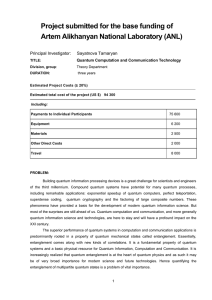
[10] AL Kholmetskii, T. Yarman, OV Missevitch, Kündig`s Experiment
... there is no outside to it, i.e. nothing can be defined in the gravitational world beyond the center, of the gravitating mass M , creating the gravitational world, and there is nothing beyond infinity, in this world. Thus, the Grand Master, should not have proposed to observe things from the outside ...
... there is no outside to it, i.e. nothing can be defined in the gravitational world beyond the center, of the gravitating mass M , creating the gravitational world, and there is nothing beyond infinity, in this world. Thus, the Grand Master, should not have proposed to observe things from the outside ...
Quantum fluctuation relations: Foundations and applications
... As often happens in science, the historical development of theories is quite tortuous. Fluctuation relations are no exception in this respect. Without any intention of providing a thorough and complete historical account, we mention below a few milestones that, in our view, mark crucial steps in the ...
... As often happens in science, the historical development of theories is quite tortuous. Fluctuation relations are no exception in this respect. Without any intention of providing a thorough and complete historical account, we mention below a few milestones that, in our view, mark crucial steps in the ...
Fault-tolerant quantum repeater with atomic ensembles and linear
... two pairs of the remote ensembles is denoted by +* = k+x with +x = xu − xd. In practice, a series of write pulses are sent into the atomic ensembles and the induced Stokes pulses are directed to the detectors. The time interval between neighboring write pulses is larger than the classical communicat ...
... two pairs of the remote ensembles is denoted by +* = k+x with +x = xu − xd. In practice, a series of write pulses are sent into the atomic ensembles and the induced Stokes pulses are directed to the detectors. The time interval between neighboring write pulses is larger than the classical communicat ...
Quantum Symmetric States - UCLA Department of Mathematics
... Thus, the expectation E can be seen as an integral (w.r.t. a probability measure on the tail algebra) — that is, as a sort of convex combination — of expectations with respect to which the random variables x1 , x2 , . . . are independent and identically distributed (i.i.d.). Dykema (TAMU) ...
... Thus, the expectation E can be seen as an integral (w.r.t. a probability measure on the tail algebra) — that is, as a sort of convex combination — of expectations with respect to which the random variables x1 , x2 , . . . are independent and identically distributed (i.i.d.). Dykema (TAMU) ...
Introduction to Quantum Entanglement
... follows that it is not satisfied at least principle of quantum mechanics. Einstein, Podolsky and Rosen came to the conclusion that some quantum effects travel faster than light, which is contradiction to the theory of relativity. The presented experiment is called the EPR paradox. In response to the ...
... follows that it is not satisfied at least principle of quantum mechanics. Einstein, Podolsky and Rosen came to the conclusion that some quantum effects travel faster than light, which is contradiction to the theory of relativity. The presented experiment is called the EPR paradox. In response to the ...
Chapter 11 The Uniform Plane Wave
... special case and to emphasize the special characteristics of wave propagation in these media, but it is not necessary to use a separate treatment; it is possible (and not very difficult) to solve the general problem once and for all. To consider wave motion in free space first, Maxwell's equations m ...
... special case and to emphasize the special characteristics of wave propagation in these media, but it is not necessary to use a separate treatment; it is possible (and not very difficult) to solve the general problem once and for all. To consider wave motion in free space first, Maxwell's equations m ...
Holographic Quantum Error Correcting Codes - Adrian Franco
... any collection of them) will be a quantum system that will find itself in a particular state. This state contains all the information about every degree of freedom of the system (such as the position of a particle, or its magnetic moment) and belongs to a set of states that must have a particular st ...
... any collection of them) will be a quantum system that will find itself in a particular state. This state contains all the information about every degree of freedom of the system (such as the position of a particle, or its magnetic moment) and belongs to a set of states that must have a particular st ...
Decoherence and the Classical Limit of Quantum
... Actually, it can be shown that for very massive bodies (such as planets) the wave packet will remain concentrated for times much longer than the life of the universe.3 But consider those macroscopic bodies subjected to non linear interaction leading to chaotic behavior (think e.g. of an asteroid sub ...
... Actually, it can be shown that for very massive bodies (such as planets) the wave packet will remain concentrated for times much longer than the life of the universe.3 But consider those macroscopic bodies subjected to non linear interaction leading to chaotic behavior (think e.g. of an asteroid sub ...
The Ghost in the Quantum Turing Machine
... the atoms probably in a small portion of the brain, or possibly all over it. The rest of the body acts so as to amplify this. (Quoted in Hodges [43]) The rest of Turing’s letter discusses the prospects for the survival of the “spirit” after death, a topic with obvious relevance to Turing at that tim ...
... the atoms probably in a small portion of the brain, or possibly all over it. The rest of the body acts so as to amplify this. (Quoted in Hodges [43]) The rest of Turing’s letter discusses the prospects for the survival of the “spirit” after death, a topic with obvious relevance to Turing at that tim ...
Presentation slides
... Semiclassically, think of quasi-particles having definite trajectories In ensemble average for C(x, t), each state is a “configuration” of trajectories Dotted trajectory is one created by action of n̂0 Suppose dotted trajectory has r right and l left collisions Then annihilated particle is |r − l| p ...
... Semiclassically, think of quasi-particles having definite trajectories In ensemble average for C(x, t), each state is a “configuration” of trajectories Dotted trajectory is one created by action of n̂0 Suppose dotted trajectory has r right and l left collisions Then annihilated particle is |r − l| p ...
61, 062310 (2000)
... identification. The next problem is how to realize these cloning and identifying transformations by physical means. The fundamental unit of quantum information transmission is the quantum bit 共qubit兲, i.e., a two-state quantum system, which is capable of existing in a superposition of Boolean states ...
... identification. The next problem is how to realize these cloning and identifying transformations by physical means. The fundamental unit of quantum information transmission is the quantum bit 共qubit兲, i.e., a two-state quantum system, which is capable of existing in a superposition of Boolean states ...
enetab - Digital Encyclopedia of Charles S. Peirce
... this way acts as the “mutual action between two things regardless of any sort of third or medium, and in particular regardless of any law of action” (Peirce 1.322). The key to Secondness is the indexical physical link, that state where “it is a real thing or fact which is a sign of its object by vir ...
... this way acts as the “mutual action between two things regardless of any sort of third or medium, and in particular regardless of any law of action” (Peirce 1.322). The key to Secondness is the indexical physical link, that state where “it is a real thing or fact which is a sign of its object by vir ...
Biological Autonomy
... back into the river, nature’s command is short: survive! This command does not inform the fish in terms of physical details and spatial coordinates what to do, such as to turn left or right. Organisms commonly have alternative means of performing the same function (Beckner 1969), therefore, they mus ...
... back into the river, nature’s command is short: survive! This command does not inform the fish in terms of physical details and spatial coordinates what to do, such as to turn left or right. Organisms commonly have alternative means of performing the same function (Beckner 1969), therefore, they mus ...
Bohr–Einstein debates

The Bohr–Einstein debates were a series of public disputes about quantum mechanics between Albert Einstein and Niels Bohr. Their debates are remembered because of their importance to the philosophy of science. An account of the debates was written by Bohr in an article titled ""Discussions with Einsteinon Epistemological Problems in Atomic Physics"". Despite their differences of opinion regarding quantum mechanics, Bohr and Einstein had a mutual admiration that was to last the rest of their lives.The debates represent one of the highest points of scientific research in the first half of the twentieth century because it called attention to an element of quantum theory, quantum non-locality, which is absolutely central to our modern understanding of the physical world. The consensus view of professional physicists has been that Bohr proved victorious, and definitively established the fundamental probabilistic character of quantum measurement.
![[10] AL Kholmetskii, T. Yarman, OV Missevitch, Kündig`s Experiment](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/010773015_1-b3d732fc642ab38b293e58aff252fdab-300x300.png)