OPEC`s Kinked Demand Curve
... Shifts in cost and horizontal shifts in demand cause less instability in price under a kinked demand curve than under a non-kinked demand curve. With a kinked demand curve, a modest shift in marginal cost will not change the profit-maximizing quantity of production and sales, or price. A proportiona ...
... Shifts in cost and horizontal shifts in demand cause less instability in price under a kinked demand curve than under a non-kinked demand curve. With a kinked demand curve, a modest shift in marginal cost will not change the profit-maximizing quantity of production and sales, or price. A proportiona ...
Nº 245
... methodologically# complicated.# The# International# Comparisons# Program# has# carried# out# this# exercise# only# 7# times# since# 1970.# For# years,# other# than# those# benchmark# periods,# PPPs# are# extrapolated#using#price#index#numbers#from#national#accounts#statistics.#Logically,#benchmarks# ...
... methodologically# complicated.# The# International# Comparisons# Program# has# carried# out# this# exercise# only# 7# times# since# 1970.# For# years,# other# than# those# benchmark# periods,# PPPs# are# extrapolated#using#price#index#numbers#from#national#accounts#statistics.#Logically,#benchmarks# ...
aggregate supply (AS) curve
... aggregate supply (AS) curve A graph that shows the relationship between the aggregate quantity of output supplied by all firms in an economy and the overall price level. Although it is called an aggregate supply curve, it is better thought of as a “price/output response” curve—a curve that traces ou ...
... aggregate supply (AS) curve A graph that shows the relationship between the aggregate quantity of output supplied by all firms in an economy and the overall price level. Although it is called an aggregate supply curve, it is better thought of as a “price/output response” curve—a curve that traces ou ...
Chapter 6
... 4. An above full-employment equilibrium is an equilibrium in which real GDP exceeds potential GDP. Figure 21.11c, (page 487/141) illustrates above full-employment equilibrium. The amount by which real GDP exceeds potential GDP is called an inflationary gap. 5. Figure 21.11(d) (page 487/141) shows ho ...
... 4. An above full-employment equilibrium is an equilibrium in which real GDP exceeds potential GDP. Figure 21.11c, (page 487/141) illustrates above full-employment equilibrium. The amount by which real GDP exceeds potential GDP is called an inflationary gap. 5. Figure 21.11(d) (page 487/141) shows ho ...
Intersectoral Linkages, Diverse Information, and Aggregate Dynamics in a Neoclassical Model ∗
... of Baxter et al. (2011) and assume that firms condition their actions on the prices directly relevant to their own choices. Including the possibility of additional noisy aggregate information is trivial, but does not change the essential features of the model. Note that even if firms in a given sec ...
... of Baxter et al. (2011) and assume that firms condition their actions on the prices directly relevant to their own choices. Including the possibility of additional noisy aggregate information is trivial, but does not change the essential features of the model. Note that even if firms in a given sec ...
Chapter 14
... uncertainty, “menu costs,” and other factors There may be confusion as to whether price changes are real or nominal. Firms may not respond immediately to changes in AD/inflation “Menu costs” – represent the costs of changing prices Changing prices may create mistrust among the firm’s custome ...
... uncertainty, “menu costs,” and other factors There may be confusion as to whether price changes are real or nominal. Firms may not respond immediately to changes in AD/inflation “Menu costs” – represent the costs of changing prices Changing prices may create mistrust among the firm’s custome ...
Business Fluctuations: Aggregate Demand and Supply Business
... uncertainty, “menu costs,” and other factors There may be confusion as to whether price changes are real or nominal. Firms may not respond immediately to changes in AD/inflation “Menu costs” – represent the costs of changing prices Changing prices may create mistrust among the firm’s customers The “ ...
... uncertainty, “menu costs,” and other factors There may be confusion as to whether price changes are real or nominal. Firms may not respond immediately to changes in AD/inflation “Menu costs” – represent the costs of changing prices Changing prices may create mistrust among the firm’s customers The “ ...
UNEMPLOYMENT, VACANCIES, WAGES
... approach both the search process and the ensuing purchase or sale decision. And that is where the literature started. But a full analysis needs to combine individual decision-making with an analysis of how the interactions of buyers and sellers determine the economic environment in which these deci ...
... approach both the search process and the ensuing purchase or sale decision. And that is where the literature started. But a full analysis needs to combine individual decision-making with an analysis of how the interactions of buyers and sellers determine the economic environment in which these deci ...
Monetary Policy Rules in the Presence of an Punnoose Jacob Christie Smith
... The LVR a¤ects macro volatilities and hence changes monetary policy. The optimal monetary policy rule under an LVR constraint transfers welfare from savers to borrowers. Removing the LVR results in gradual adjustment. ...
... The LVR a¤ects macro volatilities and hence changes monetary policy. The optimal monetary policy rule under an LVR constraint transfers welfare from savers to borrowers. Removing the LVR results in gradual adjustment. ...
Unemployment and Inflation - University of Wisconsin–La
... – Substitution bias – Quality changes ...
... – Substitution bias – Quality changes ...
McConnell 11CE Macro Key Questions and Answers
... from the goods’ benefits). If goods are non-rival, there is less incentive for private firms to produce them – those purchasing the good could simply allow others the use without compensation. Similarly, if goods are non-excludable, private firms are unlikely to produce them as the potential for pro ...
... from the goods’ benefits). If goods are non-rival, there is less incentive for private firms to produce them – those purchasing the good could simply allow others the use without compensation. Similarly, if goods are non-excludable, private firms are unlikely to produce them as the potential for pro ...
Chapter 12 Appendix A
... AD1 to AD2, because the lower real interest rate at any given inflation rate leads to higher investment spending and net exports, thereby increasing equilibrium output at each inflation rate. The rightward shift in the aggregate demand curve then moves the economy to point 2 in all the panels, with ...
... AD1 to AD2, because the lower real interest rate at any given inflation rate leads to higher investment spending and net exports, thereby increasing equilibrium output at each inflation rate. The rightward shift in the aggregate demand curve then moves the economy to point 2 in all the panels, with ...
The Relationship between Inflation and Unemployment: A
... Where Ut and U* are the actual and natural levels of unemployment; b is a coefficient showing the response of wage’s changes to the situation on the labor market; Pt and Pt-1 are respectively the prices in the current and prior periods. Phillips curve was reasonably well confirmed by empirical studi ...
... Where Ut and U* are the actual and natural levels of unemployment; b is a coefficient showing the response of wage’s changes to the situation on the labor market; Pt and Pt-1 are respectively the prices in the current and prior periods. Phillips curve was reasonably well confirmed by empirical studi ...
Module 32 Money, Output, and Prices in the Long Run
... How much does a change in the money supply change the aggregate price level in the long run? The answer is that a change in the money supply leads to a proportional change in the aggregate price level in the long run. For example, if the money supply falls 25%, the aggregate price level falls 25% in ...
... How much does a change in the money supply change the aggregate price level in the long run? The answer is that a change in the money supply leads to a proportional change in the aggregate price level in the long run. For example, if the money supply falls 25%, the aggregate price level falls 25% in ...
This PDF is a selection from an out-of-print volume from... of Economic Research
... unions doubled during the Frei government. In a six-year span, blue-collar union membership increased by 38%, white-collar union membership increased by 90%, and peasant union membership grew from less than 2,000 people (1964) to more than 114,000 people (1970); (see table 7.1). A synthesis of the e ...
... unions doubled during the Frei government. In a six-year span, blue-collar union membership increased by 38%, white-collar union membership increased by 90%, and peasant union membership grew from less than 2,000 people (1964) to more than 114,000 people (1970); (see table 7.1). A synthesis of the e ...
Chapter 23
... Households in the economy are unhappy about the increase in the price of oil and they wish it would reverse itself. Will they be any happier if policy makers increase aggregate demand? The answer here is probably not. To see why, remember the reasons for the upward sloping AS curve. As you move up a ...
... Households in the economy are unhappy about the increase in the price of oil and they wish it would reverse itself. Will they be any happier if policy makers increase aggregate demand? The answer here is probably not. To see why, remember the reasons for the upward sloping AS curve. As you move up a ...
Stock Market Crashes
... The Crash of 1929: What Followed? After the stock market crash of 1929, things only got worse. By the end of 1929 the market recovered somewhat, but in general stock prices continued in a downward spiral until 1932. By 1932 average stock prices had fallen more than 75 percent, people had lost an est ...
... The Crash of 1929: What Followed? After the stock market crash of 1929, things only got worse. By the end of 1929 the market recovered somewhat, but in general stock prices continued in a downward spiral until 1932. By 1932 average stock prices had fallen more than 75 percent, people had lost an est ...
Chap23
... • The Sticky-Price Theory • Prices of some goods and services adjust sluggishly in response to changing economic conditions. • An unexpected fall in the price level leaves some firms with higher-than-desired prices. For a variety of reasons, they may not want to or be able to change prices immediate ...
... • The Sticky-Price Theory • Prices of some goods and services adjust sluggishly in response to changing economic conditions. • An unexpected fall in the price level leaves some firms with higher-than-desired prices. For a variety of reasons, they may not want to or be able to change prices immediate ...
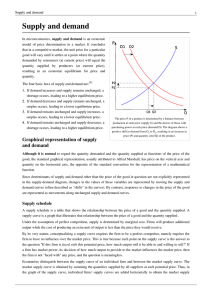
Supply and demand - David E. Harrington
... The supply-and-demand model is a partial equilibrium model of economic equilibrium, where the clearance on the market of some specific goods is obtained independently from prices and quantities in other markets. In other words, the prices of all substitutes and complements, as well as income levels ...
... The supply-and-demand model is a partial equilibrium model of economic equilibrium, where the clearance on the market of some specific goods is obtained independently from prices and quantities in other markets. In other words, the prices of all substitutes and complements, as well as income levels ...
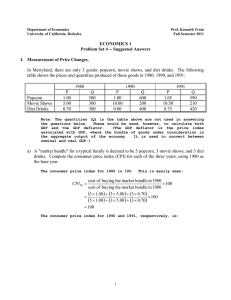
Answers. - University of California, Berkeley
... This differs from the inflation rate calculated in (b) because the “market bundle” is different. The rate of inflation is the percentage increase in the cost of buying a specific bundle of goods. Therefore it may be different for different bundles. Why might we want to change the bundle of goods use ...
... This differs from the inflation rate calculated in (b) because the “market bundle” is different. The rate of inflation is the percentage increase in the cost of buying a specific bundle of goods. Therefore it may be different for different bundles. Why might we want to change the bundle of goods use ...
3. Extension of Meade`s Model and Endogenous Dynamics
... its equilibrium state, damped cycles. So, authors were well aware that for obtaining undamped cycle, one must assume unstable stationary equilibrium. The problem was that since Frisch’s critic of Kalecki’s 1933 model, they knew that in that case, linear model give only rise to explosive cycles, exce ...
... its equilibrium state, damped cycles. So, authors were well aware that for obtaining undamped cycle, one must assume unstable stationary equilibrium. The problem was that since Frisch’s critic of Kalecki’s 1933 model, they knew that in that case, linear model give only rise to explosive cycles, exce ...
FINALTERM EXAMINATION Fall 2009 ECO401
... The interest rate parity is the basic identity that relates which of the following? ► Interest rates and exchange rates. ► Interest rates and inflation rate. ► Exchange rates and inflation rate. ► Discount rate and inflation rate. Question No: 38 ( Marks: 1 ) - Please choose one Suppose there is a s ...
... The interest rate parity is the basic identity that relates which of the following? ► Interest rates and exchange rates. ► Interest rates and inflation rate. ► Exchange rates and inflation rate. ► Discount rate and inflation rate. Question No: 38 ( Marks: 1 ) - Please choose one Suppose there is a s ...
4 Impact of High Oil Prices on African Economies
... on African countries. In the past, significant increases in the price of oil have led to worldwide economic recessions, such as the 1973 and 1979 energy crises. In many European countries, which have high taxes on fuels, such price shocks could potentially be mitigated by reducing the taxes as fuel ...
... on African countries. In the past, significant increases in the price of oil have led to worldwide economic recessions, such as the 1973 and 1979 energy crises. In many European countries, which have high taxes on fuels, such price shocks could potentially be mitigated by reducing the taxes as fuel ...