Avian & Pandemic Influenza
... Avian influenza, commonly known as "avian flu" or "bird flu," is caused by influenza type A viruses that normally only occur in birds. Avian flu is very contagious among birds and can make some domesticated birds, such as chickens, ducks and turkeys, very sick and kill them. These viruses usually do ...
... Avian influenza, commonly known as "avian flu" or "bird flu," is caused by influenza type A viruses that normally only occur in birds. Avian flu is very contagious among birds and can make some domesticated birds, such as chickens, ducks and turkeys, very sick and kill them. These viruses usually do ...
Slide 1
... Ill person may have recovered by the time the specimen was taken, so there is no evidence of the infection Pathogens do not survive trip from person to specimen container to laboratory, and DNA or RNA is in poor condition The organism being tested was not the pathogen responsible for ...
... Ill person may have recovered by the time the specimen was taken, so there is no evidence of the infection Pathogens do not survive trip from person to specimen container to laboratory, and DNA or RNA is in poor condition The organism being tested was not the pathogen responsible for ...
Infectious Abortions in Cattle
... killed vaccine on pregnant cows. Abortions may or may not be associated with illness in cow. ...
... killed vaccine on pregnant cows. Abortions may or may not be associated with illness in cow. ...
Microsporidiosis
... clinicians involved in the care of patients with HIV. Users are cautioned that, because of the rapidly changing field of HIV care, this information could become out of date quickly. Finally, it is intended that these slides be used as prepared, without changes in either content or attribution. Users ...
... clinicians involved in the care of patients with HIV. Users are cautioned that, because of the rapidly changing field of HIV care, this information could become out of date quickly. Finally, it is intended that these slides be used as prepared, without changes in either content or attribution. Users ...
Infection Control Guideline
... minimise the spread of infection, illness and disease. The following PPE, facilities and materials should be readily available in the workplace, particularly in food preparation, first aid, and special and physical education areas: Hand-basins in or near toilet facilities, first aid and food prepa ...
... minimise the spread of infection, illness and disease. The following PPE, facilities and materials should be readily available in the workplace, particularly in food preparation, first aid, and special and physical education areas: Hand-basins in or near toilet facilities, first aid and food prepa ...
Possible role of adeno-associated virus type 2 infection in
... Witkin et al. (15) established that Chlamydia trachomatis could provoke miscarriage due to strong immunological reaction to the specific bacterial protein. Moreover, C. trachomatis infections of the cervix have been associated with second trimester abortions and premature membrane rupture (16). It i ...
... Witkin et al. (15) established that Chlamydia trachomatis could provoke miscarriage due to strong immunological reaction to the specific bacterial protein. Moreover, C. trachomatis infections of the cervix have been associated with second trimester abortions and premature membrane rupture (16). It i ...
COMMUNICABLE DISEASES POLICY 1 Preface: It
... DISCUSSION: Since the disease of AIDS is a recent development, and most knowledge concerning the disease has not reached the public in a systematic fashion, there is much unwarranted concern and partial or mis-information about the disease. Until the public can be educated about the disease, its tra ...
... DISCUSSION: Since the disease of AIDS is a recent development, and most knowledge concerning the disease has not reached the public in a systematic fashion, there is much unwarranted concern and partial or mis-information about the disease. Until the public can be educated about the disease, its tra ...
control of cross infection - New Zealand Association of Orthodontists
... 3.6.4.3 As confirmation that instruments have been exposed to the verified sterilisation process, chemical indicators should be included in every load/package. Any change in colour (eg lightening) may indicate that the autoclave has become inefficient and cannot be relied upon to produce acceptable ...
... 3.6.4.3 As confirmation that instruments have been exposed to the verified sterilisation process, chemical indicators should be included in every load/package. Any change in colour (eg lightening) may indicate that the autoclave has become inefficient and cannot be relied upon to produce acceptable ...
High-level expression of recombinant dengue
... antigen for dengue viral infection were investigated. In this study, the full-length and C-terminal half of NS1 proteins (rNS1, rNS1-C) were highly expressed (10±30 mg/l) and further puri®ed and refolded. The good antigenicity of the full-length rNS1 protein was con®rmed by interaction with 19 dengu ...
... antigen for dengue viral infection were investigated. In this study, the full-length and C-terminal half of NS1 proteins (rNS1, rNS1-C) were highly expressed (10±30 mg/l) and further puri®ed and refolded. The good antigenicity of the full-length rNS1 protein was con®rmed by interaction with 19 dengu ...
Both Lewis and Secretor Status Mediate
... The reasons for this are yet unknown, but malnutrition, concomitant infections, RV strain diversity, and host factors have been proposed. The genetic makeup of ...
... The reasons for this are yet unknown, but malnutrition, concomitant infections, RV strain diversity, and host factors have been proposed. The genetic makeup of ...
Disparate developmental patterns of immune responses to bacterial
... characterise the responses we used both gene ontology (biological process) enrichment analysis and KEGG pathway analysis to identify key functional groups that were enriched across each developmental stage. Results from this analysis showed a clear difference between the antiviral and antibacterial ...
... characterise the responses we used both gene ontology (biological process) enrichment analysis and KEGG pathway analysis to identify key functional groups that were enriched across each developmental stage. Results from this analysis showed a clear difference between the antiviral and antibacterial ...
Viruses infecting the marine Prymnesiophyte
... cell lysis, and resulted in the amplification of the virus, thereby fulfilling Koch's postulates. The virus infects C. brevifilum and C. strobilus, but did not cause lysis of 8 other isolates of Chrysochromulina or 5 other genera of Prymnesiophytes that were screened (see 'Materials and methods' for ...
... cell lysis, and resulted in the amplification of the virus, thereby fulfilling Koch's postulates. The virus infects C. brevifilum and C. strobilus, but did not cause lysis of 8 other isolates of Chrysochromulina or 5 other genera of Prymnesiophytes that were screened (see 'Materials and methods' for ...
Inflammatory Disorders - Austin Community College
... Malaise, mylagias Dyspnea, lymphadenopathy Nausea, vomiting ...
... Malaise, mylagias Dyspnea, lymphadenopathy Nausea, vomiting ...
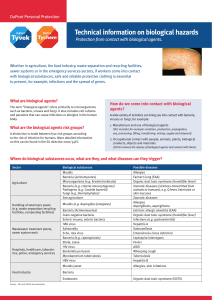
Technical information on biological hazards
... sewer systems or in the emergency services sectors, if workers come into contact with biological substances, safe and reliable protective clothing is essential to prevent, for example, infections and the spread of germs. ...
... sewer systems or in the emergency services sectors, if workers come into contact with biological substances, safe and reliable protective clothing is essential to prevent, for example, infections and the spread of germs. ...
Guidelines for Management of Community Associated Methicillin
... Disease practitioners and the BC Provincial Infection Control Network. The term, community associated-methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (CAMRSA) describes MRSA infections that appear to take their origin in the community. Many CA-MRSA infections are caused by unique clones of S. aureus tha ...
... Disease practitioners and the BC Provincial Infection Control Network. The term, community associated-methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (CAMRSA) describes MRSA infections that appear to take their origin in the community. Many CA-MRSA infections are caused by unique clones of S. aureus tha ...
Animal Models of Leishmaniasis Relevant to
... Conclusions Our mouse models may be fine at predicting vaccination success against L. major, so long as more stringent evaluation criteria are used: - Protection against ‘natural’ sand fly challenge - Potency and durability of protection comparable to naturally acquired resistance (healed infection ...
... Conclusions Our mouse models may be fine at predicting vaccination success against L. major, so long as more stringent evaluation criteria are used: - Protection against ‘natural’ sand fly challenge - Potency and durability of protection comparable to naturally acquired resistance (healed infection ...
File
... their research on Burkett’s lymphoma (Grywalska et al, 2013). EBV virions have a doublestranded, linear DNA genome encoding approximately 100 genes surrounded by a protein capsid. A protein tegument lies between the capsid and the envelope (2013). The EBV genome convert a series of products interact ...
... their research on Burkett’s lymphoma (Grywalska et al, 2013). EBV virions have a doublestranded, linear DNA genome encoding approximately 100 genes surrounded by a protein capsid. A protein tegument lies between the capsid and the envelope (2013). The EBV genome convert a series of products interact ...
Viral evasion of intracellular DNA and RNA sensing
... drugs for many other clinically important viral pathogens. The continued emergence of new and previously known viral pathogens, as well as drug-resistant variants, highlights the urgent need for the development of novel and more effective vaccines and antivirals to combat viruses and mitigate human ...
... drugs for many other clinically important viral pathogens. The continued emergence of new and previously known viral pathogens, as well as drug-resistant variants, highlights the urgent need for the development of novel and more effective vaccines and antivirals to combat viruses and mitigate human ...
View/Open
... do we understand the evolution of FMD viruses? We do have systems in place that attempt, at least, to map the global movement of the seven serotypes and related subtypes, but our understanding of what drives these movements, and what creates change in the virus and the associated disease manifestati ...
... do we understand the evolution of FMD viruses? We do have systems in place that attempt, at least, to map the global movement of the seven serotypes and related subtypes, but our understanding of what drives these movements, and what creates change in the virus and the associated disease manifestati ...
Diseases of the Oropharynx
... 3 glassfuls of gargling solution each time Every 2 hours Heat of gargling solution is probably more effective than its medicinal content ...
... 3 glassfuls of gargling solution each time Every 2 hours Heat of gargling solution is probably more effective than its medicinal content ...
Blood transfusion
... Hepatitis B Risk 1/ 200,000 due to HBsAg, antiHBc screening (7-17 % of PTH) Per unit risk 1/63-66,000 0.002% residual HBV remains in ‘negative’ donors (window 2-16 weeks) Anti-HBc testing retained as surrogate marker for HIV ...
... Hepatitis B Risk 1/ 200,000 due to HBsAg, antiHBc screening (7-17 % of PTH) Per unit risk 1/63-66,000 0.002% residual HBV remains in ‘negative’ donors (window 2-16 weeks) Anti-HBc testing retained as surrogate marker for HIV ...
dengue and its precautions - Kendriya Vidyalaya No.3 Agra
... However, the virus is not contagious and does not spread from person to person. It requires the mosquito as a medium and a person-to-mosquito-toanother-person pathway. ...
... However, the virus is not contagious and does not spread from person to person. It requires the mosquito as a medium and a person-to-mosquito-toanother-person pathway. ...
Chapter 18
... • Meningitis: is a bacterial infection of the membranes covering the brain and spinal cord (meninges) • The most common causes of meningitis are viral infections that usually get better without treatment, however, bacterial meningitis infections are extremely serious, and may result in death or brai ...
... • Meningitis: is a bacterial infection of the membranes covering the brain and spinal cord (meninges) • The most common causes of meningitis are viral infections that usually get better without treatment, however, bacterial meningitis infections are extremely serious, and may result in death or brai ...
Hepatitis B

Hepatitis B is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV) which affects the liver. It can cause both acute and chronic infections. Many people have no symptoms during the initial infection. Some develop a rapid onset of sickness with vomiting, yellowish skin, feeling tired, dark urine and abdominal pain. Often these symptoms last a few weeks and rarely does the initial infection result in death. It may take 30 to 180 days for symptoms to begin. In those who get infected around the time of birth 90% develop chronic hepatitis B while less than 10% of those infected after the age of five do. Most of those with chronic disease have no symptoms; however, cirrhosis and liver cancer may eventually develop. These complications results in the death of 15 to 25% of those with chronic disease.The virus is transmitted by exposure to infectious blood or body fluids. Infection around the time of birth or from contact with other people's blood during childhood is the most frequent method by which hepatitis B is acquired in areas where the disease is common. In areas where the disease is rare, intravenous drug use and sexual intercourse are the most frequent routes of infection. Other risk factors include working in healthcare, blood transfusions, dialysis, living with an infected person, travel in countries where the infection rate is high, and living in an institution. Tattooing and acupuncture led to a significant number of cases in the 1980s; however, this has become less common with improved sterility. The hepatitis B viruses cannot be spread by holding hands, sharing eating utensils, kissing, hugging, coughing, sneezing, or breastfeeding. The infection can be diagnosed 30 to 60 days after exposure. Diagnosis is typically by testing the blood for parts of the virus and for antibodies against the virus. It is one of five known hepatitis viruses: A, B, C, D, and E.The infection has been preventable by vaccination since 1982. Vaccination is recommended by the World Health Organization in the first day of life if possible. Two or three more doses are required at a later time for full effect. This vaccine works about 95% of the time. About 180 countries gave the vaccine as part of national programs as of 2006. It is also recommended that all blood be tested for hepatitis B before transfusion and condoms be used to prevent infection. During an initial infection, care is based on the symptoms that a person has. In those who develop chronic disease antiviral medication such as tenofovir or interferon maybe useful, however these drugs are expensive. Liver transplantation is sometimes used for cirrhosis.About a third of the world population has been infected at one point in their lives, including 240 million to 350 million who have chronic infections. Over 750,000 people die of hepatitis B each year. About 300,000 of these are due to liver cancer. The disease is now only common in East Asia and sub-Saharan Africa where between 5 and 10% of adults have chronic disease. Rates in Europe and North America are less than 1%. It was originally known as serum hepatitis. Research is looking to create foods that contain HBV vaccine. The disease may affect other great apes as well.