Has the Business Cycle Changed and Why?
... economic time series and a variety of methods designed to describe timevarying time-series processes. In so doing, we review the literature on the moderation and attempt to resolve some of its disagreements and discrepancies. This analysis is presented in Sections 2, 3, and 4. Our empirical analysis ...
... economic time series and a variety of methods designed to describe timevarying time-series processes. In so doing, we review the literature on the moderation and attempt to resolve some of its disagreements and discrepancies. This analysis is presented in Sections 2, 3, and 4. Our empirical analysis ...
eee06-Stazka2 3772739 en
... another argument in favour of the real economy view. The argument goes as follows. Real shocks alter real exchange rates as well as nominal exchange rates (under floating) or the level of international reserves (under pegged nominal rates). Obviously, disturbances that would lead to a real – and nom ...
... another argument in favour of the real economy view. The argument goes as follows. Real shocks alter real exchange rates as well as nominal exchange rates (under floating) or the level of international reserves (under pegged nominal rates). Obviously, disturbances that would lead to a real – and nom ...
Aggregate Supply and Aggregate Demand
... the highestscoring hockey player of all time? Talent, discipline, and hard work, of course. Some say his greatness came from following this father’s advice: “Skate to where the puck is going, not to where it is.” By anticipating the play — seeing two steps ahead — Gretzky was able to be in the right ...
... the highestscoring hockey player of all time? Talent, discipline, and hard work, of course. Some say his greatness came from following this father’s advice: “Skate to where the puck is going, not to where it is.” By anticipating the play — seeing two steps ahead — Gretzky was able to be in the right ...
Strategies for Controlling Inflation
... made, expectations are given. In the case of monetary policy, this means that with expectations fixed, policy-makers know that they can boost economic output (or lower unemployment) by pursuing monetary policy that is more expansionary than expected. Thus, as a result, policy-makers who have a high ...
... made, expectations are given. In the case of monetary policy, this means that with expectations fixed, policy-makers know that they can boost economic output (or lower unemployment) by pursuing monetary policy that is more expansionary than expected. Thus, as a result, policy-makers who have a high ...
Stock Prices as a Leading Indicator of Economic activity
... looking nature, assessments can be undertaken on new information before it becomes incorporated into the macroeconomic data (Kuttner, 2009). ...
... looking nature, assessments can be undertaken on new information before it becomes incorporated into the macroeconomic data (Kuttner, 2009). ...
International Spillovers and Guidelines for Policy Cooperation
... to hold even if capital account intervention is just a second-best policy measure to correct learning-by-doing externalities in the domestic economy. Our second application describes an economy that su¤ers from a shortage of aggregate demand that cannot be corrected using domestic monetary policy be ...
... to hold even if capital account intervention is just a second-best policy measure to correct learning-by-doing externalities in the domestic economy. Our second application describes an economy that su¤ers from a shortage of aggregate demand that cannot be corrected using domestic monetary policy be ...
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES AN ALTERNATIVE INTERPRETATION
... depending on the exact empirical specification, with large standard errors that do not permit us to clearly reject this hypothesis. We also find that while the Fed’s long-run response to inflation is higher in the latter period, the difference is not consistently statistically significant. Important ...
... depending on the exact empirical specification, with large standard errors that do not permit us to clearly reject this hypothesis. We also find that while the Fed’s long-run response to inflation is higher in the latter period, the difference is not consistently statistically significant. Important ...
Cambridge IGCSE and O Level Economics Workbook Answers
... for an explanation of why an increase in interest rates will affect borrowing, spending and saving. 4 The correct answer is Option A. Customers who buy shampoo are likely to need conditioner too. Option C is incorrect as sugar is not jointly demanded with tea (indeed, not all tea drinkers use sugar ...
... for an explanation of why an increase in interest rates will affect borrowing, spending and saving. 4 The correct answer is Option A. Customers who buy shampoo are likely to need conditioner too. Option C is incorrect as sugar is not jointly demanded with tea (indeed, not all tea drinkers use sugar ...
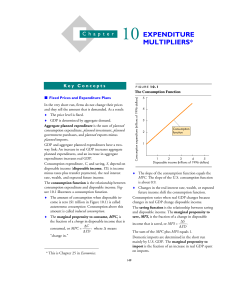
Chapter 25(10): Expenditure Multipliers
... expenditure schedule. Figure 10.2 illustrates an aggregate expenditure curve, AE = C + I + G + NX, where NX is exports minus imports. ♦ Induced expenditure is the sum of the components of aggregate expenditure that change with GDP. ♦ Autonomous expenditure is the sum of the components of aggregate e ...
... expenditure schedule. Figure 10.2 illustrates an aggregate expenditure curve, AE = C + I + G + NX, where NX is exports minus imports. ♦ Induced expenditure is the sum of the components of aggregate expenditure that change with GDP. ♦ Autonomous expenditure is the sum of the components of aggregate e ...
Adverse Selection, Slow Moving Capital and Misallocation
... by our model are qualitatively similar to those that would obtain in a model with convex adjustment costs. However, in our setting the costs of reallocating capital are endogenous to the economic environment; hence our model can help interpret recent empirical work that argues for the importance of ...
... by our model are qualitatively similar to those that would obtain in a model with convex adjustment costs. However, in our setting the costs of reallocating capital are endogenous to the economic environment; hence our model can help interpret recent empirical work that argues for the importance of ...
Essays on the Liquidity Trap, Oil Shocks, and the Great Moderation
... dynamic general equilibrium approach under the assumptions of rational expectations and nominal price rigidity. The rst chapter deals with the so-called “liquidity trap” – an issue which was raised originally by Keynes in the aftermath of the Great Depression. Since the nominal interest rate cannot ...
... dynamic general equilibrium approach under the assumptions of rational expectations and nominal price rigidity. The rst chapter deals with the so-called “liquidity trap” – an issue which was raised originally by Keynes in the aftermath of the Great Depression. Since the nominal interest rate cannot ...
Currency Wars or Efficient Spillovers?
... a version of the first welfare theorem that applies to settings in which private agents are governed by policymakers in each country and interact in a complete global market. International spillover effects in such a setting constitute pecuniary externalities that are mediated through world market ...
... a version of the first welfare theorem that applies to settings in which private agents are governed by policymakers in each country and interact in a complete global market. International spillover effects in such a setting constitute pecuniary externalities that are mediated through world market ...
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES RECONCILING POLICY DECISIONS AND DATA OUTCOMES
... “A higher level of pay settlements was much the most important factor in the faster rise of costs and prices during 1970…” (EPR, May 1971, p. 5.) ...
... “A higher level of pay settlements was much the most important factor in the faster rise of costs and prices during 1970…” (EPR, May 1971, p. 5.) ...
1 M.A.PART - I ECONOMIC PAPER
... measured on Y-axis. 45 line i.e. Y = C line I the unity line where at all levels, consumption and income are equal. The C= a + bY curve is linear consumption function curve which is based on the assumption that in the short run consumption changes by the equal amount. C = a +bY curve slopes upward f ...
... measured on Y-axis. 45 line i.e. Y = C line I the unity line where at all levels, consumption and income are equal. The C= a + bY curve is linear consumption function curve which is based on the assumption that in the short run consumption changes by the equal amount. C = a +bY curve slopes upward f ...
Keynesian and Monetarist Views on the German Unemployment
... discussed. Regarding the policy dispute, first the monetarist demand for wage moderation is reviewed, which is followed by a discussion of the Keynesian doubts on the effectiveness of this policy. In conclusion, this paper cannot hope to settle the long-running controversy on this issue, but it show ...
... discussed. Regarding the policy dispute, first the monetarist demand for wage moderation is reviewed, which is followed by a discussion of the Keynesian doubts on the effectiveness of this policy. In conclusion, this paper cannot hope to settle the long-running controversy on this issue, but it show ...
Christiano, Eichenbaum and Rebelo
... shocks that make the zero bound binding for a deterministic number of periods. Again, we find that the government-spending multiplier is larger when the zero bound binds. Allowing for capital accumulation has two effects. First, for a given size shock it reduces the likelihood that the zero bound be ...
... shocks that make the zero bound binding for a deterministic number of periods. Again, we find that the government-spending multiplier is larger when the zero bound binds. Allowing for capital accumulation has two effects. First, for a given size shock it reduces the likelihood that the zero bound be ...
NATIONAL BANK OF POLAND WORKING PAPER No. 135
... of money in monetary policy analyses. There is no consensus as to whether the There are many similar works (theoretical and empirical) indicating the importance of money as an argument of the central bank reaction function in a world of incomplete information. For example, in the work of Berg et al. ...
... of money in monetary policy analyses. There is no consensus as to whether the There are many similar works (theoretical and empirical) indicating the importance of money as an argument of the central bank reaction function in a world of incomplete information. For example, in the work of Berg et al. ...
Advanced Macroeconomics - Juridica – Kolegji Evropian
... interest rates and the balance of payments. This book attempts to explain the domestic and international factors responsible for creating the equilibrium of the balance of payments, interest rates and inflation. It is hoped that this book’s contents will help students to think, analyze and apply wha ...
... interest rates and the balance of payments. This book attempts to explain the domestic and international factors responsible for creating the equilibrium of the balance of payments, interest rates and inflation. It is hoped that this book’s contents will help students to think, analyze and apply wha ...
E A conomic Statistics in ustralia
... - ISIC Rev. 4 - CPC ver. 2 - COICOP - COFOG - BoP coherent with BPM6 ...
... - ISIC Rev. 4 - CPC ver. 2 - COICOP - COFOG - BoP coherent with BPM6 ...
A Dynamic Model of Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply
... Current inflation in one year becomes past inflation in the next year. Therefore, any exogenous factors that affect inflation in 2016 will affect both output and inflation in 2017. This in turn, will affect both output and inflation in 2018. And so on and on. In this way, output and inflation can ch ...
... Current inflation in one year becomes past inflation in the next year. Therefore, any exogenous factors that affect inflation in 2016 will affect both output and inflation in 2017. This in turn, will affect both output and inflation in 2018. And so on and on. In this way, output and inflation can ch ...
By How Much Does GDP Rise If the Government Buys More Output?
... the government purchases enter preferences in a separable fashion: they do not affect households’ marginal rate of substitution between consumption and work or between consumption this year and in any future year. Military spending is the obvious example. If instead the government provided consumers ...
... the government purchases enter preferences in a separable fashion: they do not affect households’ marginal rate of substitution between consumption and work or between consumption this year and in any future year. Military spending is the obvious example. If instead the government provided consumers ...
Fair Weather or Foul? The Macroeconomic Effects of El Niño∗
... not directly a¤ected by El Niño, his analysis rests on a strong assumption (homogeneity of impact) and it does not take into account the indirect e¤ects of El Niño shocks. We contribute to the literature that assesses the macroeconomic e¤ects of weather shocks in several dimensions, including a nove ...
... not directly a¤ected by El Niño, his analysis rests on a strong assumption (homogeneity of impact) and it does not take into account the indirect e¤ects of El Niño shocks. We contribute to the literature that assesses the macroeconomic e¤ects of weather shocks in several dimensions, including a nove ...
Principles Of Economics
... into Chapter 1, to more clearly and efficiently prepare students for the economic way of thinking and the approach to learning economics used in the text. Chapter 2 presents comparative advantage as the basis for exchange (this was Chapter 3 in the First Edition) and Chapter 3 introduces supply and ...
... into Chapter 1, to more clearly and efficiently prepare students for the economic way of thinking and the approach to learning economics used in the text. Chapter 2 presents comparative advantage as the basis for exchange (this was Chapter 3 in the First Edition) and Chapter 3 introduces supply and ...