4-3 Families of Elements
... I. How Are Elements Classified? a. Elements are classified into three groups i. Most elements are metals--they are shiny solids that can be stretched and shaped. ii. All nonmetals, except for hydrogen are found on the right side of the periodic table. iii. Nonmetals that can sometimes conduct heat/e ...
... I. How Are Elements Classified? a. Elements are classified into three groups i. Most elements are metals--they are shiny solids that can be stretched and shaped. ii. All nonmetals, except for hydrogen are found on the right side of the periodic table. iii. Nonmetals that can sometimes conduct heat/e ...
Chapter 22 Chemistry of The NonMetals
... • Little resemblance between the chemistry of nitrogen and the other elements in this group ...
... • Little resemblance between the chemistry of nitrogen and the other elements in this group ...
noble gases
... Elements that possess both metallic and non-metallic properties. Found on both sides of the zigzag line that divides the metals from the non-metals. Ex. silicon, boron, germanium, arsenic, selenium, antimony, tellurium, polonium, and astatine. ...
... Elements that possess both metallic and non-metallic properties. Found on both sides of the zigzag line that divides the metals from the non-metals. Ex. silicon, boron, germanium, arsenic, selenium, antimony, tellurium, polonium, and astatine. ...
The Periodic Table of Elements Mendeleev
... diatomic gas. • Fluorine is a reactive, pale, yellow gas. • Chlorine is a reactive green - yellow gas • Bromine is a red liquid (highly corrosive) • Iodine is a purple crystalline solid that sublimes ...
... diatomic gas. • Fluorine is a reactive, pale, yellow gas. • Chlorine is a reactive green - yellow gas • Bromine is a red liquid (highly corrosive) • Iodine is a purple crystalline solid that sublimes ...
The Periodic Table
... This family includes a non-metal (carbon), metalloids, and metals. The element carbon is called the “basis of life.” There is an entire branch of chemistry devoted to carbon compounds called ...
... This family includes a non-metal (carbon), metalloids, and metals. The element carbon is called the “basis of life.” There is an entire branch of chemistry devoted to carbon compounds called ...
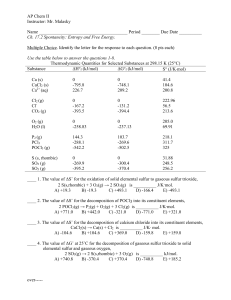
AP Chem II Instructor: Mr. Malasky Name Period ______ Due Date
... ____ 5. The value of ΔG˚ at 25˚C for the decomposition of gaseous sulfur dioxide to solid elemental sulfur and gaseous oxygen, SO2(g) → 2 S (s,rhombic) + O2(g) is __________ kJ/mol. A) +395.2 B) +269.9 C) -269.9 D) +300.4 E) -300.4 ____ 6. The value of ΔG˚ at 25˚C for the formation of POCl3 from it ...
... ____ 5. The value of ΔG˚ at 25˚C for the decomposition of gaseous sulfur dioxide to solid elemental sulfur and gaseous oxygen, SO2(g) → 2 S (s,rhombic) + O2(g) is __________ kJ/mol. A) +395.2 B) +269.9 C) -269.9 D) +300.4 E) -300.4 ____ 6. The value of ΔG˚ at 25˚C for the formation of POCl3 from it ...
pblock - Chemistry Courses
... 2nd period: Only s and p orbitals are possible with n = 2 Therefore, the maximum number of bonds is 4 (single and/or double bonds) Examples: CH4, NF4+, BH43rd (and higher periods): can use d-orbitals to make bonds E.g. ...
... 2nd period: Only s and p orbitals are possible with n = 2 Therefore, the maximum number of bonds is 4 (single and/or double bonds) Examples: CH4, NF4+, BH43rd (and higher periods): can use d-orbitals to make bonds E.g. ...
p-Block Elements, Part 1
... e.g. Li2O = 2Li+ O2− Peroxide Ion ⇒ O22− = −O – O− e.g. Na2O2 = 2 Na+ −O – O − Also, H2O2 (hydrogen peroxide) Superoxide Ion ⇒ O2− e.g. KO2 = K+ O2− Can have positive oxidation states in combination with fluorine + 2 in OF2 ...
... e.g. Li2O = 2Li+ O2− Peroxide Ion ⇒ O22− = −O – O− e.g. Na2O2 = 2 Na+ −O – O − Also, H2O2 (hydrogen peroxide) Superoxide Ion ⇒ O2− e.g. KO2 = K+ O2− Can have positive oxidation states in combination with fluorine + 2 in OF2 ...
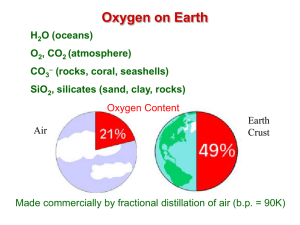
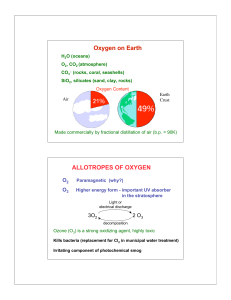
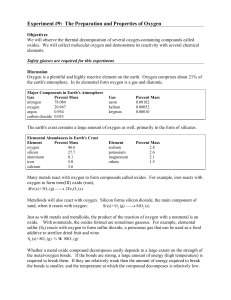
Experiment # 9 Properties of Oxygen
... Just as with metals and metalloids, the product of the reaction of oxygen with a nonmetal is an oxide. With nonmetals, the oxides formed are sometimes gaseous. For example, elemental sulfur (S8) reacts with oxygen to form sulfur dioxide, a poisonous gas that can be used as a food additive to sterili ...
... Just as with metals and metalloids, the product of the reaction of oxygen with a nonmetal is an oxide. With nonmetals, the oxides formed are sometimes gaseous. For example, elemental sulfur (S8) reacts with oxygen to form sulfur dioxide, a poisonous gas that can be used as a food additive to sterili ...
Document
... 2.7 An overview of the elements, by group Goal: Get a feeling for elements’ chemical properties ...
... 2.7 An overview of the elements, by group Goal: Get a feeling for elements’ chemical properties ...
Brown, Le May, and Bursten: Chapter 2
... divided by the ratio of these masses in the other compound gives a ratio of small whole numbers. E.g. There are three binary compounds that form between barium and nitrogen. There was 4.9021 g , 9.8050 g and 14.7060 g of Ba per 1.0000 g N in the three compounds. Show that these compounds obey the la ...
... divided by the ratio of these masses in the other compound gives a ratio of small whole numbers. E.g. There are three binary compounds that form between barium and nitrogen. There was 4.9021 g , 9.8050 g and 14.7060 g of Ba per 1.0000 g N in the three compounds. Show that these compounds obey the la ...
Oxidation Number Rules
... c. Hydrogen usually has an oxidation number of +1 except in metallic hydrides where it then has an oxidation number of -1 Examples: HCl, hydrogen is +1; NaH, hydrogen is -1. d. The halogens, unless bonded to an element with a higher electronegativity, have an oxidation number of -1. Examples: NaCl, ...
... c. Hydrogen usually has an oxidation number of +1 except in metallic hydrides where it then has an oxidation number of -1 Examples: HCl, hydrogen is +1; NaH, hydrogen is -1. d. The halogens, unless bonded to an element with a higher electronegativity, have an oxidation number of -1. Examples: NaCl, ...
Counting Atoms and Balancing Chemical Equations
... When hydrogen and oxygen bond they make the compound water. When salt and water are combined, a mixture is created. Compounds in mixtures retain their individual properties. ...
... When hydrogen and oxygen bond they make the compound water. When salt and water are combined, a mixture is created. Compounds in mixtures retain their individual properties. ...
Ch. 14 Test Review
... periods transition metals ionization energy atomic # noble gases representative electronegativity The periodic table organizes the elements into vertical ____________ and horizontal ____________ in order of increasing _________________. The table is constructed so that elements that have similar che ...
... periods transition metals ionization energy atomic # noble gases representative electronegativity The periodic table organizes the elements into vertical ____________ and horizontal ____________ in order of increasing _________________. The table is constructed so that elements that have similar che ...
Group 16: The Oxygen Family - Chemwiki
... Sulfur also exhibits a wide range of oxidation states, with values ranging from -2 to +6. It is often the central ion in a compound and can easily bond with up to 6 atoms. In the presence of hydrogen it forms the compound hydrogen sulfide, H2S, a poisonous gas incapable of forming hydrogen bonds and ...
... Sulfur also exhibits a wide range of oxidation states, with values ranging from -2 to +6. It is often the central ion in a compound and can easily bond with up to 6 atoms. In the presence of hydrogen it forms the compound hydrogen sulfide, H2S, a poisonous gas incapable of forming hydrogen bonds and ...