Detailed course outline
... causally-timed linked to other causal mechanisms—prices, quantities, investment ...
... causally-timed linked to other causal mechanisms—prices, quantities, investment ...
Oil Price Analysis: November 2014
... Year to date, the West Texas Intermediate (WTI) Cushing Oil Price (US benchmark) has fallen by close to 23%, closing 14 November at USD75.32 per barrel. The volatility of the global oil market has been heightened based on a culmination of various factors currently afflicting energy markets including ...
... Year to date, the West Texas Intermediate (WTI) Cushing Oil Price (US benchmark) has fallen by close to 23%, closing 14 November at USD75.32 per barrel. The volatility of the global oil market has been heightened based on a culmination of various factors currently afflicting energy markets including ...
Mankiw 6e PowerPoints
... Output is determined by the supply side: supplies of capital, labor technology Changes in demand for goods & services (C, I, G ) only affect prices, not quantities. ...
... Output is determined by the supply side: supplies of capital, labor technology Changes in demand for goods & services (C, I, G ) only affect prices, not quantities. ...
AP Macroeconomics Unit 5 Portfolio Questions and Answers
... likely to rise (inflation) during this phase. Recession is a period of decline in total output, income, and unemployment. It’s marked by the contraction of business activity in many sectors of the economy, GDP declines, unemployment increases. Trough (depression) : output and unemployment “botto ...
... likely to rise (inflation) during this phase. Recession is a period of decline in total output, income, and unemployment. It’s marked by the contraction of business activity in many sectors of the economy, GDP declines, unemployment increases. Trough (depression) : output and unemployment “botto ...
Chapter 5
... • Previous analysis assumes that the same markets are served with and without price discrimination • This may not be true – uniform price is affected by demand in “weak” markets – firm may then prefer not to serve such markets without price discrimination – price discrimination may open up weak mark ...
... • Previous analysis assumes that the same markets are served with and without price discrimination • This may not be true – uniform price is affected by demand in “weak” markets – firm may then prefer not to serve such markets without price discrimination – price discrimination may open up weak mark ...
Answer Key - uob.edu.bh
... 18. In the AD-AS model, after a negative supply shock hits the economy, a. the output level will increase, the price level will increase and interest rates will increase. b. the output level will decrease, the price level will decrease and interest rates will decrease. c. the output level will decre ...
... 18. In the AD-AS model, after a negative supply shock hits the economy, a. the output level will increase, the price level will increase and interest rates will increase. b. the output level will decrease, the price level will decrease and interest rates will decrease. c. the output level will decre ...
Multiple Choices Questions (75%, 3% each) 需求 1) Which of the
... 3) Consider an economy produced 10000 apples and 5000 oranges in year 1. The price of apple is $5 and the price of orange is $10. In year 2, the production of apples increased by 10% and oranges decreased by 10%. The price of the apples is $6 and the price of oranges is $8. A) (4%) Calculate the no ...
... 3) Consider an economy produced 10000 apples and 5000 oranges in year 1. The price of apple is $5 and the price of orange is $10. In year 2, the production of apples increased by 10% and oranges decreased by 10%. The price of the apples is $6 and the price of oranges is $8. A) (4%) Calculate the no ...
Other things the same, an increase in the price level, leads to an
... inflation rate higher than otherwise. ...
... inflation rate higher than otherwise. ...
Ch.10- Aggregate Demand/Aggregate Supply
... Any non-price-level change that increases aggregate spending (on domestic goods) shifts AD to the right. A drop in the foreign exchange value of the dollar (weak dollar) Increased security about jobs and future income Improvements in economic conditions in other countries A reduction in real interes ...
... Any non-price-level change that increases aggregate spending (on domestic goods) shifts AD to the right. A drop in the foreign exchange value of the dollar (weak dollar) Increased security about jobs and future income Improvements in economic conditions in other countries A reduction in real interes ...
Additional Reading 11
... value because the purchasing power of money falls. As buyers become poorer, they reduce their purchases of all goods and services which in turn reduce the aggregate expenditure (AE curve makes a parallel shift down) and contract the economy (Y decreases). On the other hand, as the price level falls, ...
... value because the purchasing power of money falls. As buyers become poorer, they reduce their purchases of all goods and services which in turn reduce the aggregate expenditure (AE curve makes a parallel shift down) and contract the economy (Y decreases). On the other hand, as the price level falls, ...
Demand, ,Supply and Equilibrium
... Qs = (price, expectations, input prices, prices of other goods, technological change, number of producers) ...
... Qs = (price, expectations, input prices, prices of other goods, technological change, number of producers) ...
The anatomy of three commodity booms
... are based on their values in international trade. The 1990 weights appear in Fig. 2 below (IMF Commodity statistics, IMF’s home page on the web). These numbers should be taken as no more than rough indicators. They have obviously changed over the long period covered by Fig. 1. Fig. 1 depicts prices ...
... are based on their values in international trade. The 1990 weights appear in Fig. 2 below (IMF Commodity statistics, IMF’s home page on the web). These numbers should be taken as no more than rough indicators. They have obviously changed over the long period covered by Fig. 1. Fig. 1 depicts prices ...
chapter_12
... foreign countries for U.S. goods ↑ (reduces exports) while prices for foreign goods in U.S. ↓ (increases imports) AD shift left (opposite occurs when exchange rates between U.S. and foreign currency ↓) Note: ∆ in net exports from change in price level does not shift AD ...
... foreign countries for U.S. goods ↑ (reduces exports) while prices for foreign goods in U.S. ↓ (increases imports) AD shift left (opposite occurs when exchange rates between U.S. and foreign currency ↓) Note: ∆ in net exports from change in price level does not shift AD ...
Unpublished mathematical appendix
... Notice that 0 > a i > ai : higher country i's government spending is more recessionary on country i's output than higher government i's spending. This is because higher government spending nanced by higher distortionary taxation lowers labor supply and lowers aggregate demand. The overall impact on ...
... Notice that 0 > a i > ai : higher country i's government spending is more recessionary on country i's output than higher government i's spending. This is because higher government spending nanced by higher distortionary taxation lowers labor supply and lowers aggregate demand. The overall impact on ...
Final Exam - Rose
... A. P4, the profit-maximizing firm would produce 30 units and incur a loss that is less than fixed cost in absolute value. B. P3, the profit-maximizing firm would produce 62 units and incur a loss equal to fixed cost in absolute value. C. P2, the profit-maximizing firm would produce 44 units, but it ...
... A. P4, the profit-maximizing firm would produce 30 units and incur a loss that is less than fixed cost in absolute value. B. P3, the profit-maximizing firm would produce 62 units and incur a loss equal to fixed cost in absolute value. C. P2, the profit-maximizing firm would produce 44 units, but it ...
No Slide Title
... is a period in which wages and some other prices do not respond to changes in economic conditions. 2) A sticky price is a price that is slow to adjust to its equilibrium level, creating sustained periods of shortage or surplus. 3) The long run in macroeconomic analysis is a period in which wages and ...
... is a period in which wages and some other prices do not respond to changes in economic conditions. 2) A sticky price is a price that is slow to adjust to its equilibrium level, creating sustained periods of shortage or surplus. 3) The long run in macroeconomic analysis is a period in which wages and ...
Economic conditions in Germany - August 2016
... the United Kingdom’s continued membership in the European Union (EU) did not appear to have had any effect on the German economy in the second quarter. The future impact of the referendum result will – at least in the short term – probably also be quite minimal. The weaker demand for new machinery ...
... the United Kingdom’s continued membership in the European Union (EU) did not appear to have had any effect on the German economy in the second quarter. The future impact of the referendum result will – at least in the short term – probably also be quite minimal. The weaker demand for new machinery ...
Inflation is a persistent increase in the general price level
... The reason for decreases in supply are usually related to increases in the prices of inputs. One major reason for cost-push inflation are supply shocks. A supply shock is an event that suddenly changes the price of a commodity or service. (sudden supply decrease) will raise prices and shift the aggr ...
... The reason for decreases in supply are usually related to increases in the prices of inputs. One major reason for cost-push inflation are supply shocks. A supply shock is an event that suddenly changes the price of a commodity or service. (sudden supply decrease) will raise prices and shift the aggr ...
Inflation - Doral Academy Preparatory
... when prices are pushed up by rising costs to producers who compete with each other for increasingly scarce resources. The increased costs are passed onto ...
... when prices are pushed up by rising costs to producers who compete with each other for increasingly scarce resources. The increased costs are passed onto ...
Chapter 6
... increases and the quantity of imports decreases because of lower foreign prices and high domestic prices. BOP improves. ...
... increases and the quantity of imports decreases because of lower foreign prices and high domestic prices. BOP improves. ...
10123481 Oil Prices in FSI
... other financial institutions. However, for some US regions and financial institutions, lower oil prices may generate formidable headwinds to growth and performance. Banks with large global operations, while enjoying the benefits of lower oil prices, may also face some additional challenges flowing f ...
... other financial institutions. However, for some US regions and financial institutions, lower oil prices may generate formidable headwinds to growth and performance. Banks with large global operations, while enjoying the benefits of lower oil prices, may also face some additional challenges flowing f ...
2013 Workshop MBA Ec..
... Not all black markets are illegal, but in the case of maximum price fixing by government, black market activity is outlawed. A black market is therefore often defined as an illegal market in which goods are sold above the maximum price set by the government. All price controls (including controls ...
... Not all black markets are illegal, but in the case of maximum price fixing by government, black market activity is outlawed. A black market is therefore often defined as an illegal market in which goods are sold above the maximum price set by the government. All price controls (including controls ...
title of document
... Not all black markets are illegal, but in the case of maximum price fixing by government, black market activity is outlawed. A black market is therefore often defined as an illegal market in which goods are sold above the maximum price set by the government. All price controls (including controls ...
... Not all black markets are illegal, but in the case of maximum price fixing by government, black market activity is outlawed. A black market is therefore often defined as an illegal market in which goods are sold above the maximum price set by the government. All price controls (including controls ...
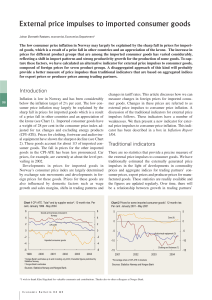
External price impulses to imported consumer goods
... impulses to imported consumer goods. In foreign trade, prices are calculated on the basis of imports measured by volume and value. Quality improvements are therefore not taken into account when calculating import prices. This makes it especially difficult to calculate import prices for audiovisual e ...
... impulses to imported consumer goods. In foreign trade, prices are calculated on the basis of imports measured by volume and value. Quality improvements are therefore not taken into account when calculating import prices. This makes it especially difficult to calculate import prices for audiovisual e ...
Power Point
... • There is not as much incentive to increase efficiency given the excess rents to the economy. • Can result in large growth in output (and employment) without a corresponding increase in TFP. • If the resource boom is temporary, can have lasting effects on a countries growth prospects! • A similar s ...
... • There is not as much incentive to increase efficiency given the excess rents to the economy. • Can result in large growth in output (and employment) without a corresponding increase in TFP. • If the resource boom is temporary, can have lasting effects on a countries growth prospects! • A similar s ...
2000s commodities boom

The 2000s commodities boom or the commodities super cycle was the rise in many physical commodity prices (such as those of food stuffs, oil, metals, chemicals, fuels and the like) which occurred during the decade of the 2000s (2000–2009), following the Great Commodities Depression of the 1980s and 1990s. The boom was largely due to the rising demand from emerging markets such as the BRIC countries, as well as the result of concerns over long-term supply availability. There was a sharp down-turn in prices during 2008 and early 2009 as a result of the credit crunch and sovereign debt crisis, but prices began to rise as demand recovered from late 2009 to mid-2010. Oil began to slip downwards after mid-2010, but peaked at $101.80 on 30 and 31 January 2011, as then Egyptian political crisis and rioting broke out, leading to concerns over both the safe use of the Suez Canal and over all security in Arabia itself. On 3 March, Libya's National Oil Corp said that output had halved due to the departure of foreign workers. As this happened, Brent Crude surged to a new high of above $116.00 a barrel as supply disruptions and potential for more unrest in the Middle East and North Africa continued to worry investors. Thus the price of oil kept rising into the 2010s. The commodities super-cycle peaked in 2011, ""driven by a combination of strong demand from emerging nations and low supply growth."" Prior to 2002, only 5 to 10 per cent of trading in the commodities market was attributable to investors. Since 2002 ""30 per cent of trading is attributable to investors in the commodities market"" which ""has caused higher price volatility.""