slides
... is in the spectrum. One can make use of the ambiguity of discretization to either have zero in the spectrum or to minimize the eigenvalue of the fundamental state. We use this as criterion for choosing the best discretization possible. In this model the best discretization would be the Abelian one w ...
... is in the spectrum. One can make use of the ambiguity of discretization to either have zero in the spectrum or to minimize the eigenvalue of the fundamental state. We use this as criterion for choosing the best discretization possible. In this model the best discretization would be the Abelian one w ...
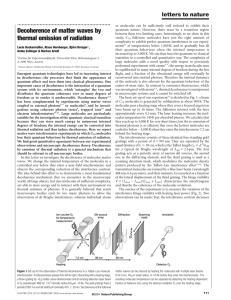
Decoherence of matter waves by thermal emission of radiation
... emission of thermal photons that carry ‘which-path’ information. Second, we notice that the count rate also varies considerably. This is explained by the dependence of the ionization efficiency in the detector D2 on the internal energy of the fullerenes. It proves that much internal energy remains i ...
... emission of thermal photons that carry ‘which-path’ information. Second, we notice that the count rate also varies considerably. This is explained by the dependence of the ionization efficiency in the detector D2 on the internal energy of the fullerenes. It proves that much internal energy remains i ...
Testing Wavefunction Collapse
... an empirical test. Bohm [3] took the view that for the present it is not possible to distinguish the various interpretations because they are contrived to reproduce the same set of quantal predictions. This conviction may be unduly pessimistic because there exist what appear to be physically meaning ...
... an empirical test. Bohm [3] took the view that for the present it is not possible to distinguish the various interpretations because they are contrived to reproduce the same set of quantal predictions. This conviction may be unduly pessimistic because there exist what appear to be physically meaning ...
Quantum Measurements with Dynamically Bistable Systems
... The dynamic bistability of the oscillator is advantageous for measurements. The idea is to make the oscillator switch between the states depending on the value of the parameter to be measured. Switching leads to a strong change in the system that can be easily detected, leading to a high signal-to-n ...
... The dynamic bistability of the oscillator is advantageous for measurements. The idea is to make the oscillator switch between the states depending on the value of the parameter to be measured. Switching leads to a strong change in the system that can be easily detected, leading to a high signal-to-n ...
CASYS'09 Computing Anticipatory Systems
... Completely separating mathematics from mathematical language and hence from the phenomena of language described by theoretical logic, recognizing that intuitionistic mathematics is an essentially languageless activity of the mind having its origin in the perception of a motion of time. This percepti ...
... Completely separating mathematics from mathematical language and hence from the phenomena of language described by theoretical logic, recognizing that intuitionistic mathematics is an essentially languageless activity of the mind having its origin in the perception of a motion of time. This percepti ...
Complete Axiomatizations for Quantum Actions
... U P (while the transitions → are arbitrarily chosen binary relations on Σ). The “measurement relation” is simply the identity s = t, and thus two states are “orthogonal” iff they are distinct, so ∼ S = Σ \ S is the complement and ∼∼ S = S. This example shows that classical P DL encodes a classical n ...
... U P (while the transitions → are arbitrarily chosen binary relations on Σ). The “measurement relation” is simply the identity s = t, and thus two states are “orthogonal” iff they are distinct, so ∼ S = Σ \ S is the complement and ∼∼ S = S. This example shows that classical P DL encodes a classical n ...
PDF - Series: APPLIED MATHEMATICS, MECHANICS, and
... and 'pull' of the longitudinal EMW waves amplitude, and similarly respective, electric and magnetic vectors. This brings up, in these EVTD2 volumes, quanta of very strong energies resulting from space substrate vibration. This latter is referred to as Substratum that, for its positive and negative p ...
... and 'pull' of the longitudinal EMW waves amplitude, and similarly respective, electric and magnetic vectors. This brings up, in these EVTD2 volumes, quanta of very strong energies resulting from space substrate vibration. This latter is referred to as Substratum that, for its positive and negative p ...
BEC and optical lattices
... Centre for Quantum Physics & Technology, Clarendon Laboratory, University of Oxford. ...
... Centre for Quantum Physics & Technology, Clarendon Laboratory, University of Oxford. ...
Quantum key distribution
Quantum key distribution (QKD) uses quantum mechanics to guarantee secure communication. It enables two parties to produce a shared random secret key known only to them, which can then be used to encrypt and decrypt messages. It is often incorrectly called quantum cryptography, as it is the most well known example of the group of quantum cryptographic tasks.An important and unique property of quantum key distribution is the ability of the two communicating users to detect the presence of any third party trying to gain knowledge of the key. This results from a fundamental aspect of quantum mechanics: the process of measuring a quantum system in general disturbs the system. A third party trying to eavesdrop on the key must in some way measure it, thus introducing detectable anomalies. By using quantum superpositions or quantum entanglement and transmitting information in quantum states, a communication system can be implemented which detects eavesdropping. If the level of eavesdropping is below a certain threshold, a key can be produced that is guaranteed to be secure (i.e. the eavesdropper has no information about it), otherwise no secure key is possible and communication is aborted.The security of encryption that uses quantum key distribution relies on the foundations of quantum mechanics, in contrast to traditional public key cryptography which relies on the computational difficulty of certain mathematical functions, and cannot provide any indication of eavesdropping at any point in the communication process, or any mathematical proof as to the actual complexity of reversing the one-way functions used. QKD has provable security based on information theory, and forward secrecy.Quantum key distribution is only used to produce and distribute a key, not to transmit any message data. This key can then be used with any chosen encryption algorithm to encrypt (and decrypt) a message, which can then be transmitted over a standard communication channel. The algorithm most commonly associated with QKD is the one-time pad, as it is provably secure when used with a secret, random key. In real world situations, it is often also used with encryption using symmetric key algorithms like the Advanced Encryption Standard algorithm. In the case of QKD this comparison is based on the assumption of perfect single-photon sources and detectors, that cannot be easily implemented.