Document
... side of the figure indicate the direction in which the particles and the collected :mass travel. IndividuaI'particles may be seen to travel at an angle across the bars, i.e. in a ventro-dorsal direction, as is indicated also by the arrows. The mechanism which causes the :movementof these partIcles a ...
... side of the figure indicate the direction in which the particles and the collected :mass travel. IndividuaI'particles may be seen to travel at an angle across the bars, i.e. in a ventro-dorsal direction, as is indicated also by the arrows. The mechanism which causes the :movementof these partIcles a ...
Ascaris- Script Objective Summary FAQs QUIZ HOME Video Index
... and it respires anaerobically by glycolysis. It is also able to consume free oxygen in the host’s intestine. 5. Excretory System: In Ascaris, the excretory system is simple and H-shaped. There is a longitudinal excretory canal in each lateral side. The anterior limbs of the H are reduced. Transverse ...
... and it respires anaerobically by glycolysis. It is also able to consume free oxygen in the host’s intestine. 5. Excretory System: In Ascaris, the excretory system is simple and H-shaped. There is a longitudinal excretory canal in each lateral side. The anterior limbs of the H are reduced. Transverse ...
Squid Lab Outreach Teacher Booklet Sept 2004.qxd
... The organs of digestion in squid include the jaws, radula, salivary glands, esophagus, liver, stomach, intestine, and anus. Squid typically eat twice a day. Food is grasped in the horny jaws and gripped by the radula, which is like a tongue with teeth. The radula transfers the food to the throat, fr ...
... The organs of digestion in squid include the jaws, radula, salivary glands, esophagus, liver, stomach, intestine, and anus. Squid typically eat twice a day. Food is grasped in the horny jaws and gripped by the radula, which is like a tongue with teeth. The radula transfers the food to the throat, fr ...
Squid Lab - National Aquarium
... The organs of digestion in squid include the jaws, radula, salivary glands, esophagus, liver, stomach, intestine and anus. Squid typically eat twice a day. Food is grasped in the horny jaws and gripped by the radula, which is like a tongue with teeth. The radula transfers the food to the throat, fro ...
... The organs of digestion in squid include the jaws, radula, salivary glands, esophagus, liver, stomach, intestine and anus. Squid typically eat twice a day. Food is grasped in the horny jaws and gripped by the radula, which is like a tongue with teeth. The radula transfers the food to the throat, fro ...
galathea-vol.03-pp_009-072
... Laterally to the foot, five pairs of gills are placed at regular intervals in the pallial groove, their original shape having been much disturbed during capture and preservation (Figs. 7, 12). The first pair of gills is situated at a slightly greater distance from the tentacle tufts than from the se ...
... Laterally to the foot, five pairs of gills are placed at regular intervals in the pallial groove, their original shape having been much disturbed during capture and preservation (Figs. 7, 12). The first pair of gills is situated at a slightly greater distance from the tentacle tufts than from the se ...
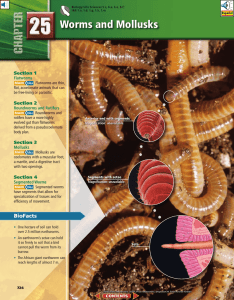
Chapter 25: Worms and Mollusks
... prey. Then food particles are sucked into the digestive tract where digestion continues. Because flatworms have only one body opening, wastes are ejected through the mouth. Parasitic flatworms have modified feeding structures called hooks and suckers, which enable them to stay attached to their host ...
... prey. Then food particles are sucked into the digestive tract where digestion continues. Because flatworms have only one body opening, wastes are ejected through the mouth. Parasitic flatworms have modified feeding structures called hooks and suckers, which enable them to stay attached to their host ...
Notes - Uintah High School FFA Chapter
... leg each time the frog makes contact with the ground. The blood flows down the horse's leg into the digital cushion, a fibrous part of the inner hoof located just above the frog which contains a network of blood vessels. The horse's weight then compresses the frog on the ground, squeezing the blood ...
... leg each time the frog makes contact with the ground. The blood flows down the horse's leg into the digital cushion, a fibrous part of the inner hoof located just above the frog which contains a network of blood vessels. The horse's weight then compresses the frog on the ground, squeezing the blood ...
Lecture 13a - BlakeMathys.com
... – Monogeneans, Trematodes, Tapeworms Live in intestine: no mouth Up to 0 Up to 20m ...
... – Monogeneans, Trematodes, Tapeworms Live in intestine: no mouth Up to 0 Up to 20m ...
Chapter 25 Worms and Mollusks
... shown in Figure 25.2, releases enzymes that begin the digestion of prey. Then food particles are sucked into the digestive tract where digestion continues. Because flatworms have only one body opening, wastes are ejected through the mouth. Parasitic flatworms have modified feeding structures called ...
... shown in Figure 25.2, releases enzymes that begin the digestion of prey. Then food particles are sucked into the digestive tract where digestion continues. Because flatworms have only one body opening, wastes are ejected through the mouth. Parasitic flatworms have modified feeding structures called ...
Body Structure - davis.k12.ut.us
... Have bilateral symmetry, a soft internal body, a digestive tract with two openings, a muscular foot, and a mantle – a membrane that surrounds the internal organs ...
... Have bilateral symmetry, a soft internal body, a digestive tract with two openings, a muscular foot, and a mantle – a membrane that surrounds the internal organs ...
Plates 41 to 56
... nerves passing to these organs are not particularly marked. Graphic reconstruction. Spec. 111. Fig. 137. The relation between the nervous system and the musculature in the anterior body region. Only muscles associated with the ventral body wall are ...
... nerves passing to these organs are not particularly marked. Graphic reconstruction. Spec. 111. Fig. 137. The relation between the nervous system and the musculature in the anterior body region. Only muscles associated with the ventral body wall are ...
27-4 Mollusks - Hamilton Local Schools
... Mollusks are soft-bodied animals that usually have an internal or external shell. Mollusks include snails, slugs, clams, squids, and octopi. Many mollusks share similar developmental ...
... Mollusks are soft-bodied animals that usually have an internal or external shell. Mollusks include snails, slugs, clams, squids, and octopi. Many mollusks share similar developmental ...
bYTEBoss
... • Segmented worms have simple nervous systems in which organs in anterior segments have become modified for sensing the environment. • Some sensory organs are sensitive to light, and eyes with lenses and retinas have evolved in certain species. ...
... • Segmented worms have simple nervous systems in which organs in anterior segments have become modified for sensing the environment. • Some sensory organs are sensitive to light, and eyes with lenses and retinas have evolved in certain species. ...
Chapter 27 BDOL IC
... • Segmented worms have simple nervous systems in which organs in anterior segments have become modified for sensing the environment. • Some sensory organs are sensitive to light, and eyes with lenses and retinas have evolved in certain species. ...
... • Segmented worms have simple nervous systems in which organs in anterior segments have become modified for sensing the environment. • Some sensory organs are sensitive to light, and eyes with lenses and retinas have evolved in certain species. ...
Visceral Manip lation Visceral Manipulation
... described treating many different digestive, respiratory and urogenital complaints . For Dr Still, almost all medical conditions had an osteopathic treatment, in some cases curative, in some cases supportive. Dr Still left few descriptions of techniques of any kind, but some of his early students, C ...
... described treating many different digestive, respiratory and urogenital complaints . For Dr Still, almost all medical conditions had an osteopathic treatment, in some cases curative, in some cases supportive. Dr Still left few descriptions of techniques of any kind, but some of his early students, C ...
Exercise 4 Bivalve Anatomy I
... Look at the visceral mass lying between you and the left gill. It is elongated along its anteroposterior axis and is compressed from side to side. Look through the body wall for the large, dark brown digestive cecum, which occupies most of the space in the anterior visceral mass. It is located immed ...
... Look at the visceral mass lying between you and the left gill. It is elongated along its anteroposterior axis and is compressed from side to side. Look through the body wall for the large, dark brown digestive cecum, which occupies most of the space in the anterior visceral mass. It is located immed ...
Investigating Animal Diversity
... Figure 1 can be used to show the usefulness of these cladistic ideas. Let’s assume that you were given data about an unknown organism that met the criteria for being an animal. You are asked to assign it to one of the ten major clades you will study in this course. Figure 20.1 tells you that you sh ...
... Figure 1 can be used to show the usefulness of these cladistic ideas. Let’s assume that you were given data about an unknown organism that met the criteria for being an animal. You are asked to assign it to one of the ten major clades you will study in this course. Figure 20.1 tells you that you sh ...
Organs or Respiration in animals
... During summer months, when it is hot and dry, frogs make burrows deep into the soil and live in burrows. This is called aestivation or summer sleep. Winter sleep/Hibernation: During several winter months when temperature is too less frog makes burrows deep into soil and live in the burrows. This is ...
... During summer months, when it is hot and dry, frogs make burrows deep into the soil and live in burrows. This is called aestivation or summer sleep. Winter sleep/Hibernation: During several winter months when temperature is too less frog makes burrows deep into soil and live in the burrows. This is ...
Light and Scanning Electron Microscope Studies of
... the surrounding tissue. The bar does not have spines but is pitted at its apex. In unextended specimens the bar is positioned in such a way that its lateral regions could exert passive pressure on the roots of the hamuli. In this position it might stabilize these sclerites while allowing greater fre ...
... the surrounding tissue. The bar does not have spines but is pitted at its apex. In unextended specimens the bar is positioned in such a way that its lateral regions could exert passive pressure on the roots of the hamuli. In this position it might stabilize these sclerites while allowing greater fre ...
Cephalopods - Cloudfront.net
... • Cephalopods exchange gasses with the seawater by forcing water through their gills, which are attached to the roof of the organism. • Water enters the mantle cavity on the outside of the gills, and the entrance of the mantle cavity closes. When the mantle contracts, water is forced through the gil ...
... • Cephalopods exchange gasses with the seawater by forcing water through their gills, which are attached to the roof of the organism. • Water enters the mantle cavity on the outside of the gills, and the entrance of the mantle cavity closes. When the mantle contracts, water is forced through the gil ...
Abalone - Two Oceans Aquarium
... is one of the country’s newer commercial fisheries, having started in the early 1980s, when squid became sought after as the restaurant delicacy, calamari. The fishery is based on the chokka or long-finned squid, Loligo vulgaris reynaudii, which is caught by handline, using a lure called a jig, when ...
... is one of the country’s newer commercial fisheries, having started in the early 1980s, when squid became sought after as the restaurant delicacy, calamari. The fishery is based on the chokka or long-finned squid, Loligo vulgaris reynaudii, which is caught by handline, using a lure called a jig, when ...
Scaly-foot gastropod

Chrysomallon squamiferum, common name the scaly-foot gastropod, is a species of deep-sea hydrothermal vent snail, a marine gastropod mollusc in the family Peltospiridae.According to WoRMS, ""the name Chrysomallon or Crysomallon squamiferum was used in several databases and academic papers prior to 2015. However, the name was first validly published in the sense of the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature by Chen et al. (2015)"".