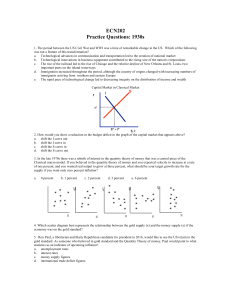
Lecture 17 - Nottingham
... – Empirical evidence suggests that the effect of i changes on demand is less than effect of Y changes – So expect that demand increases as Y increases, so prices are countercyclical ...
... – Empirical evidence suggests that the effect of i changes on demand is less than effect of Y changes – So expect that demand increases as Y increases, so prices are countercyclical ...
Martin Feldstein`s remarks
... don't mean just recently. I mean over a much longer time. And that underestimation and the resulting public perception is important -- not just to us as economists trying to understand exactly where the economy is moving, but it is important for a variety of reasons. I think the sense that real inco ...
... don't mean just recently. I mean over a much longer time. And that underestimation and the resulting public perception is important -- not just to us as economists trying to understand exactly where the economy is moving, but it is important for a variety of reasons. I think the sense that real inco ...
(PDF)
... domestic supply expanded 57 billion cubic feet.18 The U.S. Energy Information Administration reported that working natural gas in storage totaled 2,479 billion cubic feet at the end of March, which was 816 billion cubic feet greater than the 5 year maximum for the date.19 Nonfuel Import Prices. The ...
... domestic supply expanded 57 billion cubic feet.18 The U.S. Energy Information Administration reported that working natural gas in storage totaled 2,479 billion cubic feet at the end of March, which was 816 billion cubic feet greater than the 5 year maximum for the date.19 Nonfuel Import Prices. The ...
Adaptive microfoundations for emergent macroeconomics
... game theory (Shubik, 1975) does not provide a way out under rather general conditions. Whenever players are heterogeneous as regards their strategy and information sets, a full adherence to strategic behavior modeling returns computationally complex problems, that is problems whose solution time (me ...
... game theory (Shubik, 1975) does not provide a way out under rather general conditions. Whenever players are heterogeneous as regards their strategy and information sets, a full adherence to strategic behavior modeling returns computationally complex problems, that is problems whose solution time (me ...
Inflation, Recession, and Stagflation
... only one or two years in the early 1950's, and these declines were negli gible. • Price indices remained stable for some years in many of these countries. ...
... only one or two years in the early 1950's, and these declines were negli gible. • Price indices remained stable for some years in many of these countries. ...
(2008-2015Q2) (Comparison With Great Depression)
... There is bulk of research in economic literature examining the causes and dynamics of the Great Depression (GD) between the years 1929 to 1941. A mixture of various factors may have interacted to lead the economy into a turmoil of low output and high inflation along with high nominal wages. In this ...
... There is bulk of research in economic literature examining the causes and dynamics of the Great Depression (GD) between the years 1929 to 1941. A mixture of various factors may have interacted to lead the economy into a turmoil of low output and high inflation along with high nominal wages. In this ...
UNIT TWO: INTRODUCTION INTO MACROECONOMICS Part One
... Below are some of the concepts that Classical Economists believe in-and to some degree they show how the economy is self-correcting in the long run. a. Price as a Natural Stabilizer: when economies are in a recession, prices will begin to drop. They will drop to the point where that increases aggre ...
... Below are some of the concepts that Classical Economists believe in-and to some degree they show how the economy is self-correcting in the long run. a. Price as a Natural Stabilizer: when economies are in a recession, prices will begin to drop. They will drop to the point where that increases aggre ...
A Keynesian Macroeconomic Model with New
... derive these testable restrictionsfrom a Keynesianmacroeconomicmodel. The Keynesian model presented below produces results different from other Keynesian models because it presumes that monetarypolicy is implementedin a manner which causes expected aggregate demand to equal expected aggregatesupply. ...
... derive these testable restrictionsfrom a Keynesianmacroeconomicmodel. The Keynesian model presented below produces results different from other Keynesian models because it presumes that monetarypolicy is implementedin a manner which causes expected aggregate demand to equal expected aggregatesupply. ...
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES AN INTEGRATED APPROACH
... In Richard Clarida, Jordi Gali and Mark Gertler ((1999); hereafter CGG), we presented a normative analysis of monetary policy within a simple optimization-based closed economy framework. We derived the optimal policy rule and, among other things, characterized the gains from commitment. Also, we mad ...
... In Richard Clarida, Jordi Gali and Mark Gertler ((1999); hereafter CGG), we presented a normative analysis of monetary policy within a simple optimization-based closed economy framework. We derived the optimal policy rule and, among other things, characterized the gains from commitment. Also, we mad ...
chapter 7 - Spring Branch ISD
... New 7. What is the value added by all the firms A–E from the production of a product as described below? What did each firm add separately in value and what does it total? Stage of production ...
... New 7. What is the value added by all the firms A–E from the production of a product as described below? What did each firm add separately in value and what does it total? Stage of production ...
Document
... Economic aggregates—economic measures that summarize data across many different markets for goods, services, workers, and assets. (Assets are items that serve as a store of value, like cash or real estate.) For example, macroeconomics analyzes the performance of the economy by studying aggregate out ...
... Economic aggregates—economic measures that summarize data across many different markets for goods, services, workers, and assets. (Assets are items that serve as a store of value, like cash or real estate.) For example, macroeconomics analyzes the performance of the economy by studying aggregate out ...
Optimal Devaluations - Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis
... can have in fostering good–or bad!–reputation will be absent in this analysis. We first show, in Section 2, how the introduction of commodities implies that domestic costs interact with commodity prices and changes the transmission mechanism of nominal exchange rate movements. We also show that the ...
... can have in fostering good–or bad!–reputation will be absent in this analysis. We first show, in Section 2, how the introduction of commodities implies that domestic costs interact with commodity prices and changes the transmission mechanism of nominal exchange rate movements. We also show that the ...
Module History and Alternative Views of
... predicts which party will get into office based on economy in months preceding the election ...
... predicts which party will get into office based on economy in months preceding the election ...
Answer Key - McGraw-Hill Education Canada
... 43A. Unemployment is voluntary according to neoclassical theory because it is believed that markets in general, and the labour market in particular, are perfectly competitive. Unemployment (a surplus of labour) therefore can only occur if the prevailing wage rate is above the equilibrium rate. This ...
... 43A. Unemployment is voluntary according to neoclassical theory because it is believed that markets in general, and the labour market in particular, are perfectly competitive. Unemployment (a surplus of labour) therefore can only occur if the prevailing wage rate is above the equilibrium rate. This ...
Shanghai American School
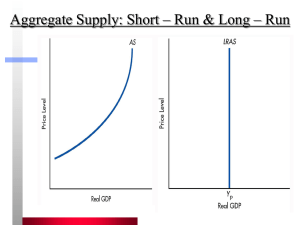
... --Demand-pull inflation: Shifts in the intermediate and vertical ranges will cause demand-pull inflation with an increase in aggregate demand (Figures 11.7). >>Shifts in the horizontal range will cause quantity changes but only mild price level changes --Decreases in AD: If AD decreases, recession a ...
... --Demand-pull inflation: Shifts in the intermediate and vertical ranges will cause demand-pull inflation with an increase in aggregate demand (Figures 11.7). >>Shifts in the horizontal range will cause quantity changes but only mild price level changes --Decreases in AD: If AD decreases, recession a ...
1 - Rose
... money supply will move the economy to point ____ in the short run and to point ____ in the long run. A. 4 ; 3 B. 4 ; 1 C. 2 ; 3 D. 2 ; 1 E. 3 ; 1 40. The economy in Figure 17 is initially in long-run equilibrium at point 1. An increase in crude oil prices will move the economy to point ____. If the ...
... money supply will move the economy to point ____ in the short run and to point ____ in the long run. A. 4 ; 3 B. 4 ; 1 C. 2 ; 3 D. 2 ; 1 E. 3 ; 1 40. The economy in Figure 17 is initially in long-run equilibrium at point 1. An increase in crude oil prices will move the economy to point ____. If the ...
Problem Set 2
... Essay Questions for Chapter 22 1) Suppose that Ahmet has just graduated from university and looking for a job. However, as a first-time job seeker he lacks the sufficient knowledge for finding the company that has the job that is available and suitable for him. Thus, he is currently unemployed. What ...
... Essay Questions for Chapter 22 1) Suppose that Ahmet has just graduated from university and looking for a job. However, as a first-time job seeker he lacks the sufficient knowledge for finding the company that has the job that is available and suitable for him. Thus, he is currently unemployed. What ...
mankiw6e-chap13_2007_
... = 19/6.7 = 2.8 percentage points of GDP were lost for each 1 percentage point reduction in inflation. CHAPTER 13 ...
... = 19/6.7 = 2.8 percentage points of GDP were lost for each 1 percentage point reduction in inflation. CHAPTER 13 ...