Common Assessment Review
... Transcription- process by which RNA is made. Part of the nucleotide sequence of a DNA molecule is copied into RNA. Occurs in the nucleus Steps: DNA is unzipped in the nucleus by an enzyme - Another enzyme, RNA polymerase, bonds “free nucleotides” to the exposed bases - Adenine bonds with uracil (A ...
... Transcription- process by which RNA is made. Part of the nucleotide sequence of a DNA molecule is copied into RNA. Occurs in the nucleus Steps: DNA is unzipped in the nucleus by an enzyme - Another enzyme, RNA polymerase, bonds “free nucleotides” to the exposed bases - Adenine bonds with uracil (A ...
m5zn_a4ac3a22336dedd
... Transcription in Eukaryotic Cells • Unlike prokaryotic cells eukaryotic cells must process the mRNA in the nucleus before it can be made into a protein • Three major modifications are made – Intron splicing – Addition of poly A tail – Additon of 5’ cap ...
... Transcription in Eukaryotic Cells • Unlike prokaryotic cells eukaryotic cells must process the mRNA in the nucleus before it can be made into a protein • Three major modifications are made – Intron splicing – Addition of poly A tail – Additon of 5’ cap ...
ch 19 gene expression in eukaryotes
... Concept 18.3: Noncoding RNAs play multiple roles in controlling gene expression • Only a small fraction of DNA codes for proteins, rRNA, and tRNA • A significant amount of the genome may be transcribed into noncoding RNAs • Noncoding RNAs regulate gene expression at two points: mRNA translation and ...
... Concept 18.3: Noncoding RNAs play multiple roles in controlling gene expression • Only a small fraction of DNA codes for proteins, rRNA, and tRNA • A significant amount of the genome may be transcribed into noncoding RNAs • Noncoding RNAs regulate gene expression at two points: mRNA translation and ...
Tutorial_9_NEW
... - Identifying new microRNA genes - Identifying the targets of specific microRNA ...
... - Identifying new microRNA genes - Identifying the targets of specific microRNA ...
Document
... Prokaryotic Chromosome (E. coli) • Large circular chromosome 4.6 x 106 bp • Genome forms a compact structure called the nucleoid • DNA organized in 50-100 loops (domains) • The ends of loops are constrained by binding to protein structure which is in contact with cell membrane ...
... Prokaryotic Chromosome (E. coli) • Large circular chromosome 4.6 x 106 bp • Genome forms a compact structure called the nucleoid • DNA organized in 50-100 loops (domains) • The ends of loops are constrained by binding to protein structure which is in contact with cell membrane ...
Chapter 25: Molecular Basis of Inheritance
... A ribosome has a binding site for mRNA as well as binding sites for two tRNA molecules at a time. As the ribosome moves down the mRNA molecule, new tRNAs arrive, and a polypeptide forms and grows longer. Translation terminates once the polypeptide is fully formed; the ribosome separates into two su ...
... A ribosome has a binding site for mRNA as well as binding sites for two tRNA molecules at a time. As the ribosome moves down the mRNA molecule, new tRNAs arrive, and a polypeptide forms and grows longer. Translation terminates once the polypeptide is fully formed; the ribosome separates into two su ...
Genes
... between complimentary bases across the 2 strands – the coding strand and the template strand – T…A and G…C • Each molecule of DNA is subdivided into thousands of segments containing a specific sequence (code) of nucleotides called genes – instruction manual for building proteins – the sequence of nu ...
... between complimentary bases across the 2 strands – the coding strand and the template strand – T…A and G…C • Each molecule of DNA is subdivided into thousands of segments containing a specific sequence (code) of nucleotides called genes – instruction manual for building proteins – the sequence of nu ...
Ch. 13 end of chapter review
... The main differences between RNA and DNA are that (1) the sugar in RNA is ribose instead of deoxyribose; (2) RNA is generally single-stranded, not double-stranded; and (3) RNA contains uracil in place of thymine. In transcription, segments of DNA serve as templates to produce complementary RNA molec ...
... The main differences between RNA and DNA are that (1) the sugar in RNA is ribose instead of deoxyribose; (2) RNA is generally single-stranded, not double-stranded; and (3) RNA contains uracil in place of thymine. In transcription, segments of DNA serve as templates to produce complementary RNA molec ...
T7 In Vitro Transcription Kit esiSCRIBE 100 Reactions (10 µl each
... generation of double-stranded (ds)RNA and guide (g)RNA for RNA interference (RNAi) experiments and CRISPR/Cas systems, respectively. Ready-totransfect esiRNAs (endoribonuclease-prepared siRNAs) and gRNAs are also available from Eupheria Biotech (www.eupheria.com). Reaction Conditions This kit contai ...
... generation of double-stranded (ds)RNA and guide (g)RNA for RNA interference (RNAi) experiments and CRISPR/Cas systems, respectively. Ready-totransfect esiRNAs (endoribonuclease-prepared siRNAs) and gRNAs are also available from Eupheria Biotech (www.eupheria.com). Reaction Conditions This kit contai ...
Nucleic Acids - University of California, Davis
... deoxyribose in DNA), base (purine,A, G, and pyrimidine, C, T or U), and phosphate group. • Nucleotide can polymerise to form polynucleotides, or “strands”. • DNA (deoxyribo nucleic acid) is a double stranded helix, where the two strands run in opposite directions and are maintained together by hydro ...
... deoxyribose in DNA), base (purine,A, G, and pyrimidine, C, T or U), and phosphate group. • Nucleotide can polymerise to form polynucleotides, or “strands”. • DNA (deoxyribo nucleic acid) is a double stranded helix, where the two strands run in opposite directions and are maintained together by hydro ...
Bio1100Ch17W
... 3. In the genetic code, nucleotide triplets specify amino acids • A single or doublet code can not provide enough ____________ (4 and 16 respectively) to code for all 20 amino acids. • Triplets of nucleotide bases are the smallest units of uniform length that can code for all the amino acids. ...
... 3. In the genetic code, nucleotide triplets specify amino acids • A single or doublet code can not provide enough ____________ (4 and 16 respectively) to code for all 20 amino acids. • Triplets of nucleotide bases are the smallest units of uniform length that can code for all the amino acids. ...
Unit 4
... The nitrogen bases found in DNA are adenine, thymine, guanine and cytosine. Pyrimidines are thymine and cytosine and purine are adenine and guanine. 7. Explain the "base-pairing rule" and describe its significance. The base-pairing rule says that each base has to bond with its complementary one like ...
... The nitrogen bases found in DNA are adenine, thymine, guanine and cytosine. Pyrimidines are thymine and cytosine and purine are adenine and guanine. 7. Explain the "base-pairing rule" and describe its significance. The base-pairing rule says that each base has to bond with its complementary one like ...
translation
... TRANSLATION: In the ribosome, tRNAs match up with their codons in the mRNA. The backsides of the tRNAs have specific amino acids attached to them. When the tRNAs line up, the amino acids bond to each other and let go of the tRNA. The chain of amino acids is called a protein. The protein then ...
... TRANSLATION: In the ribosome, tRNAs match up with their codons in the mRNA. The backsides of the tRNAs have specific amino acids attached to them. When the tRNAs line up, the amino acids bond to each other and let go of the tRNA. The chain of amino acids is called a protein. The protein then ...
Document
... 1. What is the chromosome theory of inheritance? a. Chromosomes are carried from parents to offspring on mutations. b. Genes are carried from parents to offspring on chromosomes. c. Mutations found in chromosomes are always harmful. d. Genes form RNA and are carried in the chromosome. 2. Walter Sutt ...
... 1. What is the chromosome theory of inheritance? a. Chromosomes are carried from parents to offspring on mutations. b. Genes are carried from parents to offspring on chromosomes. c. Mutations found in chromosomes are always harmful. d. Genes form RNA and are carried in the chromosome. 2. Walter Sutt ...
Recombinant DNA as a Tool in Animal Research
... methionine have a single codon each. Three triplets out of the possible 64 d o not code for amino acids; these are UAG, UAA, UGA. These serve as termination signals or periods at the end of the message. At about the time the genetic code was established, the one-way flow of information associated wi ...
... methionine have a single codon each. Three triplets out of the possible 64 d o not code for amino acids; these are UAG, UAA, UGA. These serve as termination signals or periods at the end of the message. At about the time the genetic code was established, the one-way flow of information associated wi ...
26 DNA Transcription - School of Chemistry and Biochemistry
... between a given amino acid and the correct (cognate) tRNA is catalyzed by a specific aminoacyltRNA synthetase (one for each amino acid). The aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases establish and enforce the genetic code. 4)MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are around 22 nucleotides in length and are found only in eukaryotic ce ...
... between a given amino acid and the correct (cognate) tRNA is catalyzed by a specific aminoacyltRNA synthetase (one for each amino acid). The aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases establish and enforce the genetic code. 4)MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are around 22 nucleotides in length and are found only in eukaryotic ce ...
Sept10
... rRNA and ribosomes provide the decoder. Ribosomes bring together mRNA and tRNA, and catalyze the translation of an mRNA into a polypeptide chain. Ribosomes are the site of protein synthesis. Ribosomes create peptide bonds between amino acids to create proteins ...
... rRNA and ribosomes provide the decoder. Ribosomes bring together mRNA and tRNA, and catalyze the translation of an mRNA into a polypeptide chain. Ribosomes are the site of protein synthesis. Ribosomes create peptide bonds between amino acids to create proteins ...
Translation Von der RNA zum Protein
... • RNA polymerase binds to the DNA and is associated with the so called sigma factor. • The sigma factor aids in finding the starting point of transcription: the region -10 and -35 basepairs downstream of the promoter. • The initation complex opens and the first ...
... • RNA polymerase binds to the DNA and is associated with the so called sigma factor. • The sigma factor aids in finding the starting point of transcription: the region -10 and -35 basepairs downstream of the promoter. • The initation complex opens and the first ...
Document
... DNA Polymerase – a protein complex that copies DNA to DNA RNA Polymerase – a protein complex that copies DNA to RNA Spliceosome – a protein/RNA complex that removes introns from pre-mRNA Ribosome – a protein/RNA complex that translates mRNA codons to amino acids, making proteins Intron – a non-codin ...
... DNA Polymerase – a protein complex that copies DNA to DNA RNA Polymerase – a protein complex that copies DNA to RNA Spliceosome – a protein/RNA complex that removes introns from pre-mRNA Ribosome – a protein/RNA complex that translates mRNA codons to amino acids, making proteins Intron – a non-codin ...
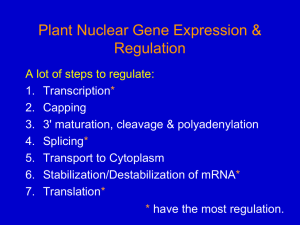
Nuclear gene expression 1
... All 3 polymerases are multi-subunit; have some large, unique subunits; and 5 small, shared subunits (at least in yeast). ...
... All 3 polymerases are multi-subunit; have some large, unique subunits; and 5 small, shared subunits (at least in yeast). ...
Chapter 4 Genetics: The Science of Heredity
... 2. The scientific study of heredity. 5. An organism’s physical appearance, or visible traits. 6. ____ RNA: RNA that copies the coded message from DNA in the nucleus and carries the message into the cytoplasm. 7. The passing of traits from parents to offspring. 11. Having two identical alleles for a ...
... 2. The scientific study of heredity. 5. An organism’s physical appearance, or visible traits. 6. ____ RNA: RNA that copies the coded message from DNA in the nucleus and carries the message into the cytoplasm. 7. The passing of traits from parents to offspring. 11. Having two identical alleles for a ...
DNA Prokaryote Transcription Steps (updated February 2013)
... promoter. The promoter has several sequences that are similar to the Pribnow and TTGACA boxes in prokaryote promoters. The TATA box (TATAAA) is almost identical to the Pribnow sequence. Only about 32% of the known eukaryote core promoters have the TATA box at -26 to -31. If the iniator (Inr) core pr ...
... promoter. The promoter has several sequences that are similar to the Pribnow and TTGACA boxes in prokaryote promoters. The TATA box (TATAAA) is almost identical to the Pribnow sequence. Only about 32% of the known eukaryote core promoters have the TATA box at -26 to -31. If the iniator (Inr) core pr ...
Life
... The Pep8de world • Although the Sydney Fox experiment looks clearly like there is something there, scien8sts have found long ago that some Pep8des can build copies of themselves without having to go through the “normal” protein syntheses • Pep8de world models look compelling but they are ...
... The Pep8de world • Although the Sydney Fox experiment looks clearly like there is something there, scien8sts have found long ago that some Pep8des can build copies of themselves without having to go through the “normal” protein syntheses • Pep8de world models look compelling but they are ...
RNA

Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule implicated in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation, and expression of genes. RNA and DNA are nucleic acids, and, along with proteins and carbohydrates, constitute the three major macromolecules essential for all known forms of life. Like DNA, RNA is assembled as a chain of nucleotides, but unlike DNA it is more often found in nature as a single-strand folded onto itself, rather than a paired double-strand. Cellular organisms use messenger RNA (mRNA) to convey genetic information (using the letters G, U, A, and C to denote the nitrogenous bases guanine, uracil, adenine, and cytosine) that directs synthesis of specific proteins. Many viruses encode their genetic information using an RNA genome.Some RNA molecules play an active role within cells by catalyzing biological reactions, controlling gene expression, or sensing and communicating responses to cellular signals. One of these active processes is protein synthesis, a universal function whereby mRNA molecules direct the assembly of proteins on ribosomes. This process uses transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to deliver amino acids to the ribosome, where ribosomal RNA (rRNA) links amino acids together to form proteins.