Comparing Microbes
... Pathogen – any microbe that causes one or more diseases. Infectious Disease - any disease that is caused by a pathogen (e.g. MRSA) Contagion – an infectious disease or infectious diseases that can be transmitted or spread from one organism to another. Carrier – an organism that is infected with and ...
... Pathogen – any microbe that causes one or more diseases. Infectious Disease - any disease that is caused by a pathogen (e.g. MRSA) Contagion – an infectious disease or infectious diseases that can be transmitted or spread from one organism to another. Carrier – an organism that is infected with and ...
Tuberculosis (TB) Fact Sheet for EMS, Public Safety, and First
... These people have a latent (inactive) infection (i.e., positive tuberculin skin test, but a normal chest x-ray and no TB symptoms) and are not infectious to others. However, in 10% of people the TB bacteria will grow and spread, causing tissue damage. People with TB disease of the lungs or airway ma ...
... These people have a latent (inactive) infection (i.e., positive tuberculin skin test, but a normal chest x-ray and no TB symptoms) and are not infectious to others. However, in 10% of people the TB bacteria will grow and spread, causing tissue damage. People with TB disease of the lungs or airway ma ...
Exotic Newcastle Disease (END) Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza
... Virus killed by extremes of pH, heat, dryness. Phenolics (eg. One Stroke Environ), oxidizing agents (eg. Virkon) and quaternary ammonium compounds (eg. Roccal-D Plus) Halogens (eg. 6% household bleach) Aldehydes in presence of organic matter Biguanides (eg. Nolvalsan-S) Dilute acids (eg. paracetic a ...
... Virus killed by extremes of pH, heat, dryness. Phenolics (eg. One Stroke Environ), oxidizing agents (eg. Virkon) and quaternary ammonium compounds (eg. Roccal-D Plus) Halogens (eg. 6% household bleach) Aldehydes in presence of organic matter Biguanides (eg. Nolvalsan-S) Dilute acids (eg. paracetic a ...
Foundations in Microbiology
... • Tick-borne • After 2-15-day incubation, patients have high fever, shaking, chills, headache, & fatigue • Progression to nausea, vomiting, muscle aches, abdominal pain; extensive damage to liver, spleen, heart, kidneys, & cranial nerves • Parasite changes & immune system tries to control it- recurr ...
... • Tick-borne • After 2-15-day incubation, patients have high fever, shaking, chills, headache, & fatigue • Progression to nausea, vomiting, muscle aches, abdominal pain; extensive damage to liver, spleen, heart, kidneys, & cranial nerves • Parasite changes & immune system tries to control it- recurr ...
Public Health England Meningitis factsheet October 2015
... • Only rarely do meningococci overcome the body's defences and cause illness. • When this does occur, the bacteria cause meningitis (infection and inflammation of the lining of the brain) and a severe condition that can spread throughout the body in the blood called septicaemia (blood poisoning). ...
... • Only rarely do meningococci overcome the body's defences and cause illness. • When this does occur, the bacteria cause meningitis (infection and inflammation of the lining of the brain) and a severe condition that can spread throughout the body in the blood called septicaemia (blood poisoning). ...
Goat Sheep Peste des Petits Ruminants FVSU
... typical microscopic lesions by histopathology. Differential diagnoses include: coccidiosis, contagious ecthyma, pasteurella pneumonia, CCPP, FMD. ...
... typical microscopic lesions by histopathology. Differential diagnoses include: coccidiosis, contagious ecthyma, pasteurella pneumonia, CCPP, FMD. ...
DISEASE NOTES
... than injury) that interferes with _____________________ _______________________, causing ________________, ____________________, or _______________ problems ...
... than injury) that interferes with _____________________ _______________________, causing ________________, ____________________, or _______________ problems ...
Fever of unknown source: Cases
... and constant abdominal pain. He has no appetite and has lost 40 lbs of weight in the last 3 months. On exam, you can palpate a large mass to his right flank. • What is the diagnosis? • What investigations would you like to do? ...
... and constant abdominal pain. He has no appetite and has lost 40 lbs of weight in the last 3 months. On exam, you can palpate a large mass to his right flank. • What is the diagnosis? • What investigations would you like to do? ...
Disease - Coach C Classes
... bacterium and virus that have been killed or weakened so it cannot cause disease. • The body recognizes these as antigens, stimulating the immune system to make antibodies to attack and kill antigen. • Memory cells are then created and if the same antigen enters the body again, these memory cells re ...
... bacterium and virus that have been killed or weakened so it cannot cause disease. • The body recognizes these as antigens, stimulating the immune system to make antibodies to attack and kill antigen. • Memory cells are then created and if the same antigen enters the body again, these memory cells re ...
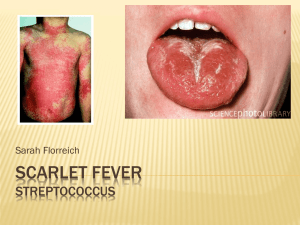
Scarlet Fever Streptococcus
... Scarlet Fever spreads the same way most diseases spread, through sneezes and coughs ...
... Scarlet Fever spreads the same way most diseases spread, through sneezes and coughs ...
Poultry Colibacillosis FVSU
... allows the E. coli access into the body. Also, subsequent to Gumboro disease, the chicken has enough immunosuppression that E. coli can gain entrance to the body. ...
... allows the E. coli access into the body. Also, subsequent to Gumboro disease, the chicken has enough immunosuppression that E. coli can gain entrance to the body. ...
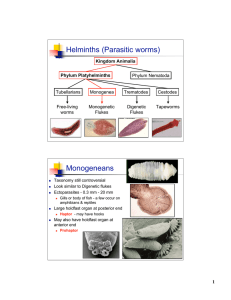
Helminths (Parasitic worms) Monogeneans
... Human infections usually come from ingestion in water or on water cress. Location in Definitive Host: Liver, particularly bile duct. ...
... Human infections usually come from ingestion in water or on water cress. Location in Definitive Host: Liver, particularly bile duct. ...
File
... ill quite suddenly, and the disease peaks rapidly in the population, such as in food poisoning. Propagated epidemics – those which are the result of direct person-to-person transmission; the microbe is spread from infected individuals to noninfected individuals. The number of infected people in th ...
... ill quite suddenly, and the disease peaks rapidly in the population, such as in food poisoning. Propagated epidemics – those which are the result of direct person-to-person transmission; the microbe is spread from infected individuals to noninfected individuals. The number of infected people in th ...
Lymphatic Filariasis
... and many Pacific islands, where 90% of the infections are caused by the Wuchereria Bancrofti parasite. Estimations suggest that of the more than 120 million people currently infected, over 30% live in Africa and 60% in Asia. India alone accounts for 40% of the global infection prevalence. Worldwide, ...
... and many Pacific islands, where 90% of the infections are caused by the Wuchereria Bancrofti parasite. Estimations suggest that of the more than 120 million people currently infected, over 30% live in Africa and 60% in Asia. India alone accounts for 40% of the global infection prevalence. Worldwide, ...
Infections
... There are ways to treat these infections. Ways to treat yeast include creams or salves. There are medicines (called “suppositories”) that can be placed in the vagina. But, if your blood sugar stays high, the infection might come back. Your doctor may give you medicine (called “antibiotics”) to fight ...
... There are ways to treat these infections. Ways to treat yeast include creams or salves. There are medicines (called “suppositories”) that can be placed in the vagina. But, if your blood sugar stays high, the infection might come back. Your doctor may give you medicine (called “antibiotics”) to fight ...
Question block created by wizard - Di-Et-Tri
... To diagnose diseases by obtaining ECGs and EEGs. To diagnose diseases by obtaining and interpreting medical images. To provide radioactive iodine to patients who suffer from thyroid disorders. To provide radiation therapy to cancer patients. vraag 3. What is meant with the term 'systemic dis ...
... To diagnose diseases by obtaining ECGs and EEGs. To diagnose diseases by obtaining and interpreting medical images. To provide radioactive iodine to patients who suffer from thyroid disorders. To provide radiation therapy to cancer patients. vraag 3. What is meant with the term 'systemic dis ...
Nosocomial Infections and Infection Control
... Anyone can get TB but some are at higher risk for developing active disease. This includes elderly (have among the highest rates) HIV infected IV drug users people in close contact with infectious TB diabetics the chronically malnourished people from countries with high TB rates peop ...
... Anyone can get TB but some are at higher risk for developing active disease. This includes elderly (have among the highest rates) HIV infected IV drug users people in close contact with infectious TB diabetics the chronically malnourished people from countries with high TB rates peop ...
Schistosomiasis

Schistosomiasis, also known as bilharzia, snail fever, and Katayama fever, is a disease caused by parasitic worms of the Schistosoma type. It may infect the urinary tract or the intestines. Signs and symptoms may include abdominal pain, diarrhea, bloody stool, or blood in the urine. In those who have been infected for a long time, liver damage, kidney failure, infertility, or bladder cancer may occur. In children it may cause poor growth and learning difficulty.The disease is spread by contact with water contaminated with the parasites. These parasites are released from infected freshwater snails. The disease is especially common among children in developing countries as they are more likely to play in contaminated water. Other high risk groups include farmers, fishermen, and people using unclean water for their daily chores. It belongs to the group of helminth infections. Diagnosis is by finding the eggs of the parasite in a person's urine or stool. It can also be confirmed by finding antibodies against the disease in the blood.Methods to prevent the disease include improving access to clean water and reducing the number of snails. In areas where the disease is common entire groups may be treated all at once and yearly with the medication praziquantel. This is done to decrease the number of people infected and therefore decrease the spread of the disease. Praziquantel is also the treatment recommended by the World Health Organization for those who are known to be infected.Schistosomiasis affects almost 210 million people worldwide, and an estimated 12,000 to 200,000 people die from it a year. The disease is most commonly found in Africa, as well as Asia and South America. Around 700 million people, in more than 70 countries, live in areas where the disease is common. Schistosomiasis is second only to malaria, as a parasitic disease with the greatest economic impact. It is classified as a neglected tropical disease.