infectious diseases: a review Modelling the influence of human
... More sophisticated models can explicitly include spatial or contact network structure, so that each individual in the population can be infected only by a constrained set of other individuals. A number of studies have considered extensions of the simple SIR model in which the incidence rate is not b ...
... More sophisticated models can explicitly include spatial or contact network structure, so that each individual in the population can be infected only by a constrained set of other individuals. A number of studies have considered extensions of the simple SIR model in which the incidence rate is not b ...
011801 Acute Pharyngitis - New England Journal of Medicine
... the full-blown syndrome; many cases are milder and nonexudative, and patients who have undergone tonsillectomy may have milder symptoms. Children less than three years of age may have coryza and crusting of the nares; exudative pharyngitis is rare in this age group. ...
... the full-blown syndrome; many cases are milder and nonexudative, and patients who have undergone tonsillectomy may have milder symptoms. Children less than three years of age may have coryza and crusting of the nares; exudative pharyngitis is rare in this age group. ...
Influenza or Stomach Flu (Gatroenteritis)?
... tract). Gastroenteritis may be caused by a virus, bacteria, parasites in spoiled food or unclean water, or another trigger such as lactose intolerance, which causes a reaction to dairy products. Influenza (flu), on the other hand, is a viral infection that mimics a cold except that it starts forcefu ...
... tract). Gastroenteritis may be caused by a virus, bacteria, parasites in spoiled food or unclean water, or another trigger such as lactose intolerance, which causes a reaction to dairy products. Influenza (flu), on the other hand, is a viral infection that mimics a cold except that it starts forcefu ...
Some New Emerging Viral Diseases in South America and East
... Iquitos virus is another new virus that has just been mentioned for a few years. It is also in the group of bunyavirus. This virus is also firstly reported from Peru. The genetic reassortment of this virus contains “the S and L segments of Oropouche virus and the M segment of a novel Simbu serogroup ...
... Iquitos virus is another new virus that has just been mentioned for a few years. It is also in the group of bunyavirus. This virus is also firstly reported from Peru. The genetic reassortment of this virus contains “the S and L segments of Oropouche virus and the M segment of a novel Simbu serogroup ...
Campylobacter and Helicobacter
... Spontaneous abortions in cattle, sheep, and swine, but generally asymptomatic carriage in animal reservoir Humans acquire via ingestion of contaminated food (particularly poultry), unpasteurized milk, or improperly treated water Infectious dose is reduced by foods that neutralize gastric acidi ...
... Spontaneous abortions in cattle, sheep, and swine, but generally asymptomatic carriage in animal reservoir Humans acquire via ingestion of contaminated food (particularly poultry), unpasteurized milk, or improperly treated water Infectious dose is reduced by foods that neutralize gastric acidi ...
Exposure Control Plan 2017 - Walla Walla Public Schools
... Testing for immunity after vaccination is not recommended routinely but is advised for persons for whom a suboptimal response may be anticipated, such as those who have received vaccine in the buttock, persons over 50 years of age, and persons known to have HIV infection. Post-vaccination testing is ...
... Testing for immunity after vaccination is not recommended routinely but is advised for persons for whom a suboptimal response may be anticipated, such as those who have received vaccine in the buttock, persons over 50 years of age, and persons known to have HIV infection. Post-vaccination testing is ...
Introduction of New vaccines
... The situation in CEE, NIS •From available data, Hib does not appear to be a major public health problem •This could be real or fictitious •If fictitious, the reasons could be –problem in the collection of csf –lack of lumbar puncture for suspected cases –problem with laboratory technique ...
... The situation in CEE, NIS •From available data, Hib does not appear to be a major public health problem •This could be real or fictitious •If fictitious, the reasons could be –problem in the collection of csf –lack of lumbar puncture for suspected cases –problem with laboratory technique ...
Medical Aspects of Chemical and Biological Warfare, Chapter 25
... and symptoms of disease in man.39,40 Pyelonephritis and cystitis and, in males, epididymoorchitis, may occur. Both diseases may mimic their tuberculous counterparts, with “sterile” pyuria on routine bacteriologic culture. With bladder and kidney infection, Brucella organisms can be cultured from the ...
... and symptoms of disease in man.39,40 Pyelonephritis and cystitis and, in males, epididymoorchitis, may occur. Both diseases may mimic their tuberculous counterparts, with “sterile” pyuria on routine bacteriologic culture. With bladder and kidney infection, Brucella organisms can be cultured from the ...
Viruses as a cause of foodborne diseases: a review of the literature
... even steaming oysters was not adequate to inactivate these viruses and to prevent illness. The clinical manifestation of Norovirus infection, however, is relatively mild. The symptoms are vomiting and diarrhoea, and (rarely) convulsion and others. Asymptomatic infections are common and may contribut ...
... even steaming oysters was not adequate to inactivate these viruses and to prevent illness. The clinical manifestation of Norovirus infection, however, is relatively mild. The symptoms are vomiting and diarrhoea, and (rarely) convulsion and others. Asymptomatic infections are common and may contribut ...
Approach to a Patient with Cough and Fever
... – Abnormal vital signs: tachypnea, tachycardia, fever – At least one abnormal chest finding: diminished breath sounds, rhonchi, crackles, wheezes • Radiographic chest examination- new infiltrates with no clear alternative cause- required to confirm diagnosis (Grade A) ...
... – Abnormal vital signs: tachypnea, tachycardia, fever – At least one abnormal chest finding: diminished breath sounds, rhonchi, crackles, wheezes • Radiographic chest examination- new infiltrates with no clear alternative cause- required to confirm diagnosis (Grade A) ...
chapter 3
... infection, otitis media or laryngitis. Lower respiratory tract infections included ≥1 doctor-diagnosed episode of bronchitis, bronchiolitis or pneumonia. Gastrointestinal infections included ≥1 doctor-diagnosed episode of vomiting or diarrhea with fever. Urinary tract infections included ≥1 doctor-d ...
... infection, otitis media or laryngitis. Lower respiratory tract infections included ≥1 doctor-diagnosed episode of bronchitis, bronchiolitis or pneumonia. Gastrointestinal infections included ≥1 doctor-diagnosed episode of vomiting or diarrhea with fever. Urinary tract infections included ≥1 doctor-d ...
Disaster Preparedness Scenario: Pandemic Influenza
... – Persons aged 50 years or older; – Children and adolescents (aged 6 months to 18 years) who are receiving long-term aspirin therapy and who might be at risk for experiencing Reye syndrome after an influenza infection; – Pregnant women; – Adults and children who have chronic pulmonary, cardiovascula ...
... – Persons aged 50 years or older; – Children and adolescents (aged 6 months to 18 years) who are receiving long-term aspirin therapy and who might be at risk for experiencing Reye syndrome after an influenza infection; – Pregnant women; – Adults and children who have chronic pulmonary, cardiovascula ...
Calcium Pyrophosphate Dihydrate Crystal Deposition Disease (Pseudogout) of Lumbar Spine Mimicking Osteomyelitis-
... weakness improved. Fourteen months after surgery, the patient of CPPD deposition mimicking infection in the lumbar spine.5 was pain-free, and ambulatory tolerance was improved. The Parkinson’s disease, however, had become more advanced. Conclusion Although infection is the most common cause of the s ...
... weakness improved. Fourteen months after surgery, the patient of CPPD deposition mimicking infection in the lumbar spine.5 was pain-free, and ambulatory tolerance was improved. The Parkinson’s disease, however, had become more advanced. Conclusion Although infection is the most common cause of the s ...
acute diarrhoea
... – Chemotherapeutic agents and radiotherapy may cause release of 5HT in the small intestine – thus activating vagal afferents, which in turn may cause release of 5HT in the area prostrema of the fourth ventricle resulting in vomiting ...
... – Chemotherapeutic agents and radiotherapy may cause release of 5HT in the small intestine – thus activating vagal afferents, which in turn may cause release of 5HT in the area prostrema of the fourth ventricle resulting in vomiting ...
Neonatal Chlamydial Infection Induces Mixed T-Cell
... Associated with the robust Th2 responses in the development of AAD were the following: eosinophil accumulation in airways and lung tissues (18.9 3 104 6 3.8 3 104 cells/ml of BALF and 20.1 6 3.0 cells/100 mm adjacent to airways, respectively), an increase in mucus-secreting cell numbers surrounding ...
... Associated with the robust Th2 responses in the development of AAD were the following: eosinophil accumulation in airways and lung tissues (18.9 3 104 6 3.8 3 104 cells/ml of BALF and 20.1 6 3.0 cells/100 mm adjacent to airways, respectively), an increase in mucus-secreting cell numbers surrounding ...
Study Session 34 Intestinal Protozoa, Ascariasis and Hookworm
... anaemia (see Box 34.1 in the discussion of hookworm infection later in this study session). You can treat mild cases yourself, and you should also give all children aged between two to five years routine treatment to kill intestinal worms, as described next. ...
... anaemia (see Box 34.1 in the discussion of hookworm infection later in this study session). You can treat mild cases yourself, and you should also give all children aged between two to five years routine treatment to kill intestinal worms, as described next. ...
Infectious Folliculitis and Dermatophytosis
... that may have a similar appearance (eg, dermatophilosis, dermatophytosis, Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis). Increasing resistance to commonly used antimicrobials also highlights the need for prompt culture and susceptibility testing. Further, the emergence of MRSA emphasizes the need for addition ...
... that may have a similar appearance (eg, dermatophilosis, dermatophytosis, Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis). Increasing resistance to commonly used antimicrobials also highlights the need for prompt culture and susceptibility testing. Further, the emergence of MRSA emphasizes the need for addition ...
Development of a Murine Model of Cerebral Aspergillosis CONCISE COMMUNICATION
... Central nervous system (CNS) Aspergillus infection has a mortality rate in humans that approaches 95%. Because no animal models are available for studying this infection, we sought to develop a murine model of CNS aspergillosis. Inconsistent data were obtained for nonimmunosuppressed CD-1, C57BL/6, ...
... Central nervous system (CNS) Aspergillus infection has a mortality rate in humans that approaches 95%. Because no animal models are available for studying this infection, we sought to develop a murine model of CNS aspergillosis. Inconsistent data were obtained for nonimmunosuppressed CD-1, C57BL/6, ...
Information on Ebola
... What is Ebola? Ebola (Ebola virus diseases – EVD) is an acute and infectious hemorrhagic disease. The first symptoms, including fever, sore throat, muscle pain and headache, typically develop between day 2 and day 21 following the infection. Subsequently, they are followed by rash, diarrhoea, vomiti ...
... What is Ebola? Ebola (Ebola virus diseases – EVD) is an acute and infectious hemorrhagic disease. The first symptoms, including fever, sore throat, muscle pain and headache, typically develop between day 2 and day 21 following the infection. Subsequently, they are followed by rash, diarrhoea, vomiti ...
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA): focus on
... intensive care unit, illustrating the severe nature of these infections. In an additional retrospective study conducted from 59 US hospitals during 2002-2003, MRSA was identified as the aetiology in 8.9% of CAP, 26.5% of healthcare-associated pneumonia, 22.9% of hospital-acquired pneumonia, and 14.6 ...
... intensive care unit, illustrating the severe nature of these infections. In an additional retrospective study conducted from 59 US hospitals during 2002-2003, MRSA was identified as the aetiology in 8.9% of CAP, 26.5% of healthcare-associated pneumonia, 22.9% of hospital-acquired pneumonia, and 14.6 ...
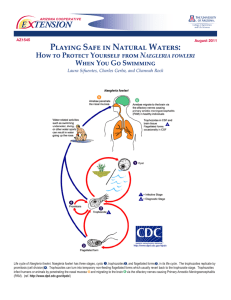
Playing Safe in Natural Waters: E TENSION Naegleria fowleri
... Where is Naegleria fowleri found? Naegleria fowleri is found around the world. In the United States, the majority of infections have been caused by Naegleria fowleri from freshwater located in southern-tier states. The amoeba is most commonly found in warm bodies of water such as ponds, lakes, river ...
... Where is Naegleria fowleri found? Naegleria fowleri is found around the world. In the United States, the majority of infections have been caused by Naegleria fowleri from freshwater located in southern-tier states. The amoeba is most commonly found in warm bodies of water such as ponds, lakes, river ...
Chapter 8: Lactate Dehydrogenase
... Which organ can be subclinically affected by immune complexes? a. Adrenals b. Kidneys c. Spleen d. Thyroid e. Liver LDV infection results in _______ viremia, during which the average titer of infectivity in the plasma is ____ ID50/ml, infected mice live a normal life span. Resistant LDV quasispecies ...
... Which organ can be subclinically affected by immune complexes? a. Adrenals b. Kidneys c. Spleen d. Thyroid e. Liver LDV infection results in _______ viremia, during which the average titer of infectivity in the plasma is ____ ID50/ml, infected mice live a normal life span. Resistant LDV quasispecies ...
3. The expanding range of parvoviruses which infect humans.
... replicated, new capsids are produced, the DNA is packaged and the new virions are released into the environment by cell lysis. However, in the absence of helper infection, only the Rep transcripts are expressed and there is limited DNA replication. In cell culture studies with high multiplicities of ...
... replicated, new capsids are produced, the DNA is packaged and the new virions are released into the environment by cell lysis. However, in the absence of helper infection, only the Rep transcripts are expressed and there is limited DNA replication. In cell culture studies with high multiplicities of ...
Chickenpox

Chickenpox, also known as varicella, is a highly contagious disease caused by the initial infection with varicella zoster virus (VZV). The disease results in a characteristic skin rash that forms small, itchy blisters, which eventually scab over. It usually starts on the face, chest, and back and then spreads to the rest of the body. Other symptoms may include fever, feeling tired, and headaches. Symptoms usually last five to ten days. Complications may occasionally include pneumonia, inflammation of the brain, or bacterial infections of the skin among others. The disease is often more severe in adults than children. Symptoms begin ten to twenty one days after exposure to the virus.Chickenpox is an airborne disease which spreads easily through the coughs and sneezes of an infected person. It may be spread from one to two days before the rash appears until all lesions have crusted over. It may also spread through contact with the blisters. Those with shingles may spread chickenpox to those who are not immune through contact with the blisters. The disease can usually be diagnosed based on the presenting symptom; however, in unusual cases may be confirmed by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing of the blister fluid or scabs. Testing for antibodies may be done to determine if a person is or is not immune. People usually only get the disease once.The varicella vaccine has resulted in a decrease in the number of cases and complications from the disease. It protects about 70 to 90 percent of people from disease with a greater benefit for severe disease. Routine immunization of children is recommended in many countries. Immunization within three days of exposure may improve outcomes in children. Treatment of those infected may include calamine lotion to help with itching, keeping the fingernails short to decrease injury from scratching, and the use of paracetamol (acetaminophen) to help with fevers. For those at increased risk of complications antiviral medication such as aciclovir are recommended.Chickenpox occurs in all parts of the world. Before routine immunization the number of cases occurring each year was similar to the number of people born. Since immunization the number of infections in the United States has decreased nearly 90%. In 2013 chickenpox resulted in 7,000 deaths globally – down from 8,900 in 1990. Death occurs in about 1 per 60,000 cases. Chickenpox was not separated from smallpox until the late 19th century. In 1888 its connection to shingles was determined. The first documented use of the term chicken pox was in 1658. Various explanations have been suggested for the use of ""chicken"" in the name, one being the relative mildness of the disease.