Tasmanian Student Immunisation Record Form
... *TST screening is recommended if the person was born in a country with high incidence of TB, or has resided for a cumulative time of more than 3 months or longer in a country with a high incidence of TB. The countries, identified in the WHO Global Tuberculosis Control Report 2013, are listed at: htt ...
... *TST screening is recommended if the person was born in a country with high incidence of TB, or has resided for a cumulative time of more than 3 months or longer in a country with a high incidence of TB. The countries, identified in the WHO Global Tuberculosis Control Report 2013, are listed at: htt ...
? HOW TO STOP
... vomiting and severe diarrhoea and these symptoms in conjunction with reduced milking lead to fatal dehydration and malnourishment. Most piglets less than one week of age will die in a naïve herd. Growing pigs and breeding animals will generally have watery diarrhoea and vomiting, which can cause inc ...
... vomiting and severe diarrhoea and these symptoms in conjunction with reduced milking lead to fatal dehydration and malnourishment. Most piglets less than one week of age will die in a naïve herd. Growing pigs and breeding animals will generally have watery diarrhoea and vomiting, which can cause inc ...
Training
... we have to treat everyone as if they are infected, and follow standard precautions at all times. The average risk of infection after accidental exposure is: – HIV –0.3% – HBV-5-30% - There is a HBV vaccine series that is available to reduce healthcare workers risk of infection. ...
... we have to treat everyone as if they are infected, and follow standard precautions at all times. The average risk of infection after accidental exposure is: – HIV –0.3% – HBV-5-30% - There is a HBV vaccine series that is available to reduce healthcare workers risk of infection. ...
Current Human Issues with H1N1
... illness remain at home until at least 24 hours after they are free of fever (100° F)…without the use of ...
... illness remain at home until at least 24 hours after they are free of fever (100° F)…without the use of ...
Who Is At Risk Of Exposure To H5N1 Avian Influenza
... illness remain at home until at least 24 hours after they are free of fever (100° F)…without the use of ...
... illness remain at home until at least 24 hours after they are free of fever (100° F)…without the use of ...
Entropion patient info
... infection and scarring. Prior to surgery the eye can be protected by taping the lower lid down and using lubricating drops and ointment. The surgery to repair entropion is usually performed under local anaesthesia with or without sedation as a day case. In most cases your doctor will tighten the eye ...
... infection and scarring. Prior to surgery the eye can be protected by taping the lower lid down and using lubricating drops and ointment. The surgery to repair entropion is usually performed under local anaesthesia with or without sedation as a day case. In most cases your doctor will tighten the eye ...
Replication of hepatitis C virus in peripheral blood mononuclear
... of therapy efficacy is not routinely used in clinical practice. Several well-known factors influence the SVR rate: age, sex, HCV genotype, baseline level of HCV viremia, liver fibrosis stage, interleukin (IL)28b polymorphism. The presence of HCV RNA negative strand in PBMCs at the end of treatment a ...
... of therapy efficacy is not routinely used in clinical practice. Several well-known factors influence the SVR rate: age, sex, HCV genotype, baseline level of HCV viremia, liver fibrosis stage, interleukin (IL)28b polymorphism. The presence of HCV RNA negative strand in PBMCs at the end of treatment a ...
Current Human Issues with H1N1
... illness remain at home until at least 24 hours after they are free of fever (100° F)…without the use of ...
... illness remain at home until at least 24 hours after they are free of fever (100° F)…without the use of ...
View Full Text-PDF
... latency. Viremia continues can first be detected, typically at least 6 months in adults and several years in young children. Although an initial persistent infection is often observed, clearance of acute infection is the norm in all immunocompetent individuals and it is correlated with a slow rise i ...
... latency. Viremia continues can first be detected, typically at least 6 months in adults and several years in young children. Although an initial persistent infection is often observed, clearance of acute infection is the norm in all immunocompetent individuals and it is correlated with a slow rise i ...
History of Virology
... plants after passage through ceramic filters fine enough to retain the smallest known bacteria. • This is generally recognized as the beginning of Virology. • Unfortunately, neither Iwanowski nor the scientific community fully realize the significance of these results. ...
... plants after passage through ceramic filters fine enough to retain the smallest known bacteria. • This is generally recognized as the beginning of Virology. • Unfortunately, neither Iwanowski nor the scientific community fully realize the significance of these results. ...
Lab Test Explanations
... the gallbladder. Low values are usually insignificant, but high values may signal liver or gallbladder disease. When it is found elevated, it is important to test the levels of the two different types of bilirubin—“direct” (conjugated) and “indirect” (unconjugated) bilirubin. If the total bilirubin ...
... the gallbladder. Low values are usually insignificant, but high values may signal liver or gallbladder disease. When it is found elevated, it is important to test the levels of the two different types of bilirubin—“direct” (conjugated) and “indirect” (unconjugated) bilirubin. If the total bilirubin ...
Management of infection prevention and control
... • WHO defines a health care-associated (also called hospital acquired) infection as an infection acquired in hospital by a patient who was admitted for a reason other than that infection and/or an infection • Occurring in a patient in a hospital or other health-care facility in whom the infection wa ...
... • WHO defines a health care-associated (also called hospital acquired) infection as an infection acquired in hospital by a patient who was admitted for a reason other than that infection and/or an infection • Occurring in a patient in a hospital or other health-care facility in whom the infection wa ...
Document
... Columbia, in 1999. 1 C. gattii is an environmental fungus that causes infection through inhalation of its spores. In BC, it has been found throughout the east coast of Vancouver Island, where it has been isolated from multiple tree species, soil, water, and air. 2 Between 1999 and 2006, 176 cases of ...
... Columbia, in 1999. 1 C. gattii is an environmental fungus that causes infection through inhalation of its spores. In BC, it has been found throughout the east coast of Vancouver Island, where it has been isolated from multiple tree species, soil, water, and air. 2 Between 1999 and 2006, 176 cases of ...
Guide to Life-cycle, Pathology, Symptomatology, and Treatment of
... infections, however, may produce only mild symptoms or go unrecognized. As additional worms are acquired, indigestion and epigastric discomfort (unrelated to meals), weakness, and weight loss become noticeable. In heavy infections, anemia, liver enlargement, slight jaundice, edema, ascites, and dia ...
... infections, however, may produce only mild symptoms or go unrecognized. As additional worms are acquired, indigestion and epigastric discomfort (unrelated to meals), weakness, and weight loss become noticeable. In heavy infections, anemia, liver enlargement, slight jaundice, edema, ascites, and dia ...
Genitourinary Infections
... Characterized by hard chancre from inflammatory response Chancre disappears in 2 to 6 weeks with or without treatment ...
... Characterized by hard chancre from inflammatory response Chancre disappears in 2 to 6 weeks with or without treatment ...
Bloodborne Pathogen
... that it cannot fight other deadly diseases. AIDS is a fatal disease, and while treatment for it is improving, there is no known cure. Estimates on the number of people infected with HIV vary, but some estimates suggest that an average of 35,000 people are infected every year in the US (in 2006, 56,3 ...
... that it cannot fight other deadly diseases. AIDS is a fatal disease, and while treatment for it is improving, there is no known cure. Estimates on the number of people infected with HIV vary, but some estimates suggest that an average of 35,000 people are infected every year in the US (in 2006, 56,3 ...
Slide 1
... causes of an initial postpartum fever (eg, pneumonia, DVT, or PTE) or persistent postpartum fever (eg, abscess, ovarian vein thrombosis, septic pelvic thrombophlebitis) in patients refractory to 48 to 72 hours of antimicrobial therapy. ...
... causes of an initial postpartum fever (eg, pneumonia, DVT, or PTE) or persistent postpartum fever (eg, abscess, ovarian vein thrombosis, septic pelvic thrombophlebitis) in patients refractory to 48 to 72 hours of antimicrobial therapy. ...
Document
... that it cannot fight other deadly diseases. AIDS is a fatal disease, and while treatment for it is improving, there is no known cure. Estimates on the number of people infected with HIV vary, but some estimates suggest that an average of 35,000 people are infected every year in the US (in 2006, 56,3 ...
... that it cannot fight other deadly diseases. AIDS is a fatal disease, and while treatment for it is improving, there is no known cure. Estimates on the number of people infected with HIV vary, but some estimates suggest that an average of 35,000 people are infected every year in the US (in 2006, 56,3 ...
The mosquitoes Aedes
... • Rash usually 2-5 days after fever starts • Other symptoms may include headache, body ache, nausea, vomiting, and redness around the eyes. In unusual cases, infection can involve the brain, eyes, heart, kidney and other organs. • Fatal infections are rare, however many patients have chronic joint p ...
... • Rash usually 2-5 days after fever starts • Other symptoms may include headache, body ache, nausea, vomiting, and redness around the eyes. In unusual cases, infection can involve the brain, eyes, heart, kidney and other organs. • Fatal infections are rare, however many patients have chronic joint p ...
Infection severity - University of Georgia
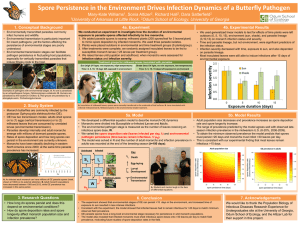
... • We developed a differential equation model to describe monarch-OE dynamics • Monarchs were divided into Susceptible or Infected Larvae and Adults. • The environmental pathogen stage is measured as the number of leaves receiving an infectious spore dose, W. • We varied the spore deposition rate (le ...
... • We developed a differential equation model to describe monarch-OE dynamics • Monarchs were divided into Susceptible or Infected Larvae and Adults. • The environmental pathogen stage is measured as the number of leaves receiving an infectious spore dose, W. • We varied the spore deposition rate (le ...
Chagas Disease: the Silent Killer
... Sánchez-Guillén et al., 2006 M.D.C. Sánchez-Guillén, A. López-Colombo, G. OrdóñezToquero, I. Gomez-Albino, J. Ramos-Jimenez, E. Torres-Rasgado, H. SalgadoRosas, M. Romero-Díaz, P. Pulido-Pérez and R. Pérez-Fuentes, Clinical forms of Trypanosoma cruzi infected individuals in the chronic phase of Chag ...
... Sánchez-Guillén et al., 2006 M.D.C. Sánchez-Guillén, A. López-Colombo, G. OrdóñezToquero, I. Gomez-Albino, J. Ramos-Jimenez, E. Torres-Rasgado, H. SalgadoRosas, M. Romero-Díaz, P. Pulido-Pérez and R. Pérez-Fuentes, Clinical forms of Trypanosoma cruzi infected individuals in the chronic phase of Chag ...
Infectious Diseases for Interns
... History taking can be difficult Symptoms and signs tend to be non-specific / atypical Several organ systems affected Blunted clinical features ...
... History taking can be difficult Symptoms and signs tend to be non-specific / atypical Several organ systems affected Blunted clinical features ...
Infectious diseases/ Haematology/ Rheumatology/ Dermatology
... Institution of supportive care to prevent progression to overwhelming sepsis and shock Empiric broad-spectrum antibiotic therapy after blood cultures drawn Ideally coverage for both gram negative and gram positive organisms; cover for gram positive cocci if central line in situ Ticarcillin/c ...
... Institution of supportive care to prevent progression to overwhelming sepsis and shock Empiric broad-spectrum antibiotic therapy after blood cultures drawn Ideally coverage for both gram negative and gram positive organisms; cover for gram positive cocci if central line in situ Ticarcillin/c ...
Free Living Amoeba
... 1-14 days incubation period symptoms usually within a few days after swimming in warm still waters infection believed to be introduced through nasal cavity and olfactory neuroepithelium symptoms include headache, lethargy, disorientation, coma rapid clinical course, death in 4-5 days after onset of ...
... 1-14 days incubation period symptoms usually within a few days after swimming in warm still waters infection believed to be introduced through nasal cavity and olfactory neuroepithelium symptoms include headache, lethargy, disorientation, coma rapid clinical course, death in 4-5 days after onset of ...
Herpes Simplex Encephalitis - University of Oklahoma Health
... have a predilection on different parts of the nervous system. Reactivation: Reactivation of an indolent or subclinical infection occurs in some viruses such as herpes simplex virus and JC virus. CSF: There is usually marked elevation of lymphocytes without reduction in glucose level. ...
... have a predilection on different parts of the nervous system. Reactivation: Reactivation of an indolent or subclinical infection occurs in some viruses such as herpes simplex virus and JC virus. CSF: There is usually marked elevation of lymphocytes without reduction in glucose level. ...
Hepatitis C

Hepatitis C is an infectious disease affecting primarily the liver, caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV). The infection is often asymptomatic, but chronic infection can lead to scarring of the liver and ultimately to cirrhosis, which is generally apparent after many years. In some cases, those with cirrhosis will go on to develop liver failure, liver cancer, or life-threatening esophageal and gastric varices.HCV is spread primarily by blood-to-blood contact associated with intravenous drug use, poorly sterilized medical equipment, and transfusions. An estimated 150–200 million people worldwide are infected with hepatitis C. The existence of hepatitis C – originally identifiable only as a type of non-A non-B hepatitis – was suggested in the 1970s and proven in 1989. Hepatitis C infects only humans and chimpanzees. It is one of five known hepatitis viruses: A, B, C, D, and E.The virus persists in the liver in about 85% of those infected. This chronic infection can be treated with medication: the standard therapy is a combination of peginterferon and ribavirin, with either boceprevir or telaprevir added in some cases. Overall, 50–80% of people treated are cured. Those who develop cirrhosis or liver cancer may require a liver transplant. Hepatitis C is the leading reason for liver transplantation, though the virus usually recurs after transplantation. No vaccine against hepatitis C is available. About 343,000 deaths due to liver cancer from hepatitis C occurred in 2013, up from 198,000 in 1990. An additional 358,000 in 2013 occurred due to cirrhosis.