled an emergi ...
Biosafety Level 2: . Special Practices
... Clinical, diagnostic, teaching, and other laboratories ...
... Clinical, diagnostic, teaching, and other laboratories ...
Community-acquired pneumonia in children: Clinical features and
... group A Streptococcus, which may follow days of upper respiratory tract infection symptoms, is considered abrupt in onset, with the febrile patient appearing ill and sometimes toxic. Respiratory distress is moderate to severe; auscultatory findings may be few and focal, limited to the involved anato ...
... group A Streptococcus, which may follow days of upper respiratory tract infection symptoms, is considered abrupt in onset, with the febrile patient appearing ill and sometimes toxic. Respiratory distress is moderate to severe; auscultatory findings may be few and focal, limited to the involved anato ...
IMCI - Mother and Child Nutrition
... recommended four to six months. The current IMCI guidelines for complementary feeding remain valid in developing countries. In areas where HIV is a public health problem all women should be encouraged to receive HIV testing and counselling. If a mother is HIV-infected and replacement feeding is acce ...
... recommended four to six months. The current IMCI guidelines for complementary feeding remain valid in developing countries. In areas where HIV is a public health problem all women should be encouraged to receive HIV testing and counselling. If a mother is HIV-infected and replacement feeding is acce ...
Intra-abdominal Infection - Infectious Diseases Society of America
... 20. For health care–associated infections, Gram stains may help define the presence of yeast (C-III). 21. Routine aerobic and anaerobic cultures from lower-risk patients with community-acquired infection are considered optional in the individual patient but may be of value in detecting epidemiologic ...
... 20. For health care–associated infections, Gram stains may help define the presence of yeast (C-III). 21. Routine aerobic and anaerobic cultures from lower-risk patients with community-acquired infection are considered optional in the individual patient but may be of value in detecting epidemiologic ...
Appendix B
... regulations, and the list of reportable diseases in each state differs. CDC and the Council of State and Territorial Epidemiologists (CSTE) have established a policy that requires state health departments to report cases of selected diseases to CDC's National Notifiable Diseases Surveillance System ...
... regulations, and the list of reportable diseases in each state differs. CDC and the Council of State and Territorial Epidemiologists (CSTE) have established a policy that requires state health departments to report cases of selected diseases to CDC's National Notifiable Diseases Surveillance System ...
Import Risk Analysis: Cattle from Australia, Canada, the
... This risk analysis is limited to the description of the risks due to disease-causing organisms associated with the importation of cattle from the USA, Canada, Australia, and the European Union (27 countries). Other risk factors that may be of commercial importance to importers (e.g. genetic diseases ...
... This risk analysis is limited to the description of the risks due to disease-causing organisms associated with the importation of cattle from the USA, Canada, Australia, and the European Union (27 countries). Other risk factors that may be of commercial importance to importers (e.g. genetic diseases ...
SARS - tfss-g4p
... Toronto were placed in quarantine, in order to protect millions of people in the city and around the world from possible exposure to a deadly disease However this was often also considered an infringement on one’s individual freedoms, thus the issue’s ethical constraints Officials should then be for ...
... Toronto were placed in quarantine, in order to protect millions of people in the city and around the world from possible exposure to a deadly disease However this was often also considered an infringement on one’s individual freedoms, thus the issue’s ethical constraints Officials should then be for ...
Diagnosis and Management of Complicated Intra
... patients with community-acquired infection are considered optional in the individual patient but may be of value in detecting epidemiological changes in the resistance patterns of pathogens associated with community-acquired intra-abdominal infection and in guiding follow-up oral therapy (B-II). 22. ...
... patients with community-acquired infection are considered optional in the individual patient but may be of value in detecting epidemiological changes in the resistance patterns of pathogens associated with community-acquired intra-abdominal infection and in guiding follow-up oral therapy (B-II). 22. ...
Diagnosis and Management of Syphilis
... B and C, gonorrhea, and chlamydial infection also should be considered. After appropriate treatment has been administered, patients should be followed with quantitative nontreponemal test titers to establish treatment response. Typically, nontreponemal test titers should become at least four times l ...
... B and C, gonorrhea, and chlamydial infection also should be considered. After appropriate treatment has been administered, patients should be followed with quantitative nontreponemal test titers to establish treatment response. Typically, nontreponemal test titers should become at least four times l ...
The Polio Vaccine - ThinkTwice Global Vaccine Institute
... Polio (poliomyelitis) is a potentially dangerous viral ailment. To combat this disease, researchers developed two polio vaccines (inactivated and live) grown in cultures made from monkey kidneys. Beginning in the 1950s, these vaccines were administered to millions of people in the United States and ...
... Polio (poliomyelitis) is a potentially dangerous viral ailment. To combat this disease, researchers developed two polio vaccines (inactivated and live) grown in cultures made from monkey kidneys. Beginning in the 1950s, these vaccines were administered to millions of people in the United States and ...
Diagnosis and Management of Complicated Intra
... patients with community-acquired infection are considered optional in the individual patient but may be of value in detecting epidemiological changes in the resistance patterns of pathogens associated with community-acquired intra-abdominal infection and in guiding follow-up oral therapy (B-II). 22. ...
... patients with community-acquired infection are considered optional in the individual patient but may be of value in detecting epidemiological changes in the resistance patterns of pathogens associated with community-acquired intra-abdominal infection and in guiding follow-up oral therapy (B-II). 22. ...
Chickenpox

Chickenpox, also known as varicella, is a highly contagious disease caused by the initial infection with varicella zoster virus (VZV). The disease results in a characteristic skin rash that forms small, itchy blisters, which eventually scab over. It usually starts on the face, chest, and back and then spreads to the rest of the body. Other symptoms may include fever, feeling tired, and headaches. Symptoms usually last five to ten days. Complications may occasionally include pneumonia, inflammation of the brain, or bacterial infections of the skin among others. The disease is often more severe in adults than children. Symptoms begin ten to twenty one days after exposure to the virus.Chickenpox is an airborne disease which spreads easily through the coughs and sneezes of an infected person. It may be spread from one to two days before the rash appears until all lesions have crusted over. It may also spread through contact with the blisters. Those with shingles may spread chickenpox to those who are not immune through contact with the blisters. The disease can usually be diagnosed based on the presenting symptom; however, in unusual cases may be confirmed by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing of the blister fluid or scabs. Testing for antibodies may be done to determine if a person is or is not immune. People usually only get the disease once.The varicella vaccine has resulted in a decrease in the number of cases and complications from the disease. It protects about 70 to 90 percent of people from disease with a greater benefit for severe disease. Routine immunization of children is recommended in many countries. Immunization within three days of exposure may improve outcomes in children. Treatment of those infected may include calamine lotion to help with itching, keeping the fingernails short to decrease injury from scratching, and the use of paracetamol (acetaminophen) to help with fevers. For those at increased risk of complications antiviral medication such as aciclovir are recommended.Chickenpox occurs in all parts of the world. Before routine immunization the number of cases occurring each year was similar to the number of people born. Since immunization the number of infections in the United States has decreased nearly 90%. In 2013 chickenpox resulted in 7,000 deaths globally – down from 8,900 in 1990. Death occurs in about 1 per 60,000 cases. Chickenpox was not separated from smallpox until the late 19th century. In 1888 its connection to shingles was determined. The first documented use of the term chicken pox was in 1658. Various explanations have been suggested for the use of ""chicken"" in the name, one being the relative mildness of the disease.