The Lymphatic System and Immunity
... infected with the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV). This highly variable virus is also responsible for infectious mononucleosis (discussed further below), and it has been suggested as a possible cause of chronic fatigue syndrome and multiple sclerosis. The EBV infects B cells, but under normal circumstances ...
... infected with the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV). This highly variable virus is also responsible for infectious mononucleosis (discussed further below), and it has been suggested as a possible cause of chronic fatigue syndrome and multiple sclerosis. The EBV infects B cells, but under normal circumstances ...
Norovirus News What`s the Diagnosis?
... (DIAIH) and the implicated medication is minocycline, which was prescribed for her acne. Minocycline is commonly used to treat adolescent acne vulgaris and often continued for months, even years at a time. Common adverse events include gastrointestinal intolerance, photosensitivity, ...
... (DIAIH) and the implicated medication is minocycline, which was prescribed for her acne. Minocycline is commonly used to treat adolescent acne vulgaris and often continued for months, even years at a time. Common adverse events include gastrointestinal intolerance, photosensitivity, ...
Illness research - HOME
... Norovirus infection can cause the sudden onset of severe vomiting and diarrhea. The virus is highly contagious and commonly spread through food or water that is contaminated by fecal matter during preparation. You can also be infected through close contact with an infected person. SYMPTOMS ...
... Norovirus infection can cause the sudden onset of severe vomiting and diarrhea. The virus is highly contagious and commonly spread through food or water that is contaminated by fecal matter during preparation. You can also be infected through close contact with an infected person. SYMPTOMS ...
Serological study of TORCH infections in Women with High Delivery
... through body secretions, as well as by sexual contact; some newborns which acquire CMV through the mother's breast milk Infected infants may have severe problems, such as hearing loss, mental retardation, pneumonia, hepatitis, or blood disorders(10). Herpes simplex virus the virus enters the infant ...
... through body secretions, as well as by sexual contact; some newborns which acquire CMV through the mother's breast milk Infected infants may have severe problems, such as hearing loss, mental retardation, pneumonia, hepatitis, or blood disorders(10). Herpes simplex virus the virus enters the infant ...
Infection Control
... To protect the Postoperative patient from cross contamination from other patients, hospital personnel and equipment. To protect the health care worker from the risk of contacting infections, such as, Hepatitis and AIDS, or other viruses that are present in blood and other body fluids. RESPONSIBILITY ...
... To protect the Postoperative patient from cross contamination from other patients, hospital personnel and equipment. To protect the health care worker from the risk of contacting infections, such as, Hepatitis and AIDS, or other viruses that are present in blood and other body fluids. RESPONSIBILITY ...
Can worms defend our hearts? Chronic Opisthorchis felineus
... previously healthy person due to accidental death, suicide, accidental violence or other traumatic injury. ...
... previously healthy person due to accidental death, suicide, accidental violence or other traumatic injury. ...
Epidemiology and Prevention of Hepatitis A in Travelers
... 1997 and 2005 demonstrated that the areas associated with the highest incidence of disease were East Africa, the Middle East, and the Indian subcontinent. Visiting friends and relatives (VFR) travelers represented 83, 91, and 70% of the cases to these three regions; the highest incidence was found i ...
... 1997 and 2005 demonstrated that the areas associated with the highest incidence of disease were East Africa, the Middle East, and the Indian subcontinent. Visiting friends and relatives (VFR) travelers represented 83, 91, and 70% of the cases to these three regions; the highest incidence was found i ...
Chlamydia trachomatis
... C. pneumoniae is the causative agent of an atypical pneumonia (walking pneumonia) similar to those caused by Mycoplasma pneumoniae and Legionella pneumoniae. In addition it can cause a pharyngitis, bronchitis, sinusitis and possibly atherosclerosis. The organism was originally called the TWAR strain ...
... C. pneumoniae is the causative agent of an atypical pneumonia (walking pneumonia) similar to those caused by Mycoplasma pneumoniae and Legionella pneumoniae. In addition it can cause a pharyngitis, bronchitis, sinusitis and possibly atherosclerosis. The organism was originally called the TWAR strain ...
Protecting Workers from Occupational Exposure to Zika Virus
... Acetaminophen (Tylenol®) to reduce fever and pain. Do not take aspirin and other NSAIDS until dengue fever can be ruled out Supportive treatment for complications ...
... Acetaminophen (Tylenol®) to reduce fever and pain. Do not take aspirin and other NSAIDS until dengue fever can be ruled out Supportive treatment for complications ...
Infection Control Update
... Acute hepatitis causes a sudden inflammation of the liver that lasts several weeks. Hepatitis is considered chronic if the liver inflammation lasts longer than six months. ...
... Acute hepatitis causes a sudden inflammation of the liver that lasts several weeks. Hepatitis is considered chronic if the liver inflammation lasts longer than six months. ...
Ebola-Virus-Advice - Hardwick Primary School
... Public Health England (PHE), in conjunction with the Department for Education, has produced advice for schools, colleges, childcare and residential settings to ensure people are properly informed about the Ebola virus. This can be found on our website. ...
... Public Health England (PHE), in conjunction with the Department for Education, has produced advice for schools, colleges, childcare and residential settings to ensure people are properly informed about the Ebola virus. This can be found on our website. ...
Bacteria/Viruses and Disease - UCO
... • Rubella — commonly known as German measles or 3-day measles — is an infection that primarily affects the skin and lymph nodes. • It is usually transmitted by droplets from the nose or throat that others breathe in. ...
... • Rubella — commonly known as German measles or 3-day measles — is an infection that primarily affects the skin and lymph nodes. • It is usually transmitted by droplets from the nose or throat that others breathe in. ...
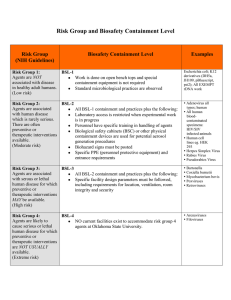
Risk Group and Biosafety Level Containment
... Agents are associated All BSL-1 containment and practices plus the following: with human disease Laboratory access is restricted when experimental work which is rarely serious. is in progress There are often Personnel have specific training in handling of agents preventive or Biological safety cabin ...
... Agents are associated All BSL-1 containment and practices plus the following: with human disease Laboratory access is restricted when experimental work which is rarely serious. is in progress There are often Personnel have specific training in handling of agents preventive or Biological safety cabin ...
Blood Transfusion and Infectious Diseases
... For red blood cell (RBC) preparations, which are stored at low temperature, the psychrophilic bacteria Yersinia enterocolitica and Serratia pose a threat while for platelet preparations stored at room temperature, indigenous bacteria on the skin including Staphylococcus epidermidis are a problem. Th ...
... For red blood cell (RBC) preparations, which are stored at low temperature, the psychrophilic bacteria Yersinia enterocolitica and Serratia pose a threat while for platelet preparations stored at room temperature, indigenous bacteria on the skin including Staphylococcus epidermidis are a problem. Th ...
the determinants of spread of ebola virus disease
... an ill person, b) being an adult family member, or c) sharing a bed during late illness, and in late stage of the disease d) sharing a meal, and e) having a conversation. Moreover, toughing of cadaver was also identified as a risk factor. The study of the 1995 outbreak did not find an increase in th ...
... an ill person, b) being an adult family member, or c) sharing a bed during late illness, and in late stage of the disease d) sharing a meal, and e) having a conversation. Moreover, toughing of cadaver was also identified as a risk factor. The study of the 1995 outbreak did not find an increase in th ...
AUSTRALIA ANTIGEN AND THE BIOLOGY OF HEPATITIS B.
... During the course of the next few months we found that the antibody in Mr. C. de B.‘s blood reacted with inherited antigenic specificities on the low density lipoproteins. We termed this the Ag system; and it has subsequently been the subject of genetic, clinical and forensic studies (11). We contin ...
... During the course of the next few months we found that the antibody in Mr. C. de B.‘s blood reacted with inherited antigenic specificities on the low density lipoproteins. We termed this the Ag system; and it has subsequently been the subject of genetic, clinical and forensic studies (11). We contin ...
Slide 1
... Studies of nursing students in Europe and US show high rates of tuberculin conversation (79100%) Standard 1920’s pulmonary text: “There is no danger from the expired air of consumptives. For this reason a TB sanatorium is probably the safest place one can be so far as the dangers of infection is con ...
... Studies of nursing students in Europe and US show high rates of tuberculin conversation (79100%) Standard 1920’s pulmonary text: “There is no danger from the expired air of consumptives. For this reason a TB sanatorium is probably the safest place one can be so far as the dangers of infection is con ...
Infectious Disease
... restrictions on the activities of well people who (may) have been exposed to a communicable disease during its period of communicability. – active surveillance is an alternative – Quarantine for the longest usual incubation period ...
... restrictions on the activities of well people who (may) have been exposed to a communicable disease during its period of communicability. – active surveillance is an alternative – Quarantine for the longest usual incubation period ...
Dr. Jing Qian, Ph.D
... C. Viruses must degrade host cell DNA in order to obtain nucleotides D. Enveloped viruses require host cell membranes to obtain their envelopes Each of the following statements concerning viruses is correct EXCEPT: A. Viruses can reproduce only within cells B. The proteins on the surface of the viru ...
... C. Viruses must degrade host cell DNA in order to obtain nucleotides D. Enveloped viruses require host cell membranes to obtain their envelopes Each of the following statements concerning viruses is correct EXCEPT: A. Viruses can reproduce only within cells B. The proteins on the surface of the viru ...
having an hiv test at the general medicine department
... In most cases pneumonia is bacterial and can be successfully treated with penicillin. For people with an impaired immune system pneumonia can be recurrent and very serious. An impaired immune system may be caused by an underlying HIV infection; however the vast majority of people with pneumonia will ...
... In most cases pneumonia is bacterial and can be successfully treated with penicillin. For people with an impaired immune system pneumonia can be recurrent and very serious. An impaired immune system may be caused by an underlying HIV infection; however the vast majority of people with pneumonia will ...
isolation of fowl adenovirus in chicken embryo liver cell culture and
... disease condition called Inclusion Body Hepatitis (IBH). In India, IBH was first reported in 3-weeks old broiler chicks, characterized by enlarged, mottled and friable liver with intranuclear inclusion bodies in the hepatocytes, causing about 15% mortality (Grewal et al., 1981). IBH along with hydro ...
... disease condition called Inclusion Body Hepatitis (IBH). In India, IBH was first reported in 3-weeks old broiler chicks, characterized by enlarged, mottled and friable liver with intranuclear inclusion bodies in the hepatocytes, causing about 15% mortality (Grewal et al., 1981). IBH along with hydro ...
Syndrom of diarrhea
... but survive, multiply and are transported to the liver, spleen, and bone marrow where they continue to replicate Second week: organisms reenter bloodstream and cause prolonged bacteremia; biliary tree and other organs are infected; gradually increasing sustained fever likely from endotoxemia Sec ...
... but survive, multiply and are transported to the liver, spleen, and bone marrow where they continue to replicate Second week: organisms reenter bloodstream and cause prolonged bacteremia; biliary tree and other organs are infected; gradually increasing sustained fever likely from endotoxemia Sec ...
Hepatitis C

Hepatitis C is an infectious disease affecting primarily the liver, caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV). The infection is often asymptomatic, but chronic infection can lead to scarring of the liver and ultimately to cirrhosis, which is generally apparent after many years. In some cases, those with cirrhosis will go on to develop liver failure, liver cancer, or life-threatening esophageal and gastric varices.HCV is spread primarily by blood-to-blood contact associated with intravenous drug use, poorly sterilized medical equipment, and transfusions. An estimated 150–200 million people worldwide are infected with hepatitis C. The existence of hepatitis C – originally identifiable only as a type of non-A non-B hepatitis – was suggested in the 1970s and proven in 1989. Hepatitis C infects only humans and chimpanzees. It is one of five known hepatitis viruses: A, B, C, D, and E.The virus persists in the liver in about 85% of those infected. This chronic infection can be treated with medication: the standard therapy is a combination of peginterferon and ribavirin, with either boceprevir or telaprevir added in some cases. Overall, 50–80% of people treated are cured. Those who develop cirrhosis or liver cancer may require a liver transplant. Hepatitis C is the leading reason for liver transplantation, though the virus usually recurs after transplantation. No vaccine against hepatitis C is available. About 343,000 deaths due to liver cancer from hepatitis C occurred in 2013, up from 198,000 in 1990. An additional 358,000 in 2013 occurred due to cirrhosis.