Colorado Tick Fever Virus
... plus and minus strands that are colinear and complementary, ~27-29 kb in length Physicochemical properties: Stable at -70°C, 4°C, and room temperature, but loss of infectivity is accelerated at higher temperatures; resistant to treatment with ether and other lipid solvents, relatively resistant to c ...
... plus and minus strands that are colinear and complementary, ~27-29 kb in length Physicochemical properties: Stable at -70°C, 4°C, and room temperature, but loss of infectivity is accelerated at higher temperatures; resistant to treatment with ether and other lipid solvents, relatively resistant to c ...
Unit 13 Infection Control
... Rules developed by the CDC to prevent the transmission and contraction of pathogens. Every body fluid must be considered a potentially infectious material, and all patients must be considered potential sources of infection, regardless of their disease or diagnosis ...
... Rules developed by the CDC to prevent the transmission and contraction of pathogens. Every body fluid must be considered a potentially infectious material, and all patients must be considered potential sources of infection, regardless of their disease or diagnosis ...
2421_Ch14.ppt
... Epidemiology - study of when and where diseases occur and how they are transmitted in populations. Descriptive epidemiology - collection of data that describe the occurrence of the disease under study. Analytical epidemiology - analyzes a particular disease to determine its probable cause. (risk fac ...
... Epidemiology - study of when and where diseases occur and how they are transmitted in populations. Descriptive epidemiology - collection of data that describe the occurrence of the disease under study. Analytical epidemiology - analyzes a particular disease to determine its probable cause. (risk fac ...
Athletes foot and fungal infections
... You can search for other information leaflets on www.patient.co.uk and your G.P. also has access to this website. It is recommended that you follow the advice in this leaflet and only contact the podiatry department should the symptoms not improve. If you are aged between 19-60 years ...
... You can search for other information leaflets on www.patient.co.uk and your G.P. also has access to this website. It is recommended that you follow the advice in this leaflet and only contact the podiatry department should the symptoms not improve. If you are aged between 19-60 years ...
Weils Disease
... Humans are considered to be a dead-end or accidental host of Leptospires. Infection may be aquired by direct or indirect contact with affected urine, tissues, or secretions. Leptospires enter the body through cut or damaged skin, but may also pass across damaged or intact mucous membranes, and the e ...
... Humans are considered to be a dead-end or accidental host of Leptospires. Infection may be aquired by direct or indirect contact with affected urine, tissues, or secretions. Leptospires enter the body through cut or damaged skin, but may also pass across damaged or intact mucous membranes, and the e ...
Campylobacter jejuni
... they are are usually occur in the summer and early fall, but cases may occur year-round. About 5% to 30% of people who have Legionnaires' disease die. 2)How is legionellosis spread? Legionella are typically associated with aerosolized water (central air conditioning, cooling towers, showers, whirlpo ...
... they are are usually occur in the summer and early fall, but cases may occur year-round. About 5% to 30% of people who have Legionnaires' disease die. 2)How is legionellosis spread? Legionella are typically associated with aerosolized water (central air conditioning, cooling towers, showers, whirlpo ...
Campylobacter jejuni
... they are are usually occur in the summer and early fall, but cases may occur year-round. About 5% to 30% of people who have Legionnaires' disease die. 2)How is legionellosis spread? Legionella are typically associated with aerosolized water (central air conditioning, cooling towers, showers, whirlpo ...
... they are are usually occur in the summer and early fall, but cases may occur year-round. About 5% to 30% of people who have Legionnaires' disease die. 2)How is legionellosis spread? Legionella are typically associated with aerosolized water (central air conditioning, cooling towers, showers, whirlpo ...
Chapter 27 Nervous System Infections
... common in glands, rash, or unimmunized chest pain. populations. Incubation Period: 1 to 2 weeks for enteroviruses. 2 to 4 weeks for mumps. ...
... common in glands, rash, or unimmunized chest pain. populations. Incubation Period: 1 to 2 weeks for enteroviruses. 2 to 4 weeks for mumps. ...
2-years postdoctoral fellowship in the CIIL
... 2-years postdoctoral fellowship in the CIILTeam Lung infection and innate immunity Starting in December 2014 at Pasteur Institute (Lille) Description of the Topic: Lung inflammatory disorders such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) are associated with an increased susceptibility to resp ...
... 2-years postdoctoral fellowship in the CIILTeam Lung infection and innate immunity Starting in December 2014 at Pasteur Institute (Lille) Description of the Topic: Lung inflammatory disorders such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) are associated with an increased susceptibility to resp ...
UF Health Jacksonville
... time period of Oct 2013- Sept 2014? We believe the data used in the report on hospital acquired infections was affected in part by the implementation of our electronic medical record system and resulting failure to capture within the new system patient conditions that were present upon admission. We ...
... time period of Oct 2013- Sept 2014? We believe the data used in the report on hospital acquired infections was affected in part by the implementation of our electronic medical record system and resulting failure to capture within the new system patient conditions that were present upon admission. We ...
MERS-CoV
... • A person with an acute respiratory infection, which may include history of fever and cough and evidence of pulmonary parenchymal disease(pneumonia, ARDS) based upon clinical or radiographic evidence of consolidation, who requires admission to hospital. ...
... • A person with an acute respiratory infection, which may include history of fever and cough and evidence of pulmonary parenchymal disease(pneumonia, ARDS) based upon clinical or radiographic evidence of consolidation, who requires admission to hospital. ...
Bloodborne Pathogens
... Currently there is no effective vaccine for HCV and treatment is difficult with side effects. 75% of people infected with HCV have no symptoms at all. 85% of people who become infected will develop chronic liver disease. ...
... Currently there is no effective vaccine for HCV and treatment is difficult with side effects. 75% of people infected with HCV have no symptoms at all. 85% of people who become infected will develop chronic liver disease. ...
Pediatric Respiratory Distress
... Items in Red Text are key performance measures used to evaluate protocol compliance and care Pulse oximetry should be monitored continuously if initial saturation is < 96%, or there is a decline in patient status despite normal pulse oximetry readings. Do not force a child into a position. They will ...
... Items in Red Text are key performance measures used to evaluate protocol compliance and care Pulse oximetry should be monitored continuously if initial saturation is < 96%, or there is a decline in patient status despite normal pulse oximetry readings. Do not force a child into a position. They will ...
Tropical Diseases
... reducing the impact of cholera and other waterborne diseases. • Oral cholera vaccines are considered an additional means to control cholera, but should not replace conventional control measures. ...
... reducing the impact of cholera and other waterborne diseases. • Oral cholera vaccines are considered an additional means to control cholera, but should not replace conventional control measures. ...
Nervous System Infections - Biology Online Learning
... • Capsule inhibits phagocytosis and neutralizes opsonins • Organisms typically cause thickening of meninges • This can often impede the flow of CSF • Also invade brain tissue producing abscesses ...
... • Capsule inhibits phagocytosis and neutralizes opsonins • Organisms typically cause thickening of meninges • This can often impede the flow of CSF • Also invade brain tissue producing abscesses ...
Unit: Universal Precautions
... Blood, saliva and other body fluids spread virus to sexual partners, unborn infants, family members • Can survive at room temperature for at least a week • May severely damage liver, leading to cirrhosis and death (1-10%) • Greater risk of liver cancer ...
... Blood, saliva and other body fluids spread virus to sexual partners, unborn infants, family members • Can survive at room temperature for at least a week • May severely damage liver, leading to cirrhosis and death (1-10%) • Greater risk of liver cancer ...
I a b s
... It is widely accepted that reducing contact between domestic and wild sheep limits pneumonia introduction, where domestic sheep transmit pathogens to bighorns. However, in some places, pneumonia persists for many years, even as local domestic inholding decline. We focused on one such system, the Hel ...
... It is widely accepted that reducing contact between domestic and wild sheep limits pneumonia introduction, where domestic sheep transmit pathogens to bighorns. However, in some places, pneumonia persists for many years, even as local domestic inholding decline. We focused on one such system, the Hel ...
Infectious diseases
... effects of the cold (for example, sore throat, runny nose or fever). • Because the cold is caused by a virus it cannot be treated with an antibiotic. ...
... effects of the cold (for example, sore throat, runny nose or fever). • Because the cold is caused by a virus it cannot be treated with an antibiotic. ...
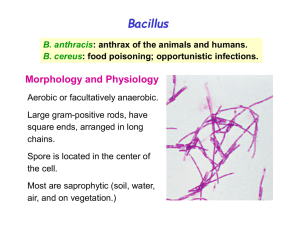
B. anthracis
... hours. The papule rapidly changes into a vesicle, then a pustule, and finally a necrotic eschar. The infection may disseminate, giving rise to septicemia. Inhalation anthrax (wool-sorters’ disease): long incubation time (2 months or more). Mediastinitis (enlargement of mediastinal lymph nodes), seps ...
... hours. The papule rapidly changes into a vesicle, then a pustule, and finally a necrotic eschar. The infection may disseminate, giving rise to septicemia. Inhalation anthrax (wool-sorters’ disease): long incubation time (2 months or more). Mediastinitis (enlargement of mediastinal lymph nodes), seps ...
Sheet #14 / Dr.Yazan / Leen Farhan
... Also the lingual tonsils and foliate papilla can get inflamed and enlarged sometimes ,, the pt presents with enlargement of posterior border of the tongue and it’s bilateral . Diagnosis of Glandular fever depends on clinical features and the presence of abnormal lymphocytes in blood smear . also we ...
... Also the lingual tonsils and foliate papilla can get inflamed and enlarged sometimes ,, the pt presents with enlargement of posterior border of the tongue and it’s bilateral . Diagnosis of Glandular fever depends on clinical features and the presence of abnormal lymphocytes in blood smear . also we ...
Chapter 13: Infection and Disease
... • Virulence is the degree of pathogenicity • Pathogenicity islands refers to gene clusters responsible for virulence • Several Events Must Occur for Disease to Develop in the Host • An exogenous infection occurs if a pathogen breaches the host’s external defense and enters sterile tissue • An endoge ...
... • Virulence is the degree of pathogenicity • Pathogenicity islands refers to gene clusters responsible for virulence • Several Events Must Occur for Disease to Develop in the Host • An exogenous infection occurs if a pathogen breaches the host’s external defense and enters sterile tissue • An endoge ...
Infection Control - Women`s and Children`s Hospital
... Complications more common and severe in chronically ill and very young children Transmitted by droplet and contact with respiratory secretions Infectious for 4 days before and after ...
... Complications more common and severe in chronically ill and very young children Transmitted by droplet and contact with respiratory secretions Infectious for 4 days before and after ...
Coccidioidomycosis

Coccidioidomycosis (/kɒkˌsɪdiɔɪdoʊmaɪˈkoʊsɪs/, kok-sid-ee-oy-doh-my-KOH-sis), commonly known as cocci, ""valley fever"", as well as ""California fever"", ""desert rheumatism"", and ""San Joaquin Valley fever"", is a mammalian fungal disease caused by Coccidioides immitis or Coccidioides posadasii. It is endemic in certain parts of Arizona, California, Nevada, New Mexico, Texas, Utah, and northern Mexico.C. immitis is a dimorphic saprophytic fungus that grows as a mycelium in the soil and produces a spherule form in the host organism. It resides in the soil in certain parts of the southwestern United States, most notably in California and Arizona. It is also commonly found in northern Mexico, and parts of Central and South America. C. immitis is dormant during long dry spells, then develops as a mold with long filaments that break off into airborne spores when it rains. The spores, known as arthroconidia, are swept into the air by disruption of the soil, such as during construction, farming, or an earthquake.Coccidioidomycosis is a common cause of community acquired pneumonia in the endemic areas of the United States. Infections usually occur due to inhalation of the arthroconidial spores after soil disruption. The disease is not contagious. In some cases the infection may recur or be permanent.