Document
... Money demand and the nominal interest rate • The Quantity Theory of Money assumes that the demand for real money balances depends only on real income Y. • We now consider another determinant of money demand: the nominal interest rate. • The nominal interest rate i is the opportunity cost of holding ...
... Money demand and the nominal interest rate • The Quantity Theory of Money assumes that the demand for real money balances depends only on real income Y. • We now consider another determinant of money demand: the nominal interest rate. • The nominal interest rate i is the opportunity cost of holding ...
Chapter 21 The IS
... openings occurring in a diminutive time interval at the beginning of each period. And we think of changes in the money stock as taking place abruptly from market opening to market opening. Agents’ decisions about portfolio composition, consumption, and investment are also thought of as being made at ...
... openings occurring in a diminutive time interval at the beginning of each period. And we think of changes in the money stock as taking place abruptly from market opening to market opening. Agents’ decisions about portfolio composition, consumption, and investment are also thought of as being made at ...
Monetary Endogeneity and the Quantity Theory
... the sources of variation in M on the one hand and V and Y on the other. Correspondingly, challenges to the Quantity Theory have taken the form of denying one sort of independence or the other. As is well known, Keynes, in The General Theory, denied the first sort (without denying the latter).1 Keyne ...
... the sources of variation in M on the one hand and V and Y on the other. Correspondingly, challenges to the Quantity Theory have taken the form of denying one sort of independence or the other. As is well known, Keynes, in The General Theory, denied the first sort (without denying the latter).1 Keyne ...
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES IS-LM AND MONETARISM Michael D. Bordo Anna J. Schwartz
... factors other than those affecting the demand for money. A third issue is that Keynes asserts that under conditions of underemployment, when interest rates are positive but low, a liquidity trap exists such that the demand for money becomes infinitely elastic. Changes in the real supply of money the ...
... factors other than those affecting the demand for money. A third issue is that Keynes asserts that under conditions of underemployment, when interest rates are positive but low, a liquidity trap exists such that the demand for money becomes infinitely elastic. Changes in the real supply of money the ...
Chapter 29 Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply
... C. demonstrate why real output and the price level are inversely related. D. include input prices and resource productivity. 7. Other things equal, if the national incomes of the major trading partners of the United States were to rise, the U.S.: A. aggregate demand curve would shift to the right. B ...
... C. demonstrate why real output and the price level are inversely related. D. include input prices and resource productivity. 7. Other things equal, if the national incomes of the major trading partners of the United States were to rise, the U.S.: A. aggregate demand curve would shift to the right. B ...
4: Inflation effect on capital budgeting decisions
... ABC Ltd is considering a new project for manufacturing of toys involving a capital outlay of Rs.6 Lakhs. The capacity of the plant is for an annual production capacity 60000 toys and the capacity utilization is during the 3 years working life of the ...
... ABC Ltd is considering a new project for manufacturing of toys involving a capital outlay of Rs.6 Lakhs. The capacity of the plant is for an annual production capacity 60000 toys and the capacity utilization is during the 3 years working life of the ...
INFLATIONARY PRESSURES IN SOUTH ASIA
... include minimum price support, buffer stock, trade and public distribution schemes. More openness changes the inflationary dynamics. Does high economic growth in some countries imply that infrastructural and other capacity constraints are contributing to inflationary pressures? Data and analysis sug ...
... include minimum price support, buffer stock, trade and public distribution schemes. More openness changes the inflationary dynamics. Does high economic growth in some countries imply that infrastructural and other capacity constraints are contributing to inflationary pressures? Data and analysis sug ...
Practice Exam PPT
... 40. Assume that the economy is at full employment. Policymakers wish to maintain the price level but want to encourage greater investment. Which of the following combinations of monetary and fiscal policies would best achieve this goal? Monetary Policy Fiscal Policy a. No change Contractionary Expa ...
... 40. Assume that the economy is at full employment. Policymakers wish to maintain the price level but want to encourage greater investment. Which of the following combinations of monetary and fiscal policies would best achieve this goal? Monetary Policy Fiscal Policy a. No change Contractionary Expa ...
UNDERLYING FACTORS OF PERSISTENT INFLATION IN ROMANIA
... generating higher wages and as a consequence the aggregate supply curve will quickly begin to shift leftward. As a result, a new equilibrium will occur with output returning at its natural level and prices being the only variable higher compared to the initial situation. Although the Keynesians do n ...
... generating higher wages and as a consequence the aggregate supply curve will quickly begin to shift leftward. As a result, a new equilibrium will occur with output returning at its natural level and prices being the only variable higher compared to the initial situation. Although the Keynesians do n ...
Inflation and Hyperinflation
... two countries also faced the grim prospects of reparation payments to the victorious allied powers, as set in the treaties of Trianon and Versailles. In Austria and Hungary, the reparation obligations were feared to be large, the mere fact that the Reparation Commission had a major, albeit unknown, ...
... two countries also faced the grim prospects of reparation payments to the victorious allied powers, as set in the treaties of Trianon and Versailles. In Austria and Hungary, the reparation obligations were feared to be large, the mere fact that the Reparation Commission had a major, albeit unknown, ...
mankiw6e-chap04_2007_
... When people are deciding whether to hold money or bonds, they don’t know what inflation will turn out to be. Hence, the nominal interest rate relevant for money demand is r + e. ...
... When people are deciding whether to hold money or bonds, they don’t know what inflation will turn out to be. Hence, the nominal interest rate relevant for money demand is r + e. ...
here - Hans-Böckler
... due to the ZLB, but rather to the existence of non-produced stores of value, including money. This problem was clearly identified by Keynes in The General Theory: “Unemployment develops, that is to say, because people want the moon; -- men cannot be employed when the object of their desire (i.e. mon ...
... due to the ZLB, but rather to the existence of non-produced stores of value, including money. This problem was clearly identified by Keynes in The General Theory: “Unemployment develops, that is to say, because people want the moon; -- men cannot be employed when the object of their desire (i.e. mon ...
MONEY AS A SOCIAL BOOKKEEPING DEVICE From Mercantilism
... its function as a means of payment in the future. This highlights the potential allocative inefficiency and global instability of such an expectation ('sunspot') equilibrium. The analysis of money as a precarious conventional equilibrium hardly made any analytical progress during the first half of t ...
... its function as a means of payment in the future. This highlights the potential allocative inefficiency and global instability of such an expectation ('sunspot') equilibrium. The analysis of money as a precarious conventional equilibrium hardly made any analytical progress during the first half of t ...
Principles of Macroeconomics, Case/Fair/Oster, 10e
... interest sensitivity or insensitivity of planned investment The responsiveness of planned investment spending to changes in the interest rate. Interest sensitivity means that planned investment spending changes a great deal in response to changes in the interest rate; interest insensitivity means li ...
... interest sensitivity or insensitivity of planned investment The responsiveness of planned investment spending to changes in the interest rate. Interest sensitivity means that planned investment spending changes a great deal in response to changes in the interest rate; interest insensitivity means li ...
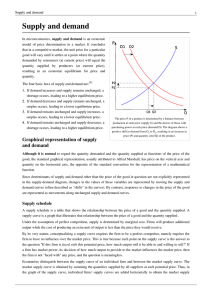
Supply and demand - David E. Harrington
... Sraffianism, that the policy of increased labor market flexibility, including the reduction of minimum wages, does not have an "intellectually coherent" argument in economic theory. This criticism of the application of the model of supply and demand generalizes, particularly to all markets for facto ...
... Sraffianism, that the policy of increased labor market flexibility, including the reduction of minimum wages, does not have an "intellectually coherent" argument in economic theory. This criticism of the application of the model of supply and demand generalizes, particularly to all markets for facto ...