Herd Health Planning - IBR
... Vulvovaginitis; IBR/IPV), is an infectious disease of cattle caused by the virus Bovine Herpesvirus-1. A few countries are now close to eradication. In order to gain access to export markets, herds may soon have to prove that they are free from IBR. How does IBR affect cattle? • The virus can infect ...
... Vulvovaginitis; IBR/IPV), is an infectious disease of cattle caused by the virus Bovine Herpesvirus-1. A few countries are now close to eradication. In order to gain access to export markets, herds may soon have to prove that they are free from IBR. How does IBR affect cattle? • The virus can infect ...
High Morbidity and Mortality in Adults Hospitalized for Respiratory
... diagnosed among the hospitalized adults: 2009, n = 123; 2010, n = 237; 2011, n = 247. The median RSV-positive rate among submitted respiratory samples during the seasonal peaks of the years was: 5.8% (interquartile range [IQR], 4.8%–6.5%), 6.6% (IQR, 5.8%–9.8%), and 9.1% (IQR, 5.7%–13.7%), respectiv ...
... diagnosed among the hospitalized adults: 2009, n = 123; 2010, n = 237; 2011, n = 247. The median RSV-positive rate among submitted respiratory samples during the seasonal peaks of the years was: 5.8% (interquartile range [IQR], 4.8%–6.5%), 6.6% (IQR, 5.8%–9.8%), and 9.1% (IQR, 5.7%–13.7%), respectiv ...
The pathogenesis of bovine virus diarrhoea virus infections
... virus free in serum or as virus associated with the cells within the buffy coat fraction of blood; the lymphocytes and monocytes are generally regarded as being particularly sensitive to BVDV infection (65). A decrease in the B-lymphocytes following acute BVDV infection has been reported (54) and a ...
... virus free in serum or as virus associated with the cells within the buffy coat fraction of blood; the lymphocytes and monocytes are generally regarded as being particularly sensitive to BVDV infection (65). A decrease in the B-lymphocytes following acute BVDV infection has been reported (54) and a ...
Biological Clinical Guidelines
... Knowing that the incubation period, from the time of contact to the time when symptoms appear is at least one day for most agents, there will not be a need to establish triage areas for: Immediate ...
... Knowing that the incubation period, from the time of contact to the time when symptoms appear is at least one day for most agents, there will not be a need to establish triage areas for: Immediate ...
Hepatitis
... Transmission fecal-oral route; Contaminated water and food The incubation period of hepatitis A virus is 2-7 weeks, AST & ALT levels usually return to reference ranges over 5-20 weeks. High risk Travellers: vaccinations; passive immunoglobins given to those exposed Mild self-limited dise ...
... Transmission fecal-oral route; Contaminated water and food The incubation period of hepatitis A virus is 2-7 weeks, AST & ALT levels usually return to reference ranges over 5-20 weeks. High risk Travellers: vaccinations; passive immunoglobins given to those exposed Mild self-limited dise ...
The Arrow of Disease - Anthropologyman.com
... The most effortless way a bug can spread is by just waiting to be transmitted passively to the next victim. That's the strategy practiced by microbes that wait for one host to be eaten by the next-salmonella bacteria, for example, which we contract by eating already-infected eggs or meat; or the wor ...
... The most effortless way a bug can spread is by just waiting to be transmitted passively to the next victim. That's the strategy practiced by microbes that wait for one host to be eaten by the next-salmonella bacteria, for example, which we contract by eating already-infected eggs or meat; or the wor ...
Aicardi-Goutières syndrome: differential diagnosis and
... Aicardi-Goutières syndrome (AGS) is a progressive encephalopathy with onset in the first year of life and a recessive autosomal pattern of inheritance. The syndrome is characterised by acquired microcephaly, basal ganglia calcifications, white matter abnormalities, chronic cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) ...
... Aicardi-Goutières syndrome (AGS) is a progressive encephalopathy with onset in the first year of life and a recessive autosomal pattern of inheritance. The syndrome is characterised by acquired microcephaly, basal ganglia calcifications, white matter abnormalities, chronic cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) ...
Tick-related Disease Thrives On Cholesterol, Study Suggests
... person may be to developing a severe case of HGA, said Yasuko Rikihisa, the study's lead author and a professor of veterinary biosciences at Ohio State University. Yet HGA is difficult to accurately diagnose, as symptoms are similar to those of the flu and include high fever, muscle aches, chills an ...
... person may be to developing a severe case of HGA, said Yasuko Rikihisa, the study's lead author and a professor of veterinary biosciences at Ohio State University. Yet HGA is difficult to accurately diagnose, as symptoms are similar to those of the flu and include high fever, muscle aches, chills an ...
Seroepidemiology of infection with herpes simplex virus types 1 and
... higher risk of HSV2 infection (6). Studies have shown that in the United States about 17% of adults have antibodies to HSV-2 and 58% against HSV-1. Over two-thirds of these persons are not aware of their infections, although they transmit most of these viruses (2,6). In similar aged adults, the numb ...
... higher risk of HSV2 infection (6). Studies have shown that in the United States about 17% of adults have antibodies to HSV-2 and 58% against HSV-1. Over two-thirds of these persons are not aware of their infections, although they transmit most of these viruses (2,6). In similar aged adults, the numb ...
Host factors and genetic susceptibility to infections due to
... and mosquitoes for diseases caused by Rickettsiae or Tularemia. Socio-demographical factors such as farming and close contact with animals are also important risk factors as documented in multiple outbreaks of C. burnetii infections reported after close exposure to animals in the Netherlands between ...
... and mosquitoes for diseases caused by Rickettsiae or Tularemia. Socio-demographical factors such as farming and close contact with animals are also important risk factors as documented in multiple outbreaks of C. burnetii infections reported after close exposure to animals in the Netherlands between ...
ACUTE GASTROENTERITIS-REVISED
... sulfamethoxazole, ampicillin, and nalidixic acid, which were once considered optimal therapies for shigellosis. Clinical trials have established the efficacy of newer fluoroquinolones for adults with shigellosis. In immunocompetent patients with campylobacteriosis, erythromycin reduces carriage of t ...
... sulfamethoxazole, ampicillin, and nalidixic acid, which were once considered optimal therapies for shigellosis. Clinical trials have established the efficacy of newer fluoroquinolones for adults with shigellosis. In immunocompetent patients with campylobacteriosis, erythromycin reduces carriage of t ...
Pott’s disease
... often develops kyphosis, which results in a hunchback. This is often referred to as Pott’s curvature. In some cases, a person with Pott’s disease may also develop paralysis, referred to as Pott’s paraplegia, when the spinal nerves become affected by the curvature. A person with Pott’s disease may ex ...
... often develops kyphosis, which results in a hunchback. This is often referred to as Pott’s curvature. In some cases, a person with Pott’s disease may also develop paralysis, referred to as Pott’s paraplegia, when the spinal nerves become affected by the curvature. A person with Pott’s disease may ex ...
Avian infectious laryngotracheitis: Virus‐host interactions in relation
... have shown that wild-strain ILTV could be detected in 38% of chickens examined 3 to 15 months after trachéal exposure, while a similar proportion of chickens infected with an Australian ILT vaccine-strain were detected from 2 to 10 months p.i. (Bagust, 1986). Also reported in this study was the find ...
... have shown that wild-strain ILTV could be detected in 38% of chickens examined 3 to 15 months after trachéal exposure, while a similar proportion of chickens infected with an Australian ILT vaccine-strain were detected from 2 to 10 months p.i. (Bagust, 1986). Also reported in this study was the find ...
Viral meningitis
... The typical viruses that cause viral meningitis can spread to close contacts, such as household members, friends and colleagues. The virus can be spread from just before an infected person gets sick; the person will then be infectious for about another week. Only some people who get infected will de ...
... The typical viruses that cause viral meningitis can spread to close contacts, such as household members, friends and colleagues. The virus can be spread from just before an infected person gets sick; the person will then be infectious for about another week. Only some people who get infected will de ...
INFECTIOUS AGENT EXCLUSION LIST FOR RATS
... Etiology: 3 major antigenic groups represented by Kilham’s rat virus (KRV or RV), Toolan’s H-1, rat parvovirus (RPV, formerly ROPV, rat orphan parvovirus); conserved nonstructural proteins so IFA for serodetection; small, single strand DNA, nonenveloped. Transmission: oronasal, fomites, transplacent ...
... Etiology: 3 major antigenic groups represented by Kilham’s rat virus (KRV or RV), Toolan’s H-1, rat parvovirus (RPV, formerly ROPV, rat orphan parvovirus); conserved nonstructural proteins so IFA for serodetection; small, single strand DNA, nonenveloped. Transmission: oronasal, fomites, transplacent ...
Cutaneous Manifestations of Human Immunodeficiency Virus: a
... Skin reactions to drugs complicate in 2–3 % of all hospitalbased treatments [25]. These reactions can range from morbilliform eruptions to life-threatening forms like TEN. HIV infection has been associated with an increased risk for SJS and TEN [26]. Increased exposures to medications or decreased i ...
... Skin reactions to drugs complicate in 2–3 % of all hospitalbased treatments [25]. These reactions can range from morbilliform eruptions to life-threatening forms like TEN. HIV infection has been associated with an increased risk for SJS and TEN [26]. Increased exposures to medications or decreased i ...
Nonspecific Infections of the Genitourinary Tract
... Symptoms: When bilateral and advanced, anemia; azotemia and hypertension Signs:Usually associated with hypertension Laboratory Findings: Azotemia, proteinuria, BUN and creatinine elevation Radiological Findings: Kidney small and ...
... Symptoms: When bilateral and advanced, anemia; azotemia and hypertension Signs:Usually associated with hypertension Laboratory Findings: Azotemia, proteinuria, BUN and creatinine elevation Radiological Findings: Kidney small and ...
Chlamydia is a sexually transmitted disease caused by an organism
... Women who have chlamydia may also be more likely to get HIV, the virus that causes AIDS, from a person who is infected with HIV. Because of the symptoms associated with chlamydia, infected individuals have a three- to five-fold increase in the risk of acquiring HIV (the virus that causes AIDS) if ex ...
... Women who have chlamydia may also be more likely to get HIV, the virus that causes AIDS, from a person who is infected with HIV. Because of the symptoms associated with chlamydia, infected individuals have a three- to five-fold increase in the risk of acquiring HIV (the virus that causes AIDS) if ex ...
Unit 4A: Purpose of Standard Precautions and when they are applied
... “This workforce solution was funded by a grant awarded by the U.S. Department of Labor’s Employment and Training Administration. The solution was created by the grantee and does not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Labor. The Department of Labor makes no guarantees ...
... “This workforce solution was funded by a grant awarded by the U.S. Department of Labor’s Employment and Training Administration. The solution was created by the grantee and does not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Labor. The Department of Labor makes no guarantees ...
Chlamydia is a sexually transmitted disease
... Women who have chlamydia may also be more likely to get HIV, the virus that causes AIDS, from a person who is infected with HIV. Because of the symptoms associated with chlamydia, infected individuals have a three- to five-fold increase in the risk of acquiring HIV (the virus that causes AIDS) if ex ...
... Women who have chlamydia may also be more likely to get HIV, the virus that causes AIDS, from a person who is infected with HIV. Because of the symptoms associated with chlamydia, infected individuals have a three- to five-fold increase in the risk of acquiring HIV (the virus that causes AIDS) if ex ...
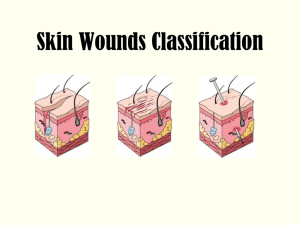
Skin Wounds Classifications-
... Impetigo o Mild itching & soreness o Eruption of small vesicles and/or pustules that rupture to form honey-colored crusts o Combo of 2 bacteria that spread rapidly when athletes in close contact with one another o Responds rapidly to proper treatment o Thorough cleansing of crusted area o Applicati ...
... Impetigo o Mild itching & soreness o Eruption of small vesicles and/or pustules that rupture to form honey-colored crusts o Combo of 2 bacteria that spread rapidly when athletes in close contact with one another o Responds rapidly to proper treatment o Thorough cleansing of crusted area o Applicati ...
BIOSAFETY
... It consists of a combination of laboratory practices, equipment and facilities suitable to the procedures being performed and hazards of the pathogen. The four biosafety levels corresponds to four risk groups. A lower risk group can be assigned a higher biosafety level, if a biological risk assessme ...
... It consists of a combination of laboratory practices, equipment and facilities suitable to the procedures being performed and hazards of the pathogen. The four biosafety levels corresponds to four risk groups. A lower risk group can be assigned a higher biosafety level, if a biological risk assessme ...
Chickenpox

Chickenpox, also known as varicella, is a highly contagious disease caused by the initial infection with varicella zoster virus (VZV). The disease results in a characteristic skin rash that forms small, itchy blisters, which eventually scab over. It usually starts on the face, chest, and back and then spreads to the rest of the body. Other symptoms may include fever, feeling tired, and headaches. Symptoms usually last five to ten days. Complications may occasionally include pneumonia, inflammation of the brain, or bacterial infections of the skin among others. The disease is often more severe in adults than children. Symptoms begin ten to twenty one days after exposure to the virus.Chickenpox is an airborne disease which spreads easily through the coughs and sneezes of an infected person. It may be spread from one to two days before the rash appears until all lesions have crusted over. It may also spread through contact with the blisters. Those with shingles may spread chickenpox to those who are not immune through contact with the blisters. The disease can usually be diagnosed based on the presenting symptom; however, in unusual cases may be confirmed by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing of the blister fluid or scabs. Testing for antibodies may be done to determine if a person is or is not immune. People usually only get the disease once.The varicella vaccine has resulted in a decrease in the number of cases and complications from the disease. It protects about 70 to 90 percent of people from disease with a greater benefit for severe disease. Routine immunization of children is recommended in many countries. Immunization within three days of exposure may improve outcomes in children. Treatment of those infected may include calamine lotion to help with itching, keeping the fingernails short to decrease injury from scratching, and the use of paracetamol (acetaminophen) to help with fevers. For those at increased risk of complications antiviral medication such as aciclovir are recommended.Chickenpox occurs in all parts of the world. Before routine immunization the number of cases occurring each year was similar to the number of people born. Since immunization the number of infections in the United States has decreased nearly 90%. In 2013 chickenpox resulted in 7,000 deaths globally – down from 8,900 in 1990. Death occurs in about 1 per 60,000 cases. Chickenpox was not separated from smallpox until the late 19th century. In 1888 its connection to shingles was determined. The first documented use of the term chicken pox was in 1658. Various explanations have been suggested for the use of ""chicken"" in the name, one being the relative mildness of the disease.