Relative British and American Income Levels during the First
... As Gallman (1966) pointed out forty years ago, the projection approach faces a fundamental index number problem since it compares income using relative prices of a single year. Maddison (1995, 2001), for example, uses 1990 prices. The problem is that the goods and services produced in 1990 bear litt ...
... As Gallman (1966) pointed out forty years ago, the projection approach faces a fundamental index number problem since it compares income using relative prices of a single year. Maddison (1995, 2001), for example, uses 1990 prices. The problem is that the goods and services produced in 1990 bear litt ...
Spring 2015 TEST 3 w/o solution
... 18. (Figure: Monetary Policy and the AD–SRAS Model) Refer to the information in the figure Monetary Policy and the AD–SRAS Model. If the economy is in a recessionary gap at point f, it could move to point g as a result of: A) an increase in the money supply. B) selling government securities in the o ...
... 18. (Figure: Monetary Policy and the AD–SRAS Model) Refer to the information in the figure Monetary Policy and the AD–SRAS Model. If the economy is in a recessionary gap at point f, it could move to point g as a result of: A) an increase in the money supply. B) selling government securities in the o ...
The Art and Science of Economics
... Problems with the CPI CPI tends to overstate inflation for the following reasons There is a quality bias because the CPI assumes the quality of the market basket remains relatively constant over time Because the CPI holds constant the kind and amount of goods and services in the typical market bask ...
... Problems with the CPI CPI tends to overstate inflation for the following reasons There is a quality bias because the CPI assumes the quality of the market basket remains relatively constant over time Because the CPI holds constant the kind and amount of goods and services in the typical market bask ...
Chapter 19 The theory of effective demand
... In this and the following chapters the focus is shifted from long-run macroeconomics to short-run macroeconomics. The long-run models concentrated on factors that are important for the economic evolution over a time horizon of at least 10-15 years. With such a horizon it is the development on the su ...
... In this and the following chapters the focus is shifted from long-run macroeconomics to short-run macroeconomics. The long-run models concentrated on factors that are important for the economic evolution over a time horizon of at least 10-15 years. With such a horizon it is the development on the su ...
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES MONETARY AND FISCAL POLICIES IN AN OPEN ECONOMY
... reducing imports relative to exports [see Mussa (1974)]. ...
... reducing imports relative to exports [see Mussa (1974)]. ...
Presentation Plus!
... macroeconomic model used to show aggregate demand by all the economic sectors. • The equation for the output-expenditure model is GDP = C + I + G + F . • Each sector spends its income on different types of goods and services. ...
... macroeconomic model used to show aggregate demand by all the economic sectors. • The equation for the output-expenditure model is GDP = C + I + G + F . • Each sector spends its income on different types of goods and services. ...
Ch. 12: Economic Fluctuations (Handout)
... Keynes believed that workers were influenced by money illusion. Meaning that workers would respond to changes in nominal wages rather than real wages. ...
... Keynes believed that workers were influenced by money illusion. Meaning that workers would respond to changes in nominal wages rather than real wages. ...
Aspects of Microeconomics and Macroeconomics with Special
... 40. Discuss the effects of shifts in the aggregate demand curve on the aggregate price level. 41. Discuss the effects of shifts in the aggregate supply curve on the aggregate price level. 42. What do you understand by supply-side economics? 43. What do you understand by inflation, and how is it meas ...
... 40. Discuss the effects of shifts in the aggregate demand curve on the aggregate price level. 41. Discuss the effects of shifts in the aggregate supply curve on the aggregate price level. 42. What do you understand by supply-side economics? 43. What do you understand by inflation, and how is it meas ...
Should the Fed have Followed the Rule - MyWeb
... a very low level despite recognizing that the economy was growing briskly. In this simulation, we assume that it started raising rates in the fourth quarter of 2003 with further increases in interest rates until it reached the rate suggested by Taylor’s rule (25 basis points at each meeting until 20 ...
... a very low level despite recognizing that the economy was growing briskly. In this simulation, we assume that it started raising rates in the fourth quarter of 2003 with further increases in interest rates until it reached the rate suggested by Taylor’s rule (25 basis points at each meeting until 20 ...
Implications of insights from behavioral economics for
... shock, consumption will be higher than the socially efficient level (the economy is “overheated”), as consumers do not take into account the negative externality on others. Thus, in booms, taxes should be raised to dampen the “overheating” of the economy. From a policy point of view, a key aspect of ...
... shock, consumption will be higher than the socially efficient level (the economy is “overheated”), as consumers do not take into account the negative externality on others. Thus, in booms, taxes should be raised to dampen the “overheating” of the economy. From a policy point of view, a key aspect of ...
Policy - QC Economics
... • Changes in velocity are not likely to offset changes in the money supply. • Changes in the money supply will largely determine changes in aggregate demand, and therefore changes in Real GDP and the price level. • An increase in the money supply will raise aggregate demand and increase both Real GD ...
... • Changes in velocity are not likely to offset changes in the money supply. • Changes in the money supply will largely determine changes in aggregate demand, and therefore changes in Real GDP and the price level. • An increase in the money supply will raise aggregate demand and increase both Real GD ...
Chapter 7
... biases of the CPI because it uses the price change and the public response to those price changes in the basket of goods and services produced in the current year and the preceding year. In practice, the GDP deflator suffers from some of the CPI’s problems because the Commerce Department does not di ...
... biases of the CPI because it uses the price change and the public response to those price changes in the basket of goods and services produced in the current year and the preceding year. In practice, the GDP deflator suffers from some of the CPI’s problems because the Commerce Department does not di ...
Keynes-Wicksell and Neoclassical Models of Money and
... money, however the money is distributed, produces an instantaneous doubling of the price level so long as the expected growth rate of the money supply is the same before and after the "blip" in the money supply. This according to KW theorists suggests that there is something amiss in the short-run d ...
... money, however the money is distributed, produces an instantaneous doubling of the price level so long as the expected growth rate of the money supply is the same before and after the "blip" in the money supply. This according to KW theorists suggests that there is something amiss in the short-run d ...
Why-nominal-gdp-matters
... productivity. But for the business community, who need a certain amount of 'near term' focus if they're to see their organizations into the 'long term', nominal GDP is far more important. Here's why: 1. Nominal GDP matters for earnings and revenue. If nominal GDP doesn't grow, revenue can only be in ...
... productivity. But for the business community, who need a certain amount of 'near term' focus if they're to see their organizations into the 'long term', nominal GDP is far more important. Here's why: 1. Nominal GDP matters for earnings and revenue. If nominal GDP doesn't grow, revenue can only be in ...
Factor Price Equalization and Stolper
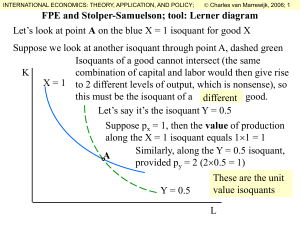
... FPE and Stolper-Samuelson; tool: Lerner diagram Let’s look at point A on the blue X = 1 isoquant for good X Suppose we look at another isoquant through point A, dashed green Isoquants of a good cannot intersect (the same combination of capital and labor would then give rise K X = 1 to 2 different le ...
... FPE and Stolper-Samuelson; tool: Lerner diagram Let’s look at point A on the blue X = 1 isoquant for good X Suppose we look at another isoquant through point A, dashed green Isoquants of a good cannot intersect (the same combination of capital and labor would then give rise K X = 1 to 2 different le ...
My lecture
... – Firms negotiate nominal wages with their workers. – When firms negotiate nominal wages, they have designed the wage according to expected price level. – If the general price level rises, the real wage paid to the workers have fallen. – Firms’ cost of production falls and they produce more. ...
... – Firms negotiate nominal wages with their workers. – When firms negotiate nominal wages, they have designed the wage according to expected price level. – If the general price level rises, the real wage paid to the workers have fallen. – Firms’ cost of production falls and they produce more. ...
ECON 4110: Money, Banking, and the Macroeconomy Final Exam
... B) the demand for real balances should increase more than proportionately with increases in real income. C) movements in the interest rate should not affect the demand for money. D) movements in the price level should not affect the demand for money. 24) An individual with a high income will probabl ...
... B) the demand for real balances should increase more than proportionately with increases in real income. C) movements in the interest rate should not affect the demand for money. D) movements in the price level should not affect the demand for money. 24) An individual with a high income will probabl ...
Ch - Pearson Canada
... a supply curve. The responsiveness of the demand for a good to a change in the price of a substitute or complement, other things remaining the same. It is calculated as the percentage change in the quantity demanded of the good divided by the percentage change in the price of the substitute or ...
... a supply curve. The responsiveness of the demand for a good to a change in the price of a substitute or complement, other things remaining the same. It is calculated as the percentage change in the quantity demanded of the good divided by the percentage change in the price of the substitute or ...
Chapter 9
... Increasing the number of workers increases output, but at a diminishing rate. Diminishing returns manifest as an eversteeper SRAS curve. ...
... Increasing the number of workers increases output, but at a diminishing rate. Diminishing returns manifest as an eversteeper SRAS curve. ...
Chapter 13 GDP Output Gap - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... gap may have been smaller than thought; workers may have resisted pay cuts; and perhaps most important, at low rates of either inflation or deflation firms may change prices less frequently, reducing the impact of output gaps. If so, this would provide a buffer to deflation in the rich world today, ...
... gap may have been smaller than thought; workers may have resisted pay cuts; and perhaps most important, at low rates of either inflation or deflation firms may change prices less frequently, reducing the impact of output gaps. If so, this would provide a buffer to deflation in the rich world today, ...
G - Madison County Schools
... Step 5. Use the CPI to compute the inflation rate from previous year 2002 (175/100 x 100 = 175%) or to get actual % (175-100)/100 x 100 =75% ...
... Step 5. Use the CPI to compute the inflation rate from previous year 2002 (175/100 x 100 = 175%) or to get actual % (175-100)/100 x 100 =75% ...