Prices vs. quantities with endogenous cost structure - CREE
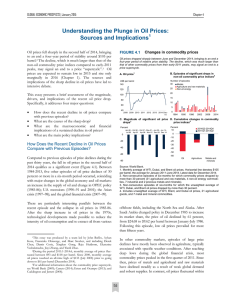
... where V ar [ ] is the variance operator. This …rst order condition implies that a higher expected production level increases the …rms’ investments in capital (decreases the optimal ). Moreover, for a given expected production level, it can be shown that the …rms choose a higher capital intensity (l ...
... where V ar [ ] is the variance operator. This …rst order condition implies that a higher expected production level increases the …rms’ investments in capital (decreases the optimal ). Moreover, for a given expected production level, it can be shown that the …rms choose a higher capital intensity (l ...
Determinants of Inflation and Feasibility of Inflation Targeting in a
... not only on the extent to which the authorities can influence the rate of inflation through money supply but also on the relative strength of other internal and external factors affecting inflation. The present study investigates possible determinants of inflation and also assesses the feasibility o ...
... not only on the extent to which the authorities can influence the rate of inflation through money supply but also on the relative strength of other internal and external factors affecting inflation. The present study investigates possible determinants of inflation and also assesses the feasibility o ...
The Costs of Fiscal Inflexibility
... both closed and open economies utilising New Classical Keynesian Synthesis models where the structural model and the description of policy makers’ objectives are consistently microfounded. (See for example, Woodford (2003) for a comprehensive treatment of the closed economy case, and Clarida et al ( ...
... both closed and open economies utilising New Classical Keynesian Synthesis models where the structural model and the description of policy makers’ objectives are consistently microfounded. (See for example, Woodford (2003) for a comprehensive treatment of the closed economy case, and Clarida et al ( ...
The Misperceptions Theory and the Nonneutrality of Money
... quickly to restore equilibrium – Besides, fiscal policy increases output by making workers worse off, since they face higher taxes – Instead, government spending should be determined by cost-benefit analysis ...
... quickly to restore equilibrium – Besides, fiscal policy increases output by making workers worse off, since they face higher taxes – Instead, government spending should be determined by cost-benefit analysis ...
Quiz: Homework 11
... Homework 11 1. In economic terms, menu costs are A. the cost of services listed in a menu. B. the costs to producer of changing prices. C. the cost of goods listed on a business rate sheet. D. the price of food on restaurant menus. Answer: B 2. According to the dynamic AD Curve, if M + v = 7%, while ...
... Homework 11 1. In economic terms, menu costs are A. the cost of services listed in a menu. B. the costs to producer of changing prices. C. the cost of goods listed on a business rate sheet. D. the price of food on restaurant menus. Answer: B 2. According to the dynamic AD Curve, if M + v = 7%, while ...
inflation - nagleeco-2009
... The link between productivity and inflation is well associated with wage levels. High productivity enables greater dynamic efficiency and hence reduces the effects of demand-pull inflation. Productivity specifically has the impact ensuring greater production of goods and therefore minimises inflati ...
... The link between productivity and inflation is well associated with wage levels. High productivity enables greater dynamic efficiency and hence reduces the effects of demand-pull inflation. Productivity specifically has the impact ensuring greater production of goods and therefore minimises inflati ...
Managing-in-a-Global-Economy-1st-Edition-Marthinsen-Test-Bank
... A. GDP measures a nation’s income, and GNP measures a nation’s output. B. Largely in the minds of the public, because economically, there is no difference. C. GDP measures the income earned from the production of all final goods and services within a nation’s borders; GNP measures the income earned ...
... A. GDP measures a nation’s income, and GNP measures a nation’s output. B. Largely in the minds of the public, because economically, there is no difference. C. GDP measures the income earned from the production of all final goods and services within a nation’s borders; GNP measures the income earned ...
macronotes - Houston H. Stokes Page
... Employment is where supply of labor = demand for labor (see figure 3-5). N* = full employment. Full employment is not max amount of work people would do, only what they would do for the level of the real wage prevailing. Define full employment as Y* where ...
... Employment is where supply of labor = demand for labor (see figure 3-5). N* = full employment. Full employment is not max amount of work people would do, only what they would do for the level of the real wage prevailing. Define full employment as Y* where ...
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES WAGES, RELATIVE PRICES AND CHOICE BETWEEN
... parity holds. Their analysis assumed that the indexation parameter is an endogenous variable set at its optimal value in each exchange rate regime. Here we will assume that because of institutional or legal constraints, the degree of indexation remains the same when the exchange rate regime changes. ...
... parity holds. Their analysis assumed that the indexation parameter is an endogenous variable set at its optimal value in each exchange rate regime. Here we will assume that because of institutional or legal constraints, the degree of indexation remains the same when the exchange rate regime changes. ...
College Board Course Description
... AP classes require extra time on the part of the teacher for preparation, personal consultation with students, and the reading of a much larger number of assignments than would normally be given to students in regular classes. Accordingly, some schools assign reduced teaching hours to any teacher of ...
... AP classes require extra time on the part of the teacher for preparation, personal consultation with students, and the reading of a much larger number of assignments than would normally be given to students in regular classes. Accordingly, some schools assign reduced teaching hours to any teacher of ...
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES THE EFFECT OF CONVENTIONAL AND UNCONVENTIONAL MONETARY
... In principle, the variables, X, might be changing over time even if the state remains constant. By studying stationary solutions to stochastic difference equations, we are assuming this does not happen. Every time the economy enters state, s, we would expect to see the same values of all of the obse ...
... In principle, the variables, X, might be changing over time even if the state remains constant. By studying stationary solutions to stochastic difference equations, we are assuming this does not happen. Every time the economy enters state, s, we would expect to see the same values of all of the obse ...
Chapter 11 Introduction Learning Objectives
... • The classical economists’ world was one of fully utilized resources. • In the 1930s, Europe and the United States entered a period of economic decline that could not be explained by the classical model • John Maynard Keynes developed an explanation that has become known as the Keynesian model. Cop ...
... • The classical economists’ world was one of fully utilized resources. • In the 1930s, Europe and the United States entered a period of economic decline that could not be explained by the classical model • John Maynard Keynes developed an explanation that has become known as the Keynesian model. Cop ...
Chapter 5: Growth and Recession in the US Economy
... just since 1980. This tendency for output and real income to increase over time when it persists is called long term economic growth. Indeed, over the past four decades pictured here, the growth rate of real GDP has averaged 3.4% per year. If that rate is maintained, real GDP will double again in on ...
... just since 1980. This tendency for output and real income to increase over time when it persists is called long term economic growth. Indeed, over the past four decades pictured here, the growth rate of real GDP has averaged 3.4% per year. If that rate is maintained, real GDP will double again in on ...
AP Macroeconomics
... AP classes require extra time on the part of the teacher for preparation, personal consultation with students, and the reading of a much larger number of assignments than would normally be given to students in regular classes . Accordingly, some schools assign reduced teaching hours to any teacher o ...
... AP classes require extra time on the part of the teacher for preparation, personal consultation with students, and the reading of a much larger number of assignments than would normally be given to students in regular classes . Accordingly, some schools assign reduced teaching hours to any teacher o ...
PDF
... into a “post-reform” phase where the effects of liberalising reforms are being digested and the benefits of further reforms are being queried. Over this period there have been numerous reviews of Ghana’s economy, and several examinations of agricultural policies and performance, including periodic W ...
... into a “post-reform” phase where the effects of liberalising reforms are being digested and the benefits of further reforms are being queried. Over this period there have been numerous reviews of Ghana’s economy, and several examinations of agricultural policies and performance, including periodic W ...
GDP
... in price in order to only retain the effect of the changes in quantity? • The solution is to measure GDP in 2 different years with the same set of prices. Then the difference in the two measures of GDP will only include the change in quantity. • Which set of prices should we use? • Depending o ...
... in price in order to only retain the effect of the changes in quantity? • The solution is to measure GDP in 2 different years with the same set of prices. Then the difference in the two measures of GDP will only include the change in quantity. • Which set of prices should we use? • Depending o ...