Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply
... Wages are often sticky as they don’t adjust immediately. Wage stickiness may be caused by union contracts or occupations that don’t change wages except once a year. Wage stickiness can be found in the wages of college professors and government workers because their wages are set once a year regardle ...
... Wages are often sticky as they don’t adjust immediately. Wage stickiness may be caused by union contracts or occupations that don’t change wages except once a year. Wage stickiness can be found in the wages of college professors and government workers because their wages are set once a year regardle ...
CH_14_13th
... • With stable prices, supply and demand in the loanable funds market are in balance at a real & nominal interest rate of 4%. • If rapid monetary expansion leads to a long-term 5% inflation rate, borrowers and lenders will build the higher inflation rate into their decision making. • As a result, the ...
... • With stable prices, supply and demand in the loanable funds market are in balance at a real & nominal interest rate of 4%. • If rapid monetary expansion leads to a long-term 5% inflation rate, borrowers and lenders will build the higher inflation rate into their decision making. • As a result, the ...
Modern Macroeconomics and Monetary Policy
... • With stable prices, supply and demand in the loanable funds market are in balance at a real & nominal interest rate of 4%. • If rapid monetary expansion leads to a long-term 5% inflation rate, borrowers and lenders will build the higher inflation rate into their decision making. • As a result, the ...
... • With stable prices, supply and demand in the loanable funds market are in balance at a real & nominal interest rate of 4%. • If rapid monetary expansion leads to a long-term 5% inflation rate, borrowers and lenders will build the higher inflation rate into their decision making. • As a result, the ...
AS-AD and the Business Cycle
... GDP. The amount by which real GDP exceeds potential GDP is called an inflationary gap. An inflationary gap occurs when the AS curve and the AD curve intersect to the right of the potential GDP line, as illustrated in the figure to the left, above. In this case real wages have fallen and workers even ...
... GDP. The amount by which real GDP exceeds potential GDP is called an inflationary gap. An inflationary gap occurs when the AS curve and the AD curve intersect to the right of the potential GDP line, as illustrated in the figure to the left, above. In this case real wages have fallen and workers even ...
File
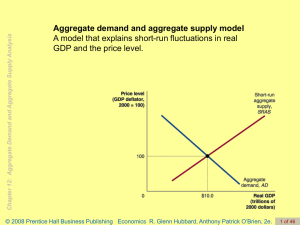
... In this section, we develop a graphical tool known as the aggregate demand curve. Later in the chapter, we will develop the aggregate supply curve. Together the aggregate demand and aggregate supply curves form an economic model that will enable us to study how output and prices are determined in bo ...
... In this section, we develop a graphical tool known as the aggregate demand curve. Later in the chapter, we will develop the aggregate supply curve. Together the aggregate demand and aggregate supply curves form an economic model that will enable us to study how output and prices are determined in bo ...
Why Monetary Policy Matters
... the level of economic activity and the rate of inflation? And, finally, how can monetary policy deliver genuine and significant benefits to society? Although the paper’s main messages apply to central banks and monetary policy in many countries, the emphasis here is on Canadian monetary policy and t ...
... the level of economic activity and the rate of inflation? And, finally, how can monetary policy deliver genuine and significant benefits to society? Although the paper’s main messages apply to central banks and monetary policy in many countries, the emphasis here is on Canadian monetary policy and t ...
Chapter 11
... • The classical economists’ world was one of fully utilized resources • In the 1930s, Europe and the United States entered a period of economic decline that could not be explained by the classical model • John Maynard Keynes developed an explanation that has become known as the Keynesian model Copyr ...
... • The classical economists’ world was one of fully utilized resources • In the 1930s, Europe and the United States entered a period of economic decline that could not be explained by the classical model • John Maynard Keynes developed an explanation that has become known as the Keynesian model Copyr ...
FRBSF E L
... dangerous distraction, risking the central bank’s attention to, and credibility in, achieving its price stability mandate. Indeed, this approach was codified in numerous central bank charters, which in some cases dictated consequences if the inflation goal was not met. Even at the Federal Reserve, w ...
... dangerous distraction, risking the central bank’s attention to, and credibility in, achieving its price stability mandate. Indeed, this approach was codified in numerous central bank charters, which in some cases dictated consequences if the inflation goal was not met. Even at the Federal Reserve, w ...
DP2006/01 Phillips curve forecasting in a small open economy Troy Matheson March 2006
... Conceptually, goods and services can be characterised as being either tradable or non-tradable. Tradable goods and services are traded internationally and have prices that are, at least in part, determined in world markets. Non-tradable goods and services, on the other hand, have prices that can be ...
... Conceptually, goods and services can be characterised as being either tradable or non-tradable. Tradable goods and services are traded internationally and have prices that are, at least in part, determined in world markets. Non-tradable goods and services, on the other hand, have prices that can be ...
APPENDIX D TO CHAPTER 10 The Self
... Why the Long-Run Aggregate Supply Curve is Vertical The long-run aggregate supply curve (LRAC) is presented in Exhibit A-1(b). The long-run aggregate supply curve shows the level of real GDP produced at different possible price levels during a time period in which nominal incomes change by the same ...
... Why the Long-Run Aggregate Supply Curve is Vertical The long-run aggregate supply curve (LRAC) is presented in Exhibit A-1(b). The long-run aggregate supply curve shows the level of real GDP produced at different possible price levels during a time period in which nominal incomes change by the same ...
6The Short-run Model for the Closed Economy
... According to the analysis above, the changes in the inflation rate generated by market forces will automatically pull the economy out of a recession as long as the central bank follows the Taylor Principle. In the long run the rates of output and employment will thus converge on their natural rates. ...
... According to the analysis above, the changes in the inflation rate generated by market forces will automatically pull the economy out of a recession as long as the central bank follows the Taylor Principle. In the long run the rates of output and employment will thus converge on their natural rates. ...
This PDF is a selec on from a published volume... Bureau of Economic Research
... shocks. Based on the analysis by Gordon (1975, 1977), Eckstein (1978), and Blinder (1979, 1982), one could argue that the bulk of the two sharp increases in inflation during the 1970s, in 1973 to 1975 and in 1978 to 1980, could be explained due to the unusual developments in food, energy, and other ...
... shocks. Based on the analysis by Gordon (1975, 1977), Eckstein (1978), and Blinder (1979, 1982), one could argue that the bulk of the two sharp increases in inflation during the 1970s, in 1973 to 1975 and in 1978 to 1980, could be explained due to the unusual developments in food, energy, and other ...
The Phillips Curve in the 1990s - Digital Commons @ IWU
... rate. In Figure 3(b), we see that every year inflation is expected to be 10%, so there is no movement of the Phillips curve. The inflation rate is constant at π1and unemployment stays at !, the natural rate of unemployment. In order to produce unexpected inflation, imagine that the money supply is i ...
... rate. In Figure 3(b), we see that every year inflation is expected to be 10%, so there is no movement of the Phillips curve. The inflation rate is constant at π1and unemployment stays at !, the natural rate of unemployment. In order to produce unexpected inflation, imagine that the money supply is i ...
Is the Phillips curve still dead?
... for labour (reflected by the wage rate), but also of the supply of labour. Even if higher nominal wages encourage new entrants into the labour market, how many of them will ultimately end up being employed by meeting the requirements of those very firms offering higher wages in the hope of attractin ...
... for labour (reflected by the wage rate), but also of the supply of labour. Even if higher nominal wages encourage new entrants into the labour market, how many of them will ultimately end up being employed by meeting the requirements of those very firms offering higher wages in the hope of attractin ...
Economics R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O'Brien, 2e.
... Monetary growth rule A plan for increasing the quantity of money at a fixed rate that does not respond to changes in economic conditions. Monetarism The macroeconomic theories of Milton Friedman and his followers; particularly the idea that the quantity of money should be increased at a constant rat ...
... Monetary growth rule A plan for increasing the quantity of money at a fixed rate that does not respond to changes in economic conditions. Monetarism The macroeconomic theories of Milton Friedman and his followers; particularly the idea that the quantity of money should be increased at a constant rat ...
Evidence from the Classical Gold Standard
... prices over our period was the changing world production of gold, we refer to the shock that has a long run impact on prices as the money supply shock.13 Using this identification of supply and money supply shocks we can measure separately the effect of each on output. Thus this identification sche ...
... prices over our period was the changing world production of gold, we refer to the shock that has a long run impact on prices as the money supply shock.13 Using this identification of supply and money supply shocks we can measure separately the effect of each on output. Thus this identification sche ...
Farms, Fertiliser, and Financial Frictions: Yields
... a composite which includes fertiliser and oil). The farmers are constrained by financial frictions, and are subject to shocks from variable weather conditions and a volatile local-currency price of imported fertiliser. The shocks are exacerbated by the financial frictions which become more severe as ...
... a composite which includes fertiliser and oil). The farmers are constrained by financial frictions, and are subject to shocks from variable weather conditions and a volatile local-currency price of imported fertiliser. The shocks are exacerbated by the financial frictions which become more severe as ...
Scribner AP Macroeconomics Syllabus 2016-17
... employment in the long and short run B. Gain understanding of how an economy responds to a short-run shock and adjusts in the long run in the absence of any public policy actions C. Examine the economic effects of government deficit budgets including “crowding out” D. Consider issues surrounding th ...
... employment in the long and short run B. Gain understanding of how an economy responds to a short-run shock and adjusts in the long run in the absence of any public policy actions C. Examine the economic effects of government deficit budgets including “crowding out” D. Consider issues surrounding th ...
12 INFLATION
... The potential difficulty with both demand-pull and cost-push inflation stories is how the one-time increase translates into an inflationary process. It is relatively easy to come up with stories as to why aggregate demand might shift continuously to the right, for example because of persistent and g ...
... The potential difficulty with both demand-pull and cost-push inflation stories is how the one-time increase translates into an inflationary process. It is relatively easy to come up with stories as to why aggregate demand might shift continuously to the right, for example because of persistent and g ...
BoZ Monetary Policy Statement July to December
... Downside risks to the euro area will weigh on global economic growth, driven largely by the Brexit effect, coupled with low crude oil prices due to high inventories. The Brexit effect may have significant medium-term implications for trade and investment flows particularly for the UK and the remaini ...
... Downside risks to the euro area will weigh on global economic growth, driven largely by the Brexit effect, coupled with low crude oil prices due to high inventories. The Brexit effect may have significant medium-term implications for trade and investment flows particularly for the UK and the remaini ...