Hydraulic/Shock-Jumps in Protoplanetary Disks
... galaxies (Roberts et al. 1979). In addition, when the gas expands upward, the pressure confinement in the direction normal to the shock front is lost, and the material expands horizontally, causing some gas to flow back over the top of the shock. As the jumping gas moves inward and out over the pres ...
... galaxies (Roberts et al. 1979). In addition, when the gas expands upward, the pressure confinement in the direction normal to the shock front is lost, and the material expands horizontally, causing some gas to flow back over the top of the shock. As the jumping gas moves inward and out over the pres ...
Shock reflection and oblique shock waves
... flight. Mathematically, it means the determination of the maximal angle c which would guarantee a stable attached oblique shock front and for any angle larger than c, the shock front will become detached. There are also extensive studies on oblique shock waves using theoretical, numerical, and exp ...
... flight. Mathematically, it means the determination of the maximal angle c which would guarantee a stable attached oblique shock front and for any angle larger than c, the shock front will become detached. There are also extensive studies on oblique shock waves using theoretical, numerical, and exp ...
ALT-2 Manual
... Connect the static port to a suitable static air pressure line. If you have a slow aircraft or an aircraft were the internal cabin pressure does not change during flight and is equivalent to the outside air pressure you may find that it is not required to connect a static port. For installations in ...
... Connect the static port to a suitable static air pressure line. If you have a slow aircraft or an aircraft were the internal cabin pressure does not change during flight and is equivalent to the outside air pressure you may find that it is not required to connect a static port. For installations in ...
performance and flight monitoring 030
... Drag offsets the loss of engine power giving improved acceleration. Drag will permit the use of greater flap angles. Both lift and engine power will require a longer take-off distance. Thrust and drag has no apparent effect on the take-off distance required. ...
... Drag offsets the loss of engine power giving improved acceleration. Drag will permit the use of greater flap angles. Both lift and engine power will require a longer take-off distance. Thrust and drag has no apparent effect on the take-off distance required. ...
Presentation
... temperature related effects cause a slight focus shift which results in some blurring (generally small compared to the diffraction limit) as well as refraction which results in boresight error. This boresight error can be significant for precise targeting systems ...
... temperature related effects cause a slight focus shift which results in some blurring (generally small compared to the diffraction limit) as well as refraction which results in boresight error. This boresight error can be significant for precise targeting systems ...
IOSR Journal of Applied Physics (IOSR-JAP) ISSN: 2278-4861.
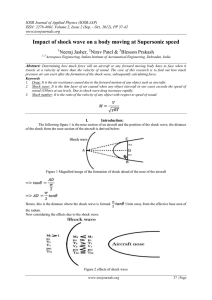
... Abstract: Determining how much force will an aircraft or any forward moving body have to face when it travels at a velocity of more than the velocity of sound. The core of this research is to find out how much pressure air can exert after the formation of the shock wave, subsequently calculating for ...
... Abstract: Determining how much force will an aircraft or any forward moving body have to face when it travels at a velocity of more than the velocity of sound. The core of this research is to find out how much pressure air can exert after the formation of the shock wave, subsequently calculating for ...
Aircraft Design - Personal.psu.edu
... The shock waves from jet airplanes that travel at supersonic speeds carry a great amount of concentrated energy resulting in great pressure variations. In fact, two booms are often produced when jets fly at supersonic speeds. Usually, these two booms coalesce into an N-shaped sound wave that propaga ...
... The shock waves from jet airplanes that travel at supersonic speeds carry a great amount of concentrated energy resulting in great pressure variations. In fact, two booms are often produced when jets fly at supersonic speeds. Usually, these two booms coalesce into an N-shaped sound wave that propaga ...
Sonic boom

A sonic boom is the sound associated with the shock waves created by an object traveling through the air faster than the speed of sound. Sonic booms generate enormous amounts of sound energy, sounding much like an explosion. The crack of a supersonic bullet passing overhead or the crack of a bullwhip are examples of a sonic boom in miniature.