LESSON 2: DEMAND AND SUPPLY
... Purpose of this lesson: to study the behaviour of people as they interact with one another in markets. Market: a group of buyers and sellers of a particular good (or service). Demand: represents the behaviour of buyers. Supply: represents the behaviour of sellers. Main assumption that we will use fo ...
... Purpose of this lesson: to study the behaviour of people as they interact with one another in markets. Market: a group of buyers and sellers of a particular good (or service). Demand: represents the behaviour of buyers. Supply: represents the behaviour of sellers. Main assumption that we will use fo ...
EDITragan_13ce_ch23
... Many economic events (especially changes in the world prices of raw materials) cause both aggregate demand and aggregate supply shocks. The overall effect on the economy depends on the relative importance of the two separate effects. ...
... Many economic events (especially changes in the world prices of raw materials) cause both aggregate demand and aggregate supply shocks. The overall effect on the economy depends on the relative importance of the two separate effects. ...
Chapter 3 - halsnarr
... Katrina shut down Gulf Coast refineries, pipe lines and Gulf of Mexico deep Gasoline water oil wells. S Demand for gasoline increases because people are trying to get out of harms way or they “hoard”. ...
... Katrina shut down Gulf Coast refineries, pipe lines and Gulf of Mexico deep Gasoline water oil wells. S Demand for gasoline increases because people are trying to get out of harms way or they “hoard”. ...
Econ 20B- Additional Problem Set I. MULTIPLE CHOICES. Choose
... a. less wealthy, so the quantity of goods and services demanded falls. b. less wealthy, so the quantity of goods and services demanded rises. c. more wealthy, so the quantity of goods and services demanded rises. d. more wealthy, so the quantity of goods and services demanded falls. ANS: A PTS: 1 DI ...
... a. less wealthy, so the quantity of goods and services demanded falls. b. less wealthy, so the quantity of goods and services demanded rises. c. more wealthy, so the quantity of goods and services demanded rises. d. more wealthy, so the quantity of goods and services demanded falls. ANS: A PTS: 1 DI ...
Takeover Offer for shares in New Britain Palm Oil Limited (NBPOL)
... • Commands a 40% market share in UK & Ireland • Currently, it sells about 200k MT of FSPO to its European customers at a sustainability premium • Also the largest supplier of segregated stearin in the UK ...
... • Commands a 40% market share in UK & Ireland • Currently, it sells about 200k MT of FSPO to its European customers at a sustainability premium • Also the largest supplier of segregated stearin in the UK ...
Econ_OnlineLectureNotes_ch13_s2
... low inflation rates for most of their lifetimes. – In the 2000s, the economy actually seemed to be experiencing a period of deflation, or a sustained drop in the price levels. – However, by mid-2008, inflation was becoming a worry. The CPI rose 1.1 percent in June. Higher production costs, fueled by ...
... low inflation rates for most of their lifetimes. – In the 2000s, the economy actually seemed to be experiencing a period of deflation, or a sustained drop in the price levels. – However, by mid-2008, inflation was becoming a worry. The CPI rose 1.1 percent in June. Higher production costs, fueled by ...
Presentation Plus!
... order to examine the concept of market equilibrium, a situation in which prices are relatively stable, and the quantity of output supplied is equal to the quantity demanded. • In a competitive market, prices are established by the forces of supply and demand. If the price is too high, a temporary ...
... order to examine the concept of market equilibrium, a situation in which prices are relatively stable, and the quantity of output supplied is equal to the quantity demanded. • In a competitive market, prices are established by the forces of supply and demand. If the price is too high, a temporary ...
02-25-2005
... – supplies of capital, labor – technology Changes in demand for goods & services (C, I, G ) only affect prices, not quantities. Complete price flexibility is a crucial assumption, so classical theory applies in the long run. CHAPTER 9 ...
... – supplies of capital, labor – technology Changes in demand for goods & services (C, I, G ) only affect prices, not quantities. Complete price flexibility is a crucial assumption, so classical theory applies in the long run. CHAPTER 9 ...
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES Laurence Ball N. thegory Manldw Working Paper No. 4677
... irrelevant The evidence that money matters implies that the economy contains an important nominal imperfection, and (as we argue below) sticky prices are the most realistic candidate for such an imperfection. ...
... irrelevant The evidence that money matters implies that the economy contains an important nominal imperfection, and (as we argue below) sticky prices are the most realistic candidate for such an imperfection. ...
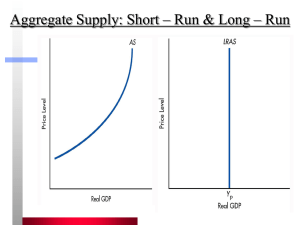
Chapter 16 The long Run AS
... Recall: In microeconomics, the short-run is defined as a period of time in which something remains fixed In Macro: The short-run is a period in which nominal wages (and other input prices) are fixed as the price level changes. Why are wages fixed in the short-run? 1. Fixed wage contracts for manager ...
... Recall: In microeconomics, the short-run is defined as a period of time in which something remains fixed In Macro: The short-run is a period in which nominal wages (and other input prices) are fixed as the price level changes. Why are wages fixed in the short-run? 1. Fixed wage contracts for manager ...
Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply
... Why the Aggregate-Supply Curve Slopes Upward in the Short Run • The Sticky-Wage Theory • Nominal wages are slow to adjust, or are “sticky” in the short run: • Wages do not adjust immediately to a rise in the price level. • A higher price level makes labor relatively cheaper. • This allows some firm ...
... Why the Aggregate-Supply Curve Slopes Upward in the Short Run • The Sticky-Wage Theory • Nominal wages are slow to adjust, or are “sticky” in the short run: • Wages do not adjust immediately to a rise in the price level. • A higher price level makes labor relatively cheaper. • This allows some firm ...
General Business 765
... 23. Which of the following statements is true? a. In calculating the CPI, the market basket of goods “priced” varies from year to year. b. Real GDP is measured in constant dollars. c. Nominal interest rates are always higher than real interest rates. d. Inflation does not benefit anyone. e. Real in ...
... 23. Which of the following statements is true? a. In calculating the CPI, the market basket of goods “priced” varies from year to year. b. Real GDP is measured in constant dollars. c. Nominal interest rates are always higher than real interest rates. d. Inflation does not benefit anyone. e. Real in ...
A Socialist Market Economy in North Korea? Systemic Restrictions
... leadership has come to the conclusion that the necessary incentives can only come from the market. And indeed, in addition to the (farmer's) markets, in the already mentioned 1998 constitution we find a number of references to issues like "kitchen gardens" (t'4bat'; art. 24), "costs, prices and prof ...
... leadership has come to the conclusion that the necessary incentives can only come from the market. And indeed, in addition to the (farmer's) markets, in the already mentioned 1998 constitution we find a number of references to issues like "kitchen gardens" (t'4bat'; art. 24), "costs, prices and prof ...
Mankiw 5/e Chapter 9: Intro to Economic Fluctuations
... – supplies of capital, labor – technology Complete price flexibility is a crucial assumption, so classical theory applies in the long run. ...
... – supplies of capital, labor – technology Complete price flexibility is a crucial assumption, so classical theory applies in the long run. ...
Post Keynesian Pricing Theory: Alternative Foundations and
... More recently, Eichner (1991)4 offered a ‘long-period’ analysis of prices in an inputoutput system of production that has its roots in Sraffa (1960) but which is linked to a ‘short-period’ analysis of pricing that is discussed below. This model determines the system-wide set of equilibrium prices th ...
... More recently, Eichner (1991)4 offered a ‘long-period’ analysis of prices in an inputoutput system of production that has its roots in Sraffa (1960) but which is linked to a ‘short-period’ analysis of pricing that is discussed below. This model determines the system-wide set of equilibrium prices th ...
Paper - IIOA!
... for the years 2001-2007 produced within the detailed supply and use framework. The established system follows mostly the principles and standards for the measurement of constant price annual national accounts data in the European Union. Major outcome of this work is the introduction of the double de ...
... for the years 2001-2007 produced within the detailed supply and use framework. The established system follows mostly the principles and standards for the measurement of constant price annual national accounts data in the European Union. Major outcome of this work is the introduction of the double de ...
2007:3 Alternative measures of inflation for monetary policy analysis
... case of cucumbers, the price the importer pays is presumably just a minor part of the consumer price. At the same time, the price of many goods, even those that are produced in Sweden, is set in the world market and is therefore directly affected by external factors. Similarly, the development of pr ...
... case of cucumbers, the price the importer pays is presumably just a minor part of the consumer price. At the same time, the price of many goods, even those that are produced in Sweden, is set in the world market and is therefore directly affected by external factors. Similarly, the development of pr ...
Jeffrey research Michael Bruno Massachusetts Avenue
... now receding. The inflation has been marked by great divergences in rates between countries. It seems to be generally agreed that the oil crisis and related events had a lot to do with this upsurge in prices and that the breakdown of the Bretton Woods system of pegged rates had a lot to •do ...
... now receding. The inflation has been marked by great divergences in rates between countries. It seems to be generally agreed that the oil crisis and related events had a lot to do with this upsurge in prices and that the breakdown of the Bretton Woods system of pegged rates had a lot to •do ...
1 - Rose
... 22. A purely competitive firm’s output is currently such that its marginal cost is $4 and marginal revenue is $5. Assuming the firm maximizes profit, the firm should: A. cut its price and raise its output. D. leave price unchanged and decrease output. B. raise its price and cut output. E. shut down ...
... 22. A purely competitive firm’s output is currently such that its marginal cost is $4 and marginal revenue is $5. Assuming the firm maximizes profit, the firm should: A. cut its price and raise its output. D. leave price unchanged and decrease output. B. raise its price and cut output. E. shut down ...
3 Macroeconomics LESSON 4 s ACTIVITY 24
... GDP is at a level with unemployment at the full-employment level and where any increase in demand will result only in an increase in prices. The economy is unable to produce any more goods and services for a sustainable period of time. ...
... GDP is at a level with unemployment at the full-employment level and where any increase in demand will result only in an increase in prices. The economy is unable to produce any more goods and services for a sustainable period of time. ...
Terms of Trade - uwcmaastricht-econ
... developing countries, specially if their production is mainly focused on a few commodities for export. This makes these countries more vulnerable: if prices of these commodities experience long-term trends in one direction or wide and abrupt fluctuations over short periods of time, effects are felt ...
... developing countries, specially if their production is mainly focused on a few commodities for export. This makes these countries more vulnerable: if prices of these commodities experience long-term trends in one direction or wide and abrupt fluctuations over short periods of time, effects are felt ...
Micro and Macroeconomics Review Questions
... To calculate the unemployment rate an economist would need the total number of unemployed people and which other number? A the inflation rate B the number of people in the labor force C the total number of discouraged workers D the total number of transactions in the resource market ...
... To calculate the unemployment rate an economist would need the total number of unemployed people and which other number? A the inflation rate B the number of people in the labor force C the total number of discouraged workers D the total number of transactions in the resource market ...
4. The Goods Market
... determines the movements in its relative price. Wages and excess demand conditions captured in the price of total supply (PT) are assumed to affect each expenditure component equally in the long run. Therefore, changes in PT do not alter relative prices in the long run. However, the pace of adjustme ...
... determines the movements in its relative price. Wages and excess demand conditions captured in the price of total supply (PT) are assumed to affect each expenditure component equally in the long run. Therefore, changes in PT do not alter relative prices in the long run. However, the pace of adjustme ...
2000s commodities boom

The 2000s commodities boom or the commodities super cycle was the rise in many physical commodity prices (such as those of food stuffs, oil, metals, chemicals, fuels and the like) which occurred during the decade of the 2000s (2000–2009), following the Great Commodities Depression of the 1980s and 1990s. The boom was largely due to the rising demand from emerging markets such as the BRIC countries, as well as the result of concerns over long-term supply availability. There was a sharp down-turn in prices during 2008 and early 2009 as a result of the credit crunch and sovereign debt crisis, but prices began to rise as demand recovered from late 2009 to mid-2010. Oil began to slip downwards after mid-2010, but peaked at $101.80 on 30 and 31 January 2011, as then Egyptian political crisis and rioting broke out, leading to concerns over both the safe use of the Suez Canal and over all security in Arabia itself. On 3 March, Libya's National Oil Corp said that output had halved due to the departure of foreign workers. As this happened, Brent Crude surged to a new high of above $116.00 a barrel as supply disruptions and potential for more unrest in the Middle East and North Africa continued to worry investors. Thus the price of oil kept rising into the 2010s. The commodities super-cycle peaked in 2011, ""driven by a combination of strong demand from emerging nations and low supply growth."" Prior to 2002, only 5 to 10 per cent of trading in the commodities market was attributable to investors. Since 2002 ""30 per cent of trading is attributable to investors in the commodities market"" which ""has caused higher price volatility.""