What are HIV and AIDS - United Blood Services for Hospitals
... If untreated, patients with AIDS will die of their infection. How is HIV spread? HIV is present in an infected person’s body fluids such as blood, semen, and vaginal secretions. The virus is spread through: Unprotected sex Exposure to the blood of infected persons Sharing contaminated needles ...
... If untreated, patients with AIDS will die of their infection. How is HIV spread? HIV is present in an infected person’s body fluids such as blood, semen, and vaginal secretions. The virus is spread through: Unprotected sex Exposure to the blood of infected persons Sharing contaminated needles ...
Measles
... abdominal pain, vomiting, diarrhea, and myalgia the characteristic rash of measles is a consequence of the cellular immune response, it may not develop in persons with impaired cellular immunity (e.g., those with AIDS). These persons have a high case-fatality rate and frequently develop giant-cell ...
... abdominal pain, vomiting, diarrhea, and myalgia the characteristic rash of measles is a consequence of the cellular immune response, it may not develop in persons with impaired cellular immunity (e.g., those with AIDS). These persons have a high case-fatality rate and frequently develop giant-cell ...
Powerpoint Integumentary
... Compare skin differences Infant: skin not mature at birth Adolescence: sebaceous glands become ...
... Compare skin differences Infant: skin not mature at birth Adolescence: sebaceous glands become ...
The Human Body in Health and Illness
... • Disease: failure of the body to function normally • Pathogens: disease-producing microorganisms • Infection: invasion of the body by a pathogen – Localized: restricted to a small area – Systemic: more widespread; usually spread through blood ...
... • Disease: failure of the body to function normally • Pathogens: disease-producing microorganisms • Infection: invasion of the body by a pathogen – Localized: restricted to a small area – Systemic: more widespread; usually spread through blood ...
Basic Microbiology: Understanding Your Enemies
... conditions) Incubation Time: dependant on infection (Ex. eye infection 24 – 72hrs) Transmission by direct contact with ...
... conditions) Incubation Time: dependant on infection (Ex. eye infection 24 – 72hrs) Transmission by direct contact with ...
Antibiotics - dr chohan`s ent day surgery
... – Prolonged period (3-6 weeks) shown more effective ...
... – Prolonged period (3-6 weeks) shown more effective ...
Clostridial Disease Enzootic abortion
... for long periods of time in soil, becoming active again if the correct conditions arise. Outbreaks of disease are often triggered by factors such as changes in management, parasitic activity and traumatic injury. Once infected animals deteriorate rapidly and are often found dead before any clinical ...
... for long periods of time in soil, becoming active again if the correct conditions arise. Outbreaks of disease are often triggered by factors such as changes in management, parasitic activity and traumatic injury. Once infected animals deteriorate rapidly and are often found dead before any clinical ...
Mycobacterium abscessus Infections among “Lipotourists” from the United
... abdominoplasty, which may cost $5000–$7000 in the United States [14], costs $1500-$2000 (in US dollars) in the Dominican Republic [13]. Familiarity with a country and its culture and language likely influences a person’s decision regarding which country he or she visits for the surgery. Only limited ...
... abdominoplasty, which may cost $5000–$7000 in the United States [14], costs $1500-$2000 (in US dollars) in the Dominican Republic [13]. Familiarity with a country and its culture and language likely influences a person’s decision regarding which country he or she visits for the surgery. Only limited ...
Proctitis
... Proctitis is defined as an inflammatory syndrome of the distal 10–12 cm of the anal canal, also called the rectum. Infectious proctitis can be sexually transmitted via genital-anal mucosal contact, but some also via mutual masturbation. N. gonorrhoeae, C. trachomatis (including lymphogranuloma vener ...
... Proctitis is defined as an inflammatory syndrome of the distal 10–12 cm of the anal canal, also called the rectum. Infectious proctitis can be sexually transmitted via genital-anal mucosal contact, but some also via mutual masturbation. N. gonorrhoeae, C. trachomatis (including lymphogranuloma vener ...
C-Diff Flier (PDF)
... colon inflammation and deadly diarrhea. This is your opportunity to work with state and national experts on a Quality Assurance Performance Improvement (QAPI) initiative to prevent and reduce C. difficile in nursing homes. The initiative will support nursing home submission of data into CDC’s Nation ...
... colon inflammation and deadly diarrhea. This is your opportunity to work with state and national experts on a Quality Assurance Performance Improvement (QAPI) initiative to prevent and reduce C. difficile in nursing homes. The initiative will support nursing home submission of data into CDC’s Nation ...
Reproductive Diseases in Cattle
... Produced by Agricultural Communications, The Texas A&M University System Educational programs of the Texas Agricultural Extension Service are open to all people without regard to race, color, sex, disability, religion, age or national origin. Issued in furtherance of Cooperative Extension Work in Ag ...
... Produced by Agricultural Communications, The Texas A&M University System Educational programs of the Texas Agricultural Extension Service are open to all people without regard to race, color, sex, disability, religion, age or national origin. Issued in furtherance of Cooperative Extension Work in Ag ...
Pink Eye
... care, school, or work when symptoms begin to improve, typically in 3 to 5 days. Medications are not usually used to treat viral pinkeye, so it is important to prevent the spread of the infection. Pinkeye caused by a herpes virus, which is rare, can be treated with an antiviral medication. Home treat ...
... care, school, or work when symptoms begin to improve, typically in 3 to 5 days. Medications are not usually used to treat viral pinkeye, so it is important to prevent the spread of the infection. Pinkeye caused by a herpes virus, which is rare, can be treated with an antiviral medication. Home treat ...
Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene
... Michigan mixtures of the nanoemulsion with either whole virus or protein have been tested as potential vaccines. Such vaccines, which do not require cold storage and can be administered via the mucosal route, are particularly suitable for applications in developing countries. Cross Infection Control ...
... Michigan mixtures of the nanoemulsion with either whole virus or protein have been tested as potential vaccines. Such vaccines, which do not require cold storage and can be administered via the mucosal route, are particularly suitable for applications in developing countries. Cross Infection Control ...
Click to edit Master title style Hepatitis B Click to edit Master title style
... Click to edit Master title style All children should get their first dose of Hepatitis B vaccine at birth and complete the vaccine series by 6– 18 months of age. All children and adolescents younger than 19 years of age who have not yet gotten the vaccine should also be vaccinated. "Catch-up" v ...
... Click to edit Master title style All children should get their first dose of Hepatitis B vaccine at birth and complete the vaccine series by 6– 18 months of age. All children and adolescents younger than 19 years of age who have not yet gotten the vaccine should also be vaccinated. "Catch-up" v ...
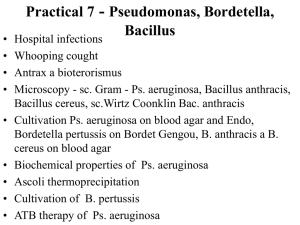
Bez nadpisu - Comenius University
... • Hospital infection - infection, that arises in connection to hospitalisation or to diagnostical, therapeutic or preventive processes. I does not necessary have to present during the hospitalisation and not every infection arising during hospitalisation is nosocomial • Risk factors - age,accompanyi ...
... • Hospital infection - infection, that arises in connection to hospitalisation or to diagnostical, therapeutic or preventive processes. I does not necessary have to present during the hospitalisation and not every infection arising during hospitalisation is nosocomial • Risk factors - age,accompanyi ...
A4 IAI - Pharm D Notes
... Gram-negative bacilli Gram-positive cocci • Healthcare Associated – common bacteria are still implicated, but a shift to other gram-negative Escherichia coli Streptococci bacteria such as Enterobacter, Pseudomonas, Klebsiella species Enterococci Staph. Aureus, and Enterococci (existing within Proteu ...
... Gram-negative bacilli Gram-positive cocci • Healthcare Associated – common bacteria are still implicated, but a shift to other gram-negative Escherichia coli Streptococci bacteria such as Enterobacter, Pseudomonas, Klebsiella species Enterococci Staph. Aureus, and Enterococci (existing within Proteu ...
Hospital for Tropical Diseases powerpoint template
... Youngest infants (immunise mothers) Teenagers (waning immunity) ...
... Youngest infants (immunise mothers) Teenagers (waning immunity) ...
MRSA - INTEGRIS Health
... MRSA is a germ, Staphylococcus aureus, which does not respond to some antibiotics. It is sometimes called a “super bug”. This means that the infection may be more difficult to treat. ...
... MRSA is a germ, Staphylococcus aureus, which does not respond to some antibiotics. It is sometimes called a “super bug”. This means that the infection may be more difficult to treat. ...
Health Center 21 – Bloodborne Pathogens Using the Bloodborne
... 7. How does the Ryan White CARE Act help patients with HIV or AIDS? 8. How does the Americans with Disabilities Act help patients with HIV or AIDS? 9. What is hepatitis? 10. What type of pathogen causes hepatitis? 11. How is each of the following types of hepatitis transmitted? a. Hepatitis A: b. He ...
... 7. How does the Ryan White CARE Act help patients with HIV or AIDS? 8. How does the Americans with Disabilities Act help patients with HIV or AIDS? 9. What is hepatitis? 10. What type of pathogen causes hepatitis? 11. How is each of the following types of hepatitis transmitted? a. Hepatitis A: b. He ...
Immunodeficiencies
... infections, autoimunity, SLE–like syndrome • C6, C7, C8, C9 – SLE–like syndrome, increased susceptibility to neisserial infections • MBL deficiency – mannan binding lectin (lectin way of complement activation), various infections, susceptibility to autoimmunity, association with allergy. ...
... infections, autoimunity, SLE–like syndrome • C6, C7, C8, C9 – SLE–like syndrome, increased susceptibility to neisserial infections • MBL deficiency – mannan binding lectin (lectin way of complement activation), various infections, susceptibility to autoimmunity, association with allergy. ...
Pobierz
... years 1980–1992. The results of these studies showed a reduction in the incidence of preterm births as a result of topical treatment with clotrimazole and lack of teratogenic effects of this drug [74,75]. Also in 1999 in Denmark it was demonstrated that fluconazole administered to women in a single ...
... years 1980–1992. The results of these studies showed a reduction in the incidence of preterm births as a result of topical treatment with clotrimazole and lack of teratogenic effects of this drug [74,75]. Also in 1999 in Denmark it was demonstrated that fluconazole administered to women in a single ...
Malaria and HIV/AIDS
... HIV prevalence, the incidence of TB infection is increased, with a resultant increase in mortality. In addition, susceptibility to HIV can be increased by other infections, notably sexually transmitted infections (STIs), leading to high rates of HIV transmission in communities with high prevalence o ...
... HIV prevalence, the incidence of TB infection is increased, with a resultant increase in mortality. In addition, susceptibility to HIV can be increased by other infections, notably sexually transmitted infections (STIs), leading to high rates of HIV transmission in communities with high prevalence o ...
Chillies
... Mode of spread Survives in the soil in host debris Roots, stems, and mummified fruits left in the field after harvest, harbor the pathogen for months Phytophthora capsici is also seed borne ...
... Mode of spread Survives in the soil in host debris Roots, stems, and mummified fruits left in the field after harvest, harbor the pathogen for months Phytophthora capsici is also seed borne ...
Focal Bacterial Infections
... a direct toxic effect of retained bile or because of ischemia related to elevated intraluminal pressure. Bacterial invasion by fecal flora is probably a secondary phenomenon.76,77 Other organisms that have been isolated from gallbladder contents or tissue include Serratia marcescens, Pseudomonas spp ...
... a direct toxic effect of retained bile or because of ischemia related to elevated intraluminal pressure. Bacterial invasion by fecal flora is probably a secondary phenomenon.76,77 Other organisms that have been isolated from gallbladder contents or tissue include Serratia marcescens, Pseudomonas spp ...