MRSA: Myths and Reality
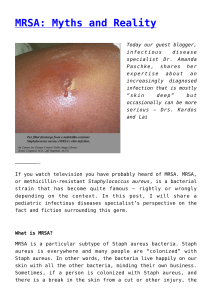
... infection there are many more who are colonized with the bacteria, so it does not make sense to exclude a child on the basis of a diagnosis. A child with a MRSA skin infection is not a danger to other children or adults. As with any skin infection, open wounds should be covered. MRSA, while it can i ...
... infection there are many more who are colonized with the bacteria, so it does not make sense to exclude a child on the basis of a diagnosis. A child with a MRSA skin infection is not a danger to other children or adults. As with any skin infection, open wounds should be covered. MRSA, while it can i ...
Data needs for evidence-based decisions: a tuberculosis modeler`s
... Figure 3 Sensitivity and uncertainty of model outcomes with parameter variation. Bars represent the change in steady-state TB incidence in a simplified model of TB transmission (Figure 1) that would occur with specified increases (black bars) and decreases (white bars) in model parameters. The model ...
... Figure 3 Sensitivity and uncertainty of model outcomes with parameter variation. Bars represent the change in steady-state TB incidence in a simplified model of TB transmission (Figure 1) that would occur with specified increases (black bars) and decreases (white bars) in model parameters. The model ...
PEDIATRIC CHRONIC FATIGUE SYNDROME Fact Sheet
... severely or partly disabled and housebound, while others can go to school and a few even do sports. Most are between these extremes. Over time, slow improvement is likely. Remissions and relapses are common. Relapses may be caused by other bacterial or viral illnesses or over-exertion. Recovery rate ...
... severely or partly disabled and housebound, while others can go to school and a few even do sports. Most are between these extremes. Over time, slow improvement is likely. Remissions and relapses are common. Relapses may be caused by other bacterial or viral illnesses or over-exertion. Recovery rate ...
Pertussis (Whooping cough)
... Reactions at the injection site such as redness or swelling are common occurring 10-20% of the time. Fever is noted in about 25% of those vaccinated. Extensive swelling at the injection site can occur with booster doses; however it is not associated with pain and fully resolves after a few days. (Th ...
... Reactions at the injection site such as redness or swelling are common occurring 10-20% of the time. Fever is noted in about 25% of those vaccinated. Extensive swelling at the injection site can occur with booster doses; however it is not associated with pain and fully resolves after a few days. (Th ...
Gonorrhea Fact Sheet
... In women, gonorrhea is a common cause of pelvic inflammatory disease (PID). About one million women each year in the United States develop PID. The symptoms may be quite mild or can be very severe and can include abdominal pain and fever. PID can lead to internal abscesses (pus-filled “pockets” tha ...
... In women, gonorrhea is a common cause of pelvic inflammatory disease (PID). About one million women each year in the United States develop PID. The symptoms may be quite mild or can be very severe and can include abdominal pain and fever. PID can lead to internal abscesses (pus-filled “pockets” tha ...
MICROBIOLOGY I GRAM STAIN OXYGEN REQUIREMENTS
... • not part of the normal flora in healthy people • environmental organism (water, soil, plants) • well adapted to survival in harsh environments • broad spectrum of disease _ superficial skin infections to fulminant ...
... • not part of the normal flora in healthy people • environmental organism (water, soil, plants) • well adapted to survival in harsh environments • broad spectrum of disease _ superficial skin infections to fulminant ...
Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP):
... may be lower (22 ), and they may require repeat vaccination (23,24 ) or an increased dose of vaccine. Because secondary antibody responses are less affected than primary antibody responses, immunization strategies should be formulated early in the course of progressive renal disease. This approach i ...
... may be lower (22 ), and they may require repeat vaccination (23,24 ) or an increased dose of vaccine. Because secondary antibody responses are less affected than primary antibody responses, immunization strategies should be formulated early in the course of progressive renal disease. This approach i ...
The spread of non-OIE-listed avian diseases through international
... that infected flocks would be detected during ante-mortem inspection. After infection, B. avium is only found in upper respiratory tract tissues and these are removed from the birds at slaughter. However, it has been previously estimated that some upper respiratory tract tissue remains in around 0.2 ...
... that infected flocks would be detected during ante-mortem inspection. After infection, B. avium is only found in upper respiratory tract tissues and these are removed from the birds at slaughter. However, it has been previously estimated that some upper respiratory tract tissue remains in around 0.2 ...
fever syndrome in surgical infections
... called respective views of the microorganism. Due to its proposed in 1881 by the methods of cultivation of microorganisms on solid and transparent media, he was able to identify different species of bacteria, making them carry pure cultures. This was followed by the opening stage of the various agen ...
... called respective views of the microorganism. Due to its proposed in 1881 by the methods of cultivation of microorganisms on solid and transparent media, he was able to identify different species of bacteria, making them carry pure cultures. This was followed by the opening stage of the various agen ...
Osteomyelitis Due to Citrobacter koseri Infection in a Diabetic Patient
... ) and C. freundii are three major species in the genus. The most common sites that Citrobacter species cause infections are urinary tract, gastrointestinal tract, wound or decubitus and other sites respectively [2]. Citrobacter infections are usually found in immunocompromised hosts, old patients an ...
... ) and C. freundii are three major species in the genus. The most common sites that Citrobacter species cause infections are urinary tract, gastrointestinal tract, wound or decubitus and other sites respectively [2]. Citrobacter infections are usually found in immunocompromised hosts, old patients an ...
(MN) Healthcare-Associated Infections (HAI) Prevention Plan
... Minnesota (MN) Healthcare-Associated Infections (HAI) Prevention Plan - Executive Summary In response to the increasing concerns about the public health impact of healthcare-associated infections (HAIs), the US Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) has developed an Action Plan to Prevent Hea ...
... Minnesota (MN) Healthcare-Associated Infections (HAI) Prevention Plan - Executive Summary In response to the increasing concerns about the public health impact of healthcare-associated infections (HAIs), the US Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) has developed an Action Plan to Prevent Hea ...
The present and future disease burden of hepatitis C virus (HCV
... of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cases and liver transplants due to HCV [5–7]. However, annual HCV-related disease burden data are not available in all countries. Robust estimates of HCV-related mortality and morbidity (numbers and trends) are needed to help policymakers develop strategies to tackl ...
... of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cases and liver transplants due to HCV [5–7]. However, annual HCV-related disease burden data are not available in all countries. Robust estimates of HCV-related mortality and morbidity (numbers and trends) are needed to help policymakers develop strategies to tackl ...
Outcomes Important to Lyme Patients
... Those impacted by Lyme care most about avoiding under‐diagnosis and increasing laboratory test innovation. By a two‐to‐one choice, participants prefer avoiding the risks associated with under‐ diagnosis versus over‐diagnosis. Persisting Lyme disease symptoms may be caused by a persisting infection ...
... Those impacted by Lyme care most about avoiding under‐diagnosis and increasing laboratory test innovation. By a two‐to‐one choice, participants prefer avoiding the risks associated with under‐ diagnosis versus over‐diagnosis. Persisting Lyme disease symptoms may be caused by a persisting infection ...
Bacterial Meningitis - Boston Public Health Commission
... are very young or very old, are at high risk for getting pneumococcal meningitis. Meningitis caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae is not contagious (spread from person to person). People in close contact with someone who has pneumococcal meningitis do not need to get antibiotics. However, there are 2 ...
... are very young or very old, are at high risk for getting pneumococcal meningitis. Meningitis caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae is not contagious (spread from person to person). People in close contact with someone who has pneumococcal meningitis do not need to get antibiotics. However, there are 2 ...
Contraindications and Precautionary Conditions for Vaccination
... Children with problem histories: There are certain groups of children in whom the advisability of whooping cough immunization requires special considerations because of their own or their family histories. For them, the risk from vaccine may be higher, but the effects of whooping cough disease could ...
... Children with problem histories: There are certain groups of children in whom the advisability of whooping cough immunization requires special considerations because of their own or their family histories. For them, the risk from vaccine may be higher, but the effects of whooping cough disease could ...
action for specified medical conditions
... *Not excluded unless unwell. Staff must be aware of the possibility that any adult or child could be infected with HIV. Children requiring antibiotic medicine, eye drops or ointment, are excluded for 36 hours from first dose or application. If the child has a repeat and the antibiotic is not continu ...
... *Not excluded unless unwell. Staff must be aware of the possibility that any adult or child could be infected with HIV. Children requiring antibiotic medicine, eye drops or ointment, are excluded for 36 hours from first dose or application. If the child has a repeat and the antibiotic is not continu ...
What Is Campylobacter?
... Campylobacter can sometimes spread beyond the intestinal tract, resulting in severe, even life-threatening infection of other parts of the body, particularly in animals or people who are very young, old, or have a weakened immune system. The risk of transmission of Campylobacter between animals and ...
... Campylobacter can sometimes spread beyond the intestinal tract, resulting in severe, even life-threatening infection of other parts of the body, particularly in animals or people who are very young, old, or have a weakened immune system. The risk of transmission of Campylobacter between animals and ...
Granulomatous Lymphadenitis
... In this review, representative types of granulomatous lymphadenitis (GLA) are described. GLA can be classified as noninfectious GLA and infectious GLA. Noninfectious GLA includes sarcoidosis and sarcoid-like reaction. The cause of sarcoidosis remains unknown, but it has good prognosis. Sarcoid-like ...
... In this review, representative types of granulomatous lymphadenitis (GLA) are described. GLA can be classified as noninfectious GLA and infectious GLA. Noninfectious GLA includes sarcoidosis and sarcoid-like reaction. The cause of sarcoidosis remains unknown, but it has good prognosis. Sarcoid-like ...
A Population Model of Malaria Transmission According to Within
... Malaria is a vector-borne infectious disease which is caused by protozoan parasites. Symptoms are characterized by high fever, chills, u-like symptoms, and in many cases, death. Malaria shares many characteristics with other protozoan parasites, which cause diseases such as African trypanosomiasis ...
... Malaria is a vector-borne infectious disease which is caused by protozoan parasites. Symptoms are characterized by high fever, chills, u-like symptoms, and in many cases, death. Malaria shares many characteristics with other protozoan parasites, which cause diseases such as African trypanosomiasis ...
2004 2013 2005 2006
... ll data from submissions to the CAHFS, including animal demographics, clinical histories, gross and histopathology, test results and diagnoses are captured and stored by the CAHFS Laboratory Information System (LIMS). Diagnostic accessions are then categorized according to a standard nomenclature de ...
... ll data from submissions to the CAHFS, including animal demographics, clinical histories, gross and histopathology, test results and diagnoses are captured and stored by the CAHFS Laboratory Information System (LIMS). Diagnostic accessions are then categorized according to a standard nomenclature de ...
Outbreak of Ebola virus disease in West Africa
... and are sensitive to sodium hypochlorite (bleach) and other disinfectants [12,13]. Freezing or refrigeration will not inactivate Ebola viruses [14,15]. The incubation period (the period between infection and first symptoms) is usually four to ten days but can be as short as two days and as long as 2 ...
... and are sensitive to sodium hypochlorite (bleach) and other disinfectants [12,13]. Freezing or refrigeration will not inactivate Ebola viruses [14,15]. The incubation period (the period between infection and first symptoms) is usually four to ten days but can be as short as two days and as long as 2 ...
Cytomegalovirus (CMV)–Encoded UL144 (Truncated Tumor
... Results. Genotype C was associated with termination of pregnancy (P p .03 ). Genotype B was associated with fewer terminations of pregnancy (P p .003 ). A possible association was found between genotype C and symptomatic disease in newborns (odds ratio, 8.81 [95% confidence interval, 0.48–164.02]; P ...
... Results. Genotype C was associated with termination of pregnancy (P p .03 ). Genotype B was associated with fewer terminations of pregnancy (P p .003 ). A possible association was found between genotype C and symptomatic disease in newborns (odds ratio, 8.81 [95% confidence interval, 0.48–164.02]; P ...
Understanding cutaneous tuberculosis: two clinical cases
... Cutaneous TB may emerge as an exogenous infection, when bacilli originating usually from a patient with active pulmonary TB enter the skin tissue through small lesions, similarly to the pattern that has been observed for NTM skin infections (Bravo & Gotuzzo, 2007). In this case, once M. tuberculosis ...
... Cutaneous TB may emerge as an exogenous infection, when bacilli originating usually from a patient with active pulmonary TB enter the skin tissue through small lesions, similarly to the pattern that has been observed for NTM skin infections (Bravo & Gotuzzo, 2007). In this case, once M. tuberculosis ...
Blocking of integrins inhibits HIV-1 infection of and complement-opsonized virions
... Another potential mechanism available to the virus to penetrate the mucosa is by exploiting dendritic cells (DCs) and Langerhans cells (LCs) localized in the stratified epithelium, where these cells can pick up HIV-1 and transfer the virus to the submucosa [8]. When HIV-1 has reached the submucosa, ...
... Another potential mechanism available to the virus to penetrate the mucosa is by exploiting dendritic cells (DCs) and Langerhans cells (LCs) localized in the stratified epithelium, where these cells can pick up HIV-1 and transfer the virus to the submucosa [8]. When HIV-1 has reached the submucosa, ...
Coccidioidomycosis

Coccidioidomycosis (/kɒkˌsɪdiɔɪdoʊmaɪˈkoʊsɪs/, kok-sid-ee-oy-doh-my-KOH-sis), commonly known as cocci, ""valley fever"", as well as ""California fever"", ""desert rheumatism"", and ""San Joaquin Valley fever"", is a mammalian fungal disease caused by Coccidioides immitis or Coccidioides posadasii. It is endemic in certain parts of Arizona, California, Nevada, New Mexico, Texas, Utah, and northern Mexico.C. immitis is a dimorphic saprophytic fungus that grows as a mycelium in the soil and produces a spherule form in the host organism. It resides in the soil in certain parts of the southwestern United States, most notably in California and Arizona. It is also commonly found in northern Mexico, and parts of Central and South America. C. immitis is dormant during long dry spells, then develops as a mold with long filaments that break off into airborne spores when it rains. The spores, known as arthroconidia, are swept into the air by disruption of the soil, such as during construction, farming, or an earthquake.Coccidioidomycosis is a common cause of community acquired pneumonia in the endemic areas of the United States. Infections usually occur due to inhalation of the arthroconidial spores after soil disruption. The disease is not contagious. In some cases the infection may recur or be permanent.























