DOPamine Hydrochloride and 5% Dextrose Injection, USP
... Dopamine is a natural catecholamine formed by the decarboxylation of 3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (DOPA). It is a precursor to norepinephrine in noradrenergic nerves and is also a neurotransmitter in certain areas of the central nervous system, especially in the nigrostriatal tract, and in a few perip ...
... Dopamine is a natural catecholamine formed by the decarboxylation of 3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (DOPA). It is a precursor to norepinephrine in noradrenergic nerves and is also a neurotransmitter in certain areas of the central nervous system, especially in the nigrostriatal tract, and in a few perip ...
Ephedrine and Other Stimulants As Ergogenic Aids
... effect on well-rested subjects is unclear, with claims of more rapid learning of new tasks, and increased physical energy, confidence, and well-being [40]. Its effects on sleep-deprived subjects are more clear, and more controversial, with regard to improved attention deployment, focus, and concentr ...
... effect on well-rested subjects is unclear, with claims of more rapid learning of new tasks, and increased physical energy, confidence, and well-being [40]. Its effects on sleep-deprived subjects are more clear, and more controversial, with regard to improved attention deployment, focus, and concentr ...
Alertness and feeding behaviors in ADHD: Does the hypocretin
... underestimated association between ADHD and abnormal eating behaviors, including binge eating. Since sleep/ alertness disturbances and eating disorders may significantly increase the functional impairment of ADHD, gaining insight into their pathophysiology as well as into their treatment is of relev ...
... underestimated association between ADHD and abnormal eating behaviors, including binge eating. Since sleep/ alertness disturbances and eating disorders may significantly increase the functional impairment of ADHD, gaining insight into their pathophysiology as well as into their treatment is of relev ...
Childhood Predictors of Adolescent Substance Use in a
... revealed that impulsivity– hyperactivity symptoms in childhood predicted later ODD symptoms in children, after controlling for prior inattention and ODD symptoms (Burns & Walsh, 2002), suggesting the prospective importance of early behavioral inhibition for the later development of problem behavior. ...
... revealed that impulsivity– hyperactivity symptoms in childhood predicted later ODD symptoms in children, after controlling for prior inattention and ODD symptoms (Burns & Walsh, 2002), suggesting the prospective importance of early behavioral inhibition for the later development of problem behavior. ...
Dopaminergic Pathways and their
... Dopamine was originally considered a precursor but by the 1950s was recognized to be pharmacologically active in its own right (for review: Blaschko, 1973). Dopamine is now accepted as a neurotransmitter in several pathways in the central nervous system and may have functional roles outside the nerv ...
... Dopamine was originally considered a precursor but by the 1950s was recognized to be pharmacologically active in its own right (for review: Blaschko, 1973). Dopamine is now accepted as a neurotransmitter in several pathways in the central nervous system and may have functional roles outside the nerv ...
Amphetamines student notes amphetaminelesson18Student
... Mental Health (NIMH). The color code shows presence of dopamine transporters. In non ADHD people, there are more transporters compared to people with ADHD. In terms of treating narcolepsy or obesity, both wakefulness and appetite suppression are experienced on many stimulants, particularly so amphet ...
... Mental Health (NIMH). The color code shows presence of dopamine transporters. In non ADHD people, there are more transporters compared to people with ADHD. In terms of treating narcolepsy or obesity, both wakefulness and appetite suppression are experienced on many stimulants, particularly so amphet ...
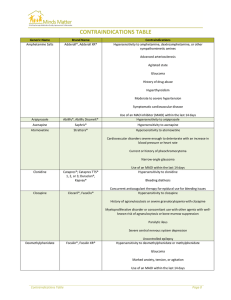
contraindications table
... hydroxyzine, zolpidem): Increase CNS depression Lithium, metoclopramide, stimulants: May enhance neurotoxic effects MAO inhibitors: May enhance orthostatic hypotensive effects Myelosuppressive medications (carbamazepine): May increase risk for bone marrow suppression ...
... hydroxyzine, zolpidem): Increase CNS depression Lithium, metoclopramide, stimulants: May enhance neurotoxic effects MAO inhibitors: May enhance orthostatic hypotensive effects Myelosuppressive medications (carbamazepine): May increase risk for bone marrow suppression ...
Adderall (amphetamine)
... Amphetamine and dextroamphetamine are known to produce euphoria (feeling high), increased energy, and wakefulness, which carry a potential for abuse (using more than prescribed to feel high). This potential for abuse has caused amphetamine medications to become highly regulated in the United States. ...
... Amphetamine and dextroamphetamine are known to produce euphoria (feeling high), increased energy, and wakefulness, which carry a potential for abuse (using more than prescribed to feel high). This potential for abuse has caused amphetamine medications to become highly regulated in the United States. ...
Stimulants - Australian Indigenous HealthInfoNet
... as sugar, baking soda, or cheaper drugs. This is done to maximise profit. The following list shows the usual characteristics of the main stimulants sold in Australia. • Ecstasy (MDMA): usually comes as tablets but also in capsules or powder. The colour of the powder ranges from white to yellow to b ...
... as sugar, baking soda, or cheaper drugs. This is done to maximise profit. The following list shows the usual characteristics of the main stimulants sold in Australia. • Ecstasy (MDMA): usually comes as tablets but also in capsules or powder. The colour of the powder ranges from white to yellow to b ...
Amphetamine-induced release of dopamine from the substantia
... dissected bilaterally by knife cuts made just caudal to the mammillary bodies, just rostral to the pons, lateral to the interpeduncular nucleus, and along a line extending through the medial lemniscus to the lateral edge of the brain stem ventral to the medial geniculate. Included in the sample were ...
... dissected bilaterally by knife cuts made just caudal to the mammillary bodies, just rostral to the pons, lateral to the interpeduncular nucleus, and along a line extending through the medial lemniscus to the lateral edge of the brain stem ventral to the medial geniculate. Included in the sample were ...
Neuroimaging and ADHD: fMRI, PET, DTI Findings, and
... including fronto-striatal, fronto-parietal, fronto-cerebellar, fronto-striato-parieto-cerebellar, and fronto-temporal circuitry (Nigg & Casey, 2005; Rubia et al., 2009a, 2009b; Schneider et al., 2010; Silk, Vance, Rinehart, Bradshaw, & Cunnington, 2008). In addition to circuitry, specific structures ...
... including fronto-striatal, fronto-parietal, fronto-cerebellar, fronto-striato-parieto-cerebellar, and fronto-temporal circuitry (Nigg & Casey, 2005; Rubia et al., 2009a, 2009b; Schneider et al., 2010; Silk, Vance, Rinehart, Bradshaw, & Cunnington, 2008). In addition to circuitry, specific structures ...
Strattera (atomoxetine)
... The effects of Strattera overdose are not fully known, because this medication was only recently introduced and clinical experience is limited. It is probably less dangerous in overdose than tricyclic and monoamine oxidase inhibitor antidepressants. Any suspected overdose should be treated as an eme ...
... The effects of Strattera overdose are not fully known, because this medication was only recently introduced and clinical experience is limited. It is probably less dangerous in overdose than tricyclic and monoamine oxidase inhibitor antidepressants. Any suspected overdose should be treated as an eme ...
Characterizing cognition in ADHD: beyond executive dysfunction
... challenges the Stop task’s assumption of SSRT invariance and undermines the feasibility of using a tracking procedure to establish appropriate interval between Stop and Go signals to produce equal proportions of successful and failed inhibitions [18]. More generally, the Stop task imposes subtle but ...
... challenges the Stop task’s assumption of SSRT invariance and undermines the feasibility of using a tracking procedure to establish appropriate interval between Stop and Go signals to produce equal proportions of successful and failed inhibitions [18]. More generally, the Stop task imposes subtle but ...
Monoaminergic dysfunction in recreational users of
... National Adult Reading Test (Nelson, 1982). It is relatively insensitive to cognitive deterioration due to neurologic disorders and was used to evaluate the premorbid IQ. We selected five domains sensitive to DAergic function: executive function, attention, memory, mood and impulsivity. Tests were ad ...
... National Adult Reading Test (Nelson, 1982). It is relatively insensitive to cognitive deterioration due to neurologic disorders and was used to evaluate the premorbid IQ. We selected five domains sensitive to DAergic function: executive function, attention, memory, mood and impulsivity. Tests were ad ...
PET Imaging Studies - Office of Scientific and Technical Information
... shorter the time between the administration of a drug and its behavioral effects, the more intense the behavioral stimulation (Balster and Schuster, 1973). Cocaine exists in two enantiomers, (-)-cocaine which is the natural product and (+)cocaine which is produced synthetically. Only-(-)-cocaine is ...
... shorter the time between the administration of a drug and its behavioral effects, the more intense the behavioral stimulation (Balster and Schuster, 1973). Cocaine exists in two enantiomers, (-)-cocaine which is the natural product and (+)cocaine which is produced synthetically. Only-(-)-cocaine is ...
Differential Influences of Ethanol on Early Exposure to Racemic
... unchanged (LeVasseur et al., 2008). Both the hydrolysis of dl-MPH to ritalinic acid and the transesterification with ethanol to yield l-EPH are primarily catalyzed by hepatic CES1 (Bourland et al., 1997; Sun et al., 2004; Zhu et al., 2008; 2009). Presystemic hydrolysis of oral dlMPH results in the r ...
... unchanged (LeVasseur et al., 2008). Both the hydrolysis of dl-MPH to ritalinic acid and the transesterification with ethanol to yield l-EPH are primarily catalyzed by hepatic CES1 (Bourland et al., 1997; Sun et al., 2004; Zhu et al., 2008; 2009). Presystemic hydrolysis of oral dlMPH results in the r ...
Modafinil - North East Sleep Society
... 150 - 500 mg/day Moderate efficacy, long half life Best side effect profile Schedule IV, most expensive Methylphenidate 5 - 100 mg/day Short half life formulation, variable dosing Used alone or in combination Sympathomimetic effects, mood alterations ...
... 150 - 500 mg/day Moderate efficacy, long half life Best side effect profile Schedule IV, most expensive Methylphenidate 5 - 100 mg/day Short half life formulation, variable dosing Used alone or in combination Sympathomimetic effects, mood alterations ...
AHA Scientific Statement
... included cardiac structural abnormalities such as aberrant origin of coronary artery, idiopathic hypertrophic subaortic stenosis, bicuspid aortic valve, and cardiac hypertrophy. Other factors listed were unexplained increased or toxic amphetamine level, family history of ventricular arrhythmia, and ...
... included cardiac structural abnormalities such as aberrant origin of coronary artery, idiopathic hypertrophic subaortic stenosis, bicuspid aortic valve, and cardiac hypertrophy. Other factors listed were unexplained increased or toxic amphetamine level, family history of ventricular arrhythmia, and ...
Temporal reproduction and its neuroanatomical correlates in adults
... Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is one of the most common neuropsychiatric disorders in childhood and adolescence (Kieling et al., 2010) and is one of the most underdiagnosed psychiatric disorders in adults (Faraone, 2007). It is defined with age inappropriate symptoms of hyperactivi ...
... Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is one of the most common neuropsychiatric disorders in childhood and adolescence (Kieling et al., 2010) and is one of the most underdiagnosed psychiatric disorders in adults (Faraone, 2007). It is defined with age inappropriate symptoms of hyperactivi ...
MEDICAL OPTIONS FOR PARKINSON`S
... occur if a chest or urinary tract infection is present. Medical review is recommended. Dyskinesia (involuntary movements) may develop with long term levodopa therapy. This can occur at various times in the drug cycle, for example, peak dose or end of dose. Adjustment of medication may be made by you ...
... occur if a chest or urinary tract infection is present. Medical review is recommended. Dyskinesia (involuntary movements) may develop with long term levodopa therapy. This can occur at various times in the drug cycle, for example, peak dose or end of dose. Adjustment of medication may be made by you ...
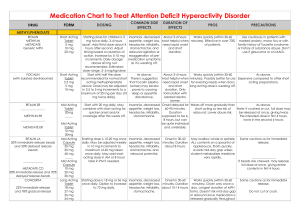
ADD-ADHD_Medication_..
... and gaps in coverage. hypertension, tachycardia, or to one week, but cardiovascular or cerebrovascular full effect may not Doesn't cause a "high," thus it disease because it can increase be evident for a does not lead to abuse, and so blood pressure and heart rate. Has month or more. a) it is not a ...
... and gaps in coverage. hypertension, tachycardia, or to one week, but cardiovascular or cerebrovascular full effect may not Doesn't cause a "high," thus it disease because it can increase be evident for a does not lead to abuse, and so blood pressure and heart rate. Has month or more. a) it is not a ...
Carlisi_preprint_revisions2
... subjects, underpinned by reduced fronto-striato-limbic activation. This study tested whether a single acute dose of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) fluoxetine upregulates and normalises reduced fronto-striato-limbic neurofunctional activation in ADHD during TD. Methods Twelve boys ...
... subjects, underpinned by reduced fronto-striato-limbic activation. This study tested whether a single acute dose of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) fluoxetine upregulates and normalises reduced fronto-striato-limbic neurofunctional activation in ADHD during TD. Methods Twelve boys ...
Neurobiology of ADHD Gail Tripp , Review
... 3.1. Executive functions Executive functions may be defined as ‘‘neurocognitive processes that maintain an appropriate problem-solving set to attain a later goal’’ (Willcutt et al., 2005). There is good evidence of impairment in a variety of executive function measures amongst groups of children with ...
... 3.1. Executive functions Executive functions may be defined as ‘‘neurocognitive processes that maintain an appropriate problem-solving set to attain a later goal’’ (Willcutt et al., 2005). There is good evidence of impairment in a variety of executive function measures amongst groups of children with ...
Methylphenidate
Methylphenidate (trade names Concerta, Methylin, Medikinet, Ritalin, Equasym XL, Quillivant XR, Metadate) is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant of the phenethylamine and piperidine classes that is used in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and narcolepsy. Methylphenidate has been studied and researched for over 50 years and has a very good efficacy and safety record for the treatment of ADHD. The original patent was owned by CIBA, now Novartis Corporation. It was first licensed by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1955 for treating what was then known as hyperactivity.Prescribed to patients beginning in 1960, the drug has become increasingly prescribed since the 1990s, when the diagnosis of ADHD itself became more widely accepted. Between 2007 and 2012 methylphenidate prescriptions increased by 50% in Britain and in 2013 global methylphenidate consumption increased to 2.4 billion doses, a 66% increase compared to the year before. The US continues to account for more than 80% of global consumption.ADHD and other similar conditions are believed to be linked to sub-performance of the dopamine and norepinephrine functions in the brain, primarily in the prefrontal cortex, responsible for self-regulatory function (e.g., inhibition, motivation, and memory) and executive function (e.g., reasoning, organizing, problem solving, and planning). Methylphenidate's mechanism of action involves the inhibition of catecholamine reuptake, primarily as a dopamine reuptake inhibitor. Methylphenidate acts by blocking the dopamine transporter and norepinephrine transporter, leading to increased concentrations of dopamine and norepinephrine within the synaptic cleft. This effect in turn leads to increased neurotransmission of dopamine and norepinephrine. Methylphenidate is also a 5HT1A receptor agonist.