
Long run Aggregate Supply
... full employment -- a level o f output for which the number of jobs created equals the number of qualified persons available to fill the jobs. This is equilibrium in the labor market. People are frictionally and structurally unemployed. There is no cyclical unemployment. another wa y to state full em ...
... full employment -- a level o f output for which the number of jobs created equals the number of qualified persons available to fill the jobs. This is equilibrium in the labor market. People are frictionally and structurally unemployed. There is no cyclical unemployment. another wa y to state full em ...
Practice Test Here… - Greece Social Studies
... 22. What is the difference between Gross Domestic Product and Gross National Product? 23. Give an example of three items that would not be counted in Gross Domestic Product. 24. What are the forces that can cause aggregate demand to shift? 25. What are the forces that can cause aggregate supply to s ...
... 22. What is the difference between Gross Domestic Product and Gross National Product? 23. Give an example of three items that would not be counted in Gross Domestic Product. 24. What are the forces that can cause aggregate demand to shift? 25. What are the forces that can cause aggregate supply to s ...
Section IV Vocabulary review Matching Social insurance automatic
... 1. __________________________________ is the investment spending that a business intends to do during a given period. 2. __________________________________is the level of real GDP the economy would produce if all prices were fully flexible. 3. _____________________________ are nominal wages that are ...
... 1. __________________________________ is the investment spending that a business intends to do during a given period. 2. __________________________________is the level of real GDP the economy would produce if all prices were fully flexible. 3. _____________________________ are nominal wages that are ...
INSTITUTE OF ACTUARIES OF INDIA EXAMINATIONS 24
... B) Weak growth in aggregate demand keeps the economy below potential GDP, so unemployment rises but inflation falls C) Aggregate demand grows so quickly that the inflation rate rises as unemployment rises D) Long-run aggregate supply increases fast enough so that inflation falls as unemployment fall ...
... B) Weak growth in aggregate demand keeps the economy below potential GDP, so unemployment rises but inflation falls C) Aggregate demand grows so quickly that the inflation rate rises as unemployment rises D) Long-run aggregate supply increases fast enough so that inflation falls as unemployment fall ...
10th IAEE European Conference
... potential evidence of asymmetries in the link between oil prices and economic activity. Second, contrary to previous studies three methods, the linear model, the switching model (RS-R) and a threshold model (TA-R) are utilized to examine the dynamics of this relationship. The regime-switching model ...
... potential evidence of asymmetries in the link between oil prices and economic activity. Second, contrary to previous studies three methods, the linear model, the switching model (RS-R) and a threshold model (TA-R) are utilized to examine the dynamics of this relationship. The regime-switching model ...
Slides
... result in a substantial increase in the rate of personal bankruptcies, which could lead to a secondary string of bankruptcies of financial institutions as well. Another long-run consequence could be a decline in consumer and business confidence, and another, possibly worldwide, recession.” ...
... result in a substantial increase in the rate of personal bankruptcies, which could lead to a secondary string of bankruptcies of financial institutions as well. Another long-run consequence could be a decline in consumer and business confidence, and another, possibly worldwide, recession.” ...
Unit 5 RP
... each year. What will happen to nominal GDP and the price level the next year if the FED keeps the money supply constant? c. What money supply should the FED set next year if it wants to keep the price level stable? d. What money supply should the FED set next year if it wants inflation of 10%? 8. Su ...
... each year. What will happen to nominal GDP and the price level the next year if the FED keeps the money supply constant? c. What money supply should the FED set next year if it wants to keep the price level stable? d. What money supply should the FED set next year if it wants inflation of 10%? 8. Su ...
Section 1: Guided Reading and Review
... answer in the blank provided. You will not use all the terms. ...
... answer in the blank provided. You will not use all the terms. ...
Inflation - Murphonomics
... Problems in Measuring Inflation Inflation is measured by using a weighted basket of goods and looking at the changes in price. This method is known as the Consumer Price Index. However, in practice, there are many practical difficulties for measuring inflation. 1. There is no such thing as the avera ...
... Problems in Measuring Inflation Inflation is measured by using a weighted basket of goods and looking at the changes in price. This method is known as the Consumer Price Index. However, in practice, there are many practical difficulties for measuring inflation. 1. There is no such thing as the avera ...
Presentationstitel
... solicitation for the purchase or sale of any financial instrument. The information contained herein has no regard to the specific investment objectives, the financial situation or particular needs of any particular recipient. Relevant and specific professional advice should always be obtained before ...
... solicitation for the purchase or sale of any financial instrument. The information contained herein has no regard to the specific investment objectives, the financial situation or particular needs of any particular recipient. Relevant and specific professional advice should always be obtained before ...
Inflation - Murphonomics
... 2. Changes in the quality of goods. Changes in the quality of goods mean that price rises may not reflect inflation, but just the fact it is a different good. For example, computers have many more features than 10 years ago, so it is difficult to compare prices because they are effectively different ...
... 2. Changes in the quality of goods. Changes in the quality of goods mean that price rises may not reflect inflation, but just the fact it is a different good. For example, computers have many more features than 10 years ago, so it is difficult to compare prices because they are effectively different ...
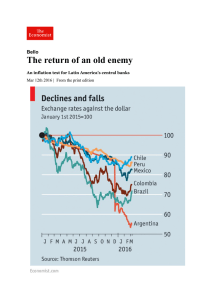
The return of an old enemy | The Economist
... Official statistics put the rise in the consumer-price index in Venezuela last year at 181%, the world’s highest; the IMF forecasts 720% this year. Venezuela is extreme in its ...
... Official statistics put the rise in the consumer-price index in Venezuela last year at 181%, the world’s highest; the IMF forecasts 720% this year. Venezuela is extreme in its ...
Unemployment and Inflation
... • Cyclical unemployment - caused by recessions. People aren’t buying goods so workers are laid off. ...
... • Cyclical unemployment - caused by recessions. People aren’t buying goods so workers are laid off. ...
Economic terms
... The ratio of national income to the quantity of money in circulation; velocity measures the average number of times money changes hands in generating national income per year (monetarist theory). Inelastic Demand A term used when the percentage change in quantity demanded is smaller than the percent ...
... The ratio of national income to the quantity of money in circulation; velocity measures the average number of times money changes hands in generating national income per year (monetarist theory). Inelastic Demand A term used when the percentage change in quantity demanded is smaller than the percent ...
Stiglitz + Welsh, A selection of terms (for HØKON1101)
... the argument that industries must be protected from foreign competition while they are young, until they have a chance to acquire the skills to enable them to compete on equal terms inferior good a good the consumption of which falls as income rises infinite elasticity the situation that exists when ...
... the argument that industries must be protected from foreign competition while they are young, until they have a chance to acquire the skills to enable them to compete on equal terms inferior good a good the consumption of which falls as income rises infinite elasticity the situation that exists when ...
tma07 - john p birchall
... The second possibility assumes that costs do rise as output increases, this would be the case if recruiting extra labour could only be done by offering higher wages. In this case the AS curve would slope up to the right and would still retain the vertical character when full employment is reached. ...
... The second possibility assumes that costs do rise as output increases, this would be the case if recruiting extra labour could only be done by offering higher wages. In this case the AS curve would slope up to the right and would still retain the vertical character when full employment is reached. ...
The Stockholm School
... Purchasing Power Parity General equilibrium … extension of Walras A writer less generous than Cassel would be hard to find. Marx at least paid tribute to Quesnay and Ricardo. Cassel paid tribute to nobody. Walras had written the first system of simultaneous equations of general equilibrium. Pareto h ...
... Purchasing Power Parity General equilibrium … extension of Walras A writer less generous than Cassel would be hard to find. Marx at least paid tribute to Quesnay and Ricardo. Cassel paid tribute to nobody. Walras had written the first system of simultaneous equations of general equilibrium. Pareto h ...
Chapter 7 Review Questions Price Indexes and Inflation Dr
... It is the tendency of people to protect themselves against inflation by purchasing more of goods which have become relatively cheaper (that may have risen in price, but less than other goods) and to avoid goods which have become relatively more expensive. _True_7. The core PCE deflator is the measur ...
... It is the tendency of people to protect themselves against inflation by purchasing more of goods which have become relatively cheaper (that may have risen in price, but less than other goods) and to avoid goods which have become relatively more expensive. _True_7. The core PCE deflator is the measur ...
Chapter 30: Money Growth and Inflation Principles of Economics, 7
... independent of the money supply, so changes in the money supply result in changes in prices. iii. Figure 3: Nominal GDP, the Quantity of Money, and the Velocity of Money. P. 641. iv. We now have all the elements necessary to explain the equilibrium price level and inflation: ...
... independent of the money supply, so changes in the money supply result in changes in prices. iii. Figure 3: Nominal GDP, the Quantity of Money, and the Velocity of Money. P. 641. iv. We now have all the elements necessary to explain the equilibrium price level and inflation: ...
Business_cycle_intro [tryb zgodności]
... • shocks: exogenous changes in aggregate supply or demand • Shocks temporarily push the economy away from fullemployment. ...
... • shocks: exogenous changes in aggregate supply or demand • Shocks temporarily push the economy away from fullemployment. ...






















![Business_cycle_intro [tryb zgodności]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/017135785_1-b01d420c7557f888d44471e9e012fe51-300x300.png)