Viral Haemorrhagic Fever Policy - Portsmouth Hospitals NHS Trust
... Viral haemorrhagic fevers - a group of illnesses that are caused by several distinct families of viruses e.g. Ebola, Lassa fever, Crimean Congo haemorrhagic fever, Dengue fever, Yellow fever. Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever (CCHF) - is transmitted through the bite of an infected tick, contaminatio ...
... Viral haemorrhagic fevers - a group of illnesses that are caused by several distinct families of viruses e.g. Ebola, Lassa fever, Crimean Congo haemorrhagic fever, Dengue fever, Yellow fever. Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever (CCHF) - is transmitted through the bite of an infected tick, contaminatio ...
Escherichia coli 0157:H7
... What is viral gastroenteritis? Sometimes called the “stomach flu,” viral gastroenteritis is inflammation of the stomach and intestine caused by a virus. Many viruses can cause gastroenteritis, the most common is Norovirus. What are the symptoms of viral gastroenteritis? The most common symptoms of v ...
... What is viral gastroenteritis? Sometimes called the “stomach flu,” viral gastroenteritis is inflammation of the stomach and intestine caused by a virus. Many viruses can cause gastroenteritis, the most common is Norovirus. What are the symptoms of viral gastroenteritis? The most common symptoms of v ...
HIV-Related Opportunistic Infections Are Still Relevant in - IAS-USA
... starting antiretroviral therapy had it.4, 6,7 A cryptococcal antigen titer result greater than or equal to 1:8 was 100% sensitive and 96% specific for predicting cryptococcal meningitis during the first year of antiretroviral therapy in those with no history of the disease. Only 56% of those who ...
... starting antiretroviral therapy had it.4, 6,7 A cryptococcal antigen titer result greater than or equal to 1:8 was 100% sensitive and 96% specific for predicting cryptococcal meningitis during the first year of antiretroviral therapy in those with no history of the disease. Only 56% of those who ...
“Toxoplasmosis, Cytomegalovirus infection, Herpes simplex I, II types”.
... Congenital Toxoplasmosis. When a mother acquires the infection during gestation, the organism may disseminate hematogenously to the placenta. When this occurs, infection may be transmitted to the fetus transplacentally or during vaginal delivery. Of untreated maternal infections acquired in the fir ...
... Congenital Toxoplasmosis. When a mother acquires the infection during gestation, the organism may disseminate hematogenously to the placenta. When this occurs, infection may be transmitted to the fetus transplacentally or during vaginal delivery. Of untreated maternal infections acquired in the fir ...
Document
... •Treatment is supportive, using either oral or intravenous rehydration , For severe cases: •Intravenous fluids and blood transfusions •The rate of infection has increased dramatically over the last 50 years, with around 50–100 million people being infected yearly. •Is a global disease currently is e ...
... •Treatment is supportive, using either oral or intravenous rehydration , For severe cases: •Intravenous fluids and blood transfusions •The rate of infection has increased dramatically over the last 50 years, with around 50–100 million people being infected yearly. •Is a global disease currently is e ...
What You Need to Know About Staph/MRSA Skin Infections
... working with doctors and other healthcare providers to better understand why this is happening and how to prevent antibiotic (drug) resistant Staph/MRSA skin infections from spreading. What is a Staph/MRSA skin infection? It can be a pimple, rash, boil, or an open wound. Staph/MRSA is often misdiagn ...
... working with doctors and other healthcare providers to better understand why this is happening and how to prevent antibiotic (drug) resistant Staph/MRSA skin infections from spreading. What is a Staph/MRSA skin infection? It can be a pimple, rash, boil, or an open wound. Staph/MRSA is often misdiagn ...
Canine Distemper Virus and other Infectious Respiratory
... degree of immunity. Very mild forms may be confused with kennel cough. Severe forms may result in acute death. Treatment during the acute systemic phase is supportive and may also include antibiotics for treatment of secondary bacterial infections. Some, but not all, dogs who recover from the system ...
... degree of immunity. Very mild forms may be confused with kennel cough. Severe forms may result in acute death. Treatment during the acute systemic phase is supportive and may also include antibiotics for treatment of secondary bacterial infections. Some, but not all, dogs who recover from the system ...
3. The expanding range of parvoviruses which infect humans.
... mammalian and avian species. Till date at least nine different dependovirus serotypes have been described in primates [5], and AAVs -1, -2, -3, 8 and 9 are common human infections [5,6]. ...
... mammalian and avian species. Till date at least nine different dependovirus serotypes have been described in primates [5], and AAVs -1, -2, -3, 8 and 9 are common human infections [5,6]. ...
GHC Infection Control and Employee Health Plan, D-07-003
... b. Control activities include: i. Case finding ii. Reporting of information about infections iii. Development and implementation of prevention strategies iv. Outbreak intervention and control 2. Compile and analyze surveillance data to identify trends in healthcare associated, community, and occupat ...
... b. Control activities include: i. Case finding ii. Reporting of information about infections iii. Development and implementation of prevention strategies iv. Outbreak intervention and control 2. Compile and analyze surveillance data to identify trends in healthcare associated, community, and occupat ...
Extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli (ESBLs)
... in hospitals, were in elderly individuals or others with underlying medical conditions, most particularly those undergoing catheterisation. In some cases, patients were recently hospitalised, which means that the patient may have become colonised or infected whilst in hospital. For some community ca ...
... in hospitals, were in elderly individuals or others with underlying medical conditions, most particularly those undergoing catheterisation. In some cases, patients were recently hospitalised, which means that the patient may have become colonised or infected whilst in hospital. For some community ca ...
Standard Precautions - Amazon Web Services
... shall be placed in bags which meet the requirements of bags used of medical waste. Pregnant Employees Pregnant health-care workers are not known to be at a greater risk of contracting HIV or HBV infection than healthcare workers who are not pregnant; however, if a health-care worker develops HIV or ...
... shall be placed in bags which meet the requirements of bags used of medical waste. Pregnant Employees Pregnant health-care workers are not known to be at a greater risk of contracting HIV or HBV infection than healthcare workers who are not pregnant; however, if a health-care worker develops HIV or ...
Herpes Zoster - Boston Health Care for the Homeless Program
... Immunocompromised patients with zoster are at risk of developing widespread infection with VZV, called disseminated herpes zoster. This potentially serious illness may result in skin lesions over the entire body and infection of internal organs. This infection is thought to be more contagious than t ...
... Immunocompromised patients with zoster are at risk of developing widespread infection with VZV, called disseminated herpes zoster. This potentially serious illness may result in skin lesions over the entire body and infection of internal organs. This infection is thought to be more contagious than t ...
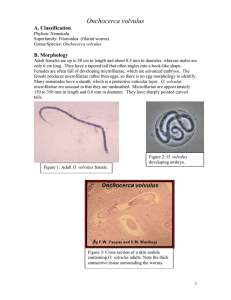
Classification
... be infected. This disease usually causes blindness and disfigurement. Both the adult worms and the microfilariae can cause the disease. The adults generally cause no symptoms, except the growth of subcutaneous nodules called onchocercomas. Onchocercomas are formed from collagen fibers encompassing a ...
... be infected. This disease usually causes blindness and disfigurement. Both the adult worms and the microfilariae can cause the disease. The adults generally cause no symptoms, except the growth of subcutaneous nodules called onchocercomas. Onchocercomas are formed from collagen fibers encompassing a ...
Association Bulletin #14-05 - Babesiosis
... The expanding geographic range of B. microti, increasing incidence of babesiosis, and the threat to the blood supply led the Council of State and Territorial Epidemiologists (CSTE) to designate babesiosis as a nationally notifiable disease in 2011,7 although not all states have made it a reportable ...
... The expanding geographic range of B. microti, increasing incidence of babesiosis, and the threat to the blood supply led the Council of State and Territorial Epidemiologists (CSTE) to designate babesiosis as a nationally notifiable disease in 2011,7 although not all states have made it a reportable ...
STIs in Boston: Gonorrhea Brief 2014
... at some point during the year. Most were men (59%), and 56% were Black residents. The majority of cases with both infections resided in North Dorchester, South Dorchester, the South End, and Mattapan, and 75% were 15-29 years old. Future Directions: While the rate of chlamydia infection in Boston is ...
... at some point during the year. Most were men (59%), and 56% were Black residents. The majority of cases with both infections resided in North Dorchester, South Dorchester, the South End, and Mattapan, and 75% were 15-29 years old. Future Directions: While the rate of chlamydia infection in Boston is ...
Open access
... 18, 2016) has been documented in 35 countries and territories in the Americas. It is believed that most transmission has occurred through mosquito bites and from mother to fetus. Sexual transmission has been documented in Florida and Texas.3 ZIKA DISEASE SYMPTOMS ...
... 18, 2016) has been documented in 35 countries and territories in the Americas. It is believed that most transmission has occurred through mosquito bites and from mother to fetus. Sexual transmission has been documented in Florida and Texas.3 ZIKA DISEASE SYMPTOMS ...
Protection Against Viral Illnesses
... with respiratory tract infections. In a study published in Infection Control and Hospital Epidemiology, doctors at two Pennsylvania hospitals were found to be using antibiotics to treat patients with viral infections, which are known to not respond to the drugs..... This study reflects what is going ...
... with respiratory tract infections. In a study published in Infection Control and Hospital Epidemiology, doctors at two Pennsylvania hospitals were found to be using antibiotics to treat patients with viral infections, which are known to not respond to the drugs..... This study reflects what is going ...
Acute Pancreatitis - Pitt Pharmacy Portfolio
... 1-10 cases per 100,000 persons Major cause of sudden, unexpected death (~20% ...
... 1-10 cases per 100,000 persons Major cause of sudden, unexpected death (~20% ...
Influenza - National Academies
... § Individuals are contagious for 1 to 4 days before the onset of symptoms and about 5 days after the first symptoms q ...
... § Individuals are contagious for 1 to 4 days before the onset of symptoms and about 5 days after the first symptoms q ...
(Aedes) detritus, as a potential vector for Japanese encephalitis virus
... Johnson N, Fooks AR, Solomon T and Baylis M. Evaluation of a temperate climate mosquito, Ochlerotatus (Aedes) detritus, as a potential vector for Japanese encephalitis virus. Medical and ...
... Johnson N, Fooks AR, Solomon T and Baylis M. Evaluation of a temperate climate mosquito, Ochlerotatus (Aedes) detritus, as a potential vector for Japanese encephalitis virus. Medical and ...
Assessing risks of disease transmission between wildlife and livestock
... Saiga herds vary in size through the year, from huge aggregations during calving to small groups during summer grazing, with intermediate group size during migration and mating. Herd structure is also quite labile, and individuals can leave and join different groups through the year (Grachev and Bek ...
... Saiga herds vary in size through the year, from huge aggregations during calving to small groups during summer grazing, with intermediate group size during migration and mating. Herd structure is also quite labile, and individuals can leave and join different groups through the year (Grachev and Bek ...
Campylobacter - International Scientific Forum on Home Hygiene
... infection can be found in a 2009 IFH report11 Who is at risk? Anyone can be infected by Campylobacter but those most at risk are babies, young children under 5 years of age, those over 60 and others with reduced immunity. People who work with farm animals or in the meat industry and travellers to de ...
... infection can be found in a 2009 IFH report11 Who is at risk? Anyone can be infected by Campylobacter but those most at risk are babies, young children under 5 years of age, those over 60 and others with reduced immunity. People who work with farm animals or in the meat industry and travellers to de ...
Mathematical modelling of infectious disease transmission
... • Vaccinated people are less likely to become infected and less likely to infect others. Therefore, vaccines can protect vaccinated and unvaccinated people. • If some people are vaccinated, epidemics may be smaller. • If enough people are vaccinated, epidemics should not spread and there is “herd im ...
... • Vaccinated people are less likely to become infected and less likely to infect others. Therefore, vaccines can protect vaccinated and unvaccinated people. • If some people are vaccinated, epidemics may be smaller. • If enough people are vaccinated, epidemics should not spread and there is “herd im ...
Bubonic Plague
... painful lymph nodes. The case fatality rate for infected persons who are not treated is 50%-60%. If bubonic plague is left untreated Septicemic plague can occur as a complication. When the Y. pestis bacteria spreads into the bloodstream it can cause a blood infection called septicemia, it can develo ...
... painful lymph nodes. The case fatality rate for infected persons who are not treated is 50%-60%. If bubonic plague is left untreated Septicemic plague can occur as a complication. When the Y. pestis bacteria spreads into the bloodstream it can cause a blood infection called septicemia, it can develo ...
Hepatitis C

Hepatitis C is an infectious disease affecting primarily the liver, caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV). The infection is often asymptomatic, but chronic infection can lead to scarring of the liver and ultimately to cirrhosis, which is generally apparent after many years. In some cases, those with cirrhosis will go on to develop liver failure, liver cancer, or life-threatening esophageal and gastric varices.HCV is spread primarily by blood-to-blood contact associated with intravenous drug use, poorly sterilized medical equipment, and transfusions. An estimated 150–200 million people worldwide are infected with hepatitis C. The existence of hepatitis C – originally identifiable only as a type of non-A non-B hepatitis – was suggested in the 1970s and proven in 1989. Hepatitis C infects only humans and chimpanzees. It is one of five known hepatitis viruses: A, B, C, D, and E.The virus persists in the liver in about 85% of those infected. This chronic infection can be treated with medication: the standard therapy is a combination of peginterferon and ribavirin, with either boceprevir or telaprevir added in some cases. Overall, 50–80% of people treated are cured. Those who develop cirrhosis or liver cancer may require a liver transplant. Hepatitis C is the leading reason for liver transplantation, though the virus usually recurs after transplantation. No vaccine against hepatitis C is available. About 343,000 deaths due to liver cancer from hepatitis C occurred in 2013, up from 198,000 in 1990. An additional 358,000 in 2013 occurred due to cirrhosis.