there is no essence
... The word right in the following list is a translation of a word that might better be translated as correct ...
... The word right in the following list is a translation of a word that might better be translated as correct ...
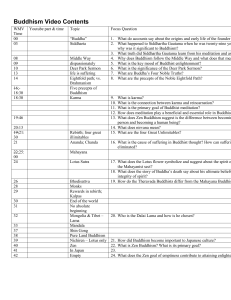
Buddhism Video Contents
... What does Zen Buddhism suggest is the difference between becomin person and becoming a human being? 14. What does nirvana mean? 15. What are the four Great Unlimitables? ...
... What does Zen Buddhism suggest is the difference between becomin person and becoming a human being? 14. What does nirvana mean? 15. What are the four Great Unlimitables? ...
Hinduism - LincolnPhillips
... many different forms as well. If you practice Hinduism, the goal of life is to achieve maksha, or union with Brahman. However, on your way to this, you must reach atman, which is another way of saying Brahman, which means your essential self. If you cannot reach maoksha in one life, then you will ge ...
... many different forms as well. If you practice Hinduism, the goal of life is to achieve maksha, or union with Brahman. However, on your way to this, you must reach atman, which is another way of saying Brahman, which means your essential self. If you cannot reach maoksha in one life, then you will ge ...
Hinduism : Unity and diversity
... -Brahman- the creator -Vishnu- the preserver -Shiva- the destroyer *each represents aspects of the Brahman* The Goal of life: Every Hindu has an essential self called atman (really just another name for Brahman) -The ultimate goal of existence is to achieve Moksha (union) with Brahman In order to ac ...
... -Brahman- the creator -Vishnu- the preserver -Shiva- the destroyer *each represents aspects of the Brahman* The Goal of life: Every Hindu has an essential self called atman (really just another name for Brahman) -The ultimate goal of existence is to achieve Moksha (union) with Brahman In order to ac ...
Exam Revision Slides
... If they act from a selfish perspective they will have a less favourable rebirth in the future The illusion of a self means that the person goes through life focussed on the self, they ignore other more important things that will bring them closer to enlightenment ...
... If they act from a selfish perspective they will have a less favourable rebirth in the future The illusion of a self means that the person goes through life focussed on the self, they ignore other more important things that will bring them closer to enlightenment ...
File - History With Mrs. Heacock
... The terms dharma and karma often get confused by introductory Hinduism students and with good reason -- they are both products of the cycle of birth and death (reincarnation), but they have entirely different spheres of purpose. Karma is the accumulation of debt of action in the course of a person's ...
... The terms dharma and karma often get confused by introductory Hinduism students and with good reason -- they are both products of the cycle of birth and death (reincarnation), but they have entirely different spheres of purpose. Karma is the accumulation of debt of action in the course of a person's ...
Ch 6a Foundations of Indian Civ - Somerset Academy Silver Palms
... suffering; desire causes suffering) and of the Eightfold Path that would lead to enlightenment -some took vows of celibacy, nonviolence, and ...
... suffering; desire causes suffering) and of the Eightfold Path that would lead to enlightenment -some took vows of celibacy, nonviolence, and ...
Chapter 6: Buddhism in Its First Phase Chapter Objectives After
... 2. The Positive: Living Toward Transcendent Bliss ...
... 2. The Positive: Living Toward Transcendent Bliss ...
Buddhism Presentation
... • 3) The cessation of suffering: freedom from attachment and aversion. ...
... • 3) The cessation of suffering: freedom from attachment and aversion. ...
Introduction to BUDDHISM
... one should shun extremes. One should avoid the pursuit of worldly desires on the one hand and severe, ascetic discipline on the other. • Buddha did not think of himself as the creator of a new religion. Rather, he felt the need to purify the religion of his day. ...
... one should shun extremes. One should avoid the pursuit of worldly desires on the one hand and severe, ascetic discipline on the other. • Buddha did not think of himself as the creator of a new religion. Rather, he felt the need to purify the religion of his day. ...
WH-‐3.2 Notes -‐ Hinduism and Buddhism Develop Origins of
... 2. The cause of all suffering is people’s selfish desire for the temporary pleasures of this world. 3. The way to end all suffering is to end all desires. 4. The way to overcome such desires ...
... 2. The cause of all suffering is people’s selfish desire for the temporary pleasures of this world. 3. The way to end all suffering is to end all desires. 4. The way to overcome such desires ...
Dependent Origination Presentation
... caused into existence. Nothing has been created ex nihilo. • This is useful in understanding how there can be rebirth without a belief in a soul. When a person is alive they generate karma, this does not simply disappear at death. Instead, due to the remaining karmic seeds a new being is caused into ...
... caused into existence. Nothing has been created ex nihilo. • This is useful in understanding how there can be rebirth without a belief in a soul. When a person is alive they generate karma, this does not simply disappear at death. Instead, due to the remaining karmic seeds a new being is caused into ...
Karma - University of Bristol
... • Karma, within Buddhist thought, is a system of cause and effect. Rather than being linked to ritual actions karma is understood to concern all intentional thoughts and actions. • What this means is that actions have a moral quality to them. Intentional actions that are good and well meaning will ...
... • Karma, within Buddhist thought, is a system of cause and effect. Rather than being linked to ritual actions karma is understood to concern all intentional thoughts and actions. • What this means is that actions have a moral quality to them. Intentional actions that are good and well meaning will ...
Buddhism - deanworldhistory
... • Every action results in another action • Positive actions result in good karma; negative ones lead to bad karma. • "According to the seed that’s sown, So is the fruit you reap there from, Doer of good will gather good, Doer of evil, evil reaps, Down is the seed and thou shalt taste The fruit there ...
... • Every action results in another action • Positive actions result in good karma; negative ones lead to bad karma. • "According to the seed that’s sown, So is the fruit you reap there from, Doer of good will gather good, Doer of evil, evil reaps, Down is the seed and thou shalt taste The fruit there ...
Karma and Rebirth
... while what we are thinking, saying, and doing now will form our future. The karma of past, present, and future events are connected by the law of cause and effect. For instance, if one generates bad karma by hurting or killing sentient beings, one will have to endure the negative consequences of the ...
... while what we are thinking, saying, and doing now will form our future. The karma of past, present, and future events are connected by the law of cause and effect. For instance, if one generates bad karma by hurting or killing sentient beings, one will have to endure the negative consequences of the ...
View presentation - Child Funeral Charity
... • Family and guests should be encouraged to join in the chanting (possible call and respond) • Guests should stand in front of the altar and bow with their hands clasped together or observe a moment of silence • Head coverings should be removed when a Buddhist teaching or a sermon is being delivered ...
... • Family and guests should be encouraged to join in the chanting (possible call and respond) • Guests should stand in front of the altar and bow with their hands clasped together or observe a moment of silence • Head coverings should be removed when a Buddhist teaching or a sermon is being delivered ...
Making Sense of Ch`an
... • All teachings are based on it . If a teaching does not accord with it , then it is not the teaching of the Buddha • Impermanence is implicit in this teaching. • Main implication : we think we are an independent entity , but we are , in fact , ...
... • All teachings are based on it . If a teaching does not accord with it , then it is not the teaching of the Buddha • Impermanence is implicit in this teaching. • Main implication : we think we are an independent entity , but we are , in fact , ...
Death and Dying Presentation
... In China there are a number of rituals that are performed in memory of the dead during the course of the ghost month. During this period the ‘spirits’ of the dead are invited to the Buddhist monasteries to participate. One of the most important aspects is the recitation of the name Amitābha or the s ...
... In China there are a number of rituals that are performed in memory of the dead during the course of the ghost month. During this period the ‘spirits’ of the dead are invited to the Buddhist monasteries to participate. One of the most important aspects is the recitation of the name Amitābha or the s ...
Beliefs and Practices of Buddhism
... is said that if your motivation is good the result will be good. Equally, if your motivation is bad there will be a similar negative result. This quite naturally leads on to Karma, which is fundamental to Buddhist teaching. Karma means action, it is the natural law of cause and effect. It tells us t ...
... is said that if your motivation is good the result will be good. Equally, if your motivation is bad there will be a similar negative result. This quite naturally leads on to Karma, which is fundamental to Buddhist teaching. Karma means action, it is the natural law of cause and effect. It tells us t ...
File
... • Siddhartha Gautama founded the new religion of Buddhism • Four Noble Truths 1. All life is full of suffering, pain, and sorrow 2. The cause of suffering is the desire for things that are really illusions, such as riches, power, and long life 3. The only cure for suffering is to overcome desire 4. ...
... • Siddhartha Gautama founded the new religion of Buddhism • Four Noble Truths 1. All life is full of suffering, pain, and sorrow 2. The cause of suffering is the desire for things that are really illusions, such as riches, power, and long life 3. The only cure for suffering is to overcome desire 4. ...
Karma in Buddhism

Karma (Sanskrit, also karman, Pāli: kamma) is a Sanskrit term that literally means ""action"" or ""doing"". In the Buddhist tradition, karma refers to action driven by intention (cetanā) which leads to future consequences. Those intentions are considered to be the determining factor in the kind of rebirth in samsara, the cycle of rebirth.