Bismuth, lansoprazole, amoxicillin and metronidazole or - Gut
... limited its usefulness. The combination of amoxicillin and metronidazole-containing bismuth therapy has not been widely used in clinical practice. Studies done almost 20 years ago suggested it was less effective than clarithromycin-based triple therapy, but that study was based on a clinical trial u ...
... limited its usefulness. The combination of amoxicillin and metronidazole-containing bismuth therapy has not been widely used in clinical practice. Studies done almost 20 years ago suggested it was less effective than clarithromycin-based triple therapy, but that study was based on a clinical trial u ...
Antimicrobial Prophylaxis in Adults
... or pelvic lymphadenectomy. Recurrent cellulitis has been observed in the upper extremity after lymphadenectomy performed at the time of mastectomy for breast cancer. Antimicrobial prophylaxis may be a useful addition to the control of lymphedema with local measures and treatment of concurrent tinea ...
... or pelvic lymphadenectomy. Recurrent cellulitis has been observed in the upper extremity after lymphadenectomy performed at the time of mastectomy for breast cancer. Antimicrobial prophylaxis may be a useful addition to the control of lymphedema with local measures and treatment of concurrent tinea ...
Probiotics and Prebiotics: Frequently Asked Questions
... Because antibiotics can kill the bacteria in the whole intestinal tract, it is important to add back both of these types of bacteria for people who have just taken antibiotics. Some of the most-researched probiotics are: ...
... Because antibiotics can kill the bacteria in the whole intestinal tract, it is important to add back both of these types of bacteria for people who have just taken antibiotics. Some of the most-researched probiotics are: ...
The Care and Treatment of Skin and Soft Tissue Infections among
... or cocaine are lipophobic and therefore are not easily absorbed intramuscularly (IM) or subcutaneously (SQ). These substances when injected IM or SQ will immediately induce a burning sensation and initiate an inflammatory response. This inflammatory response can be a precursor for developing an SSTI ...
... or cocaine are lipophobic and therefore are not easily absorbed intramuscularly (IM) or subcutaneously (SQ). These substances when injected IM or SQ will immediately induce a burning sensation and initiate an inflammatory response. This inflammatory response can be a precursor for developing an SSTI ...
Integrated Care Pathway for - British Society of Gastroenterology
... attention of the endoscopist to the patients to whom antibiotics should be given. The conditions which render the patient at high risk of developing endocarditis are listed later. ...
... attention of the endoscopist to the patients to whom antibiotics should be given. The conditions which render the patient at high risk of developing endocarditis are listed later. ...
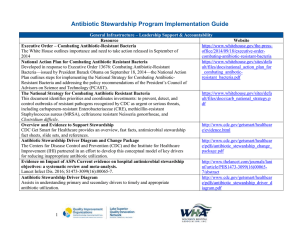
ASP-Implementation-Guide-June-2016
... and the dissemination of resistant microorganisms will reduce these adverse effects and their attendant costs. Appropriate antimicrobial stewardship that includes optimal selection, dose and duration of treatment, as well as control of antibiotic use, will prevent or slow the emergence of resistance ...
... and the dissemination of resistant microorganisms will reduce these adverse effects and their attendant costs. Appropriate antimicrobial stewardship that includes optimal selection, dose and duration of treatment, as well as control of antibiotic use, will prevent or slow the emergence of resistance ...
What is MRSA? How serious is MRSA? How does someone get
... MRSA is short for Meticillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus. Staphylococcus aureus is a bacterium (bug or germ) that about 30 per cent of us carry on our skin or in our nose without knowing about it. This is called ‘colonisation’. The inside of our nose and other moist areas of skin are most likely ...
... MRSA is short for Meticillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus. Staphylococcus aureus is a bacterium (bug or germ) that about 30 per cent of us carry on our skin or in our nose without knowing about it. This is called ‘colonisation’. The inside of our nose and other moist areas of skin are most likely ...
Inflammation of the Vagina (Vaginitis)
... duration of inflammation may be days to months, but typically have intermittent signs; normally resolves with time or after the first “heat” or “estrus” • Adult-onset vaginitis (inflammation of the vagina in the adult pet)— usually resolves after correction or removal of the underlying cause; antibi ...
... duration of inflammation may be days to months, but typically have intermittent signs; normally resolves with time or after the first “heat” or “estrus” • Adult-onset vaginitis (inflammation of the vagina in the adult pet)— usually resolves after correction or removal of the underlying cause; antibi ...
the role of medicines
... Medicines can also help your body fight the pathogens that cause illness. Antibiotics are a class of drug that destroy disease-causing microorganisms, called bacteria. Antibiotics such as penicillin work either by killing harmful bacteria in the body or by preventing bacteria from reproducing. ...
... Medicines can also help your body fight the pathogens that cause illness. Antibiotics are a class of drug that destroy disease-causing microorganisms, called bacteria. Antibiotics such as penicillin work either by killing harmful bacteria in the body or by preventing bacteria from reproducing. ...
inflammation_of_the_vagina
... duration of inflammation may be days to months, but typically have intermittent signs; normally resolves with time or after the first “heat” or “estrus” • Adult-onset vaginitis (inflammation of the vagina in the adult pet)— usually resolves after correction or removal of the underlying cause; antibi ...
... duration of inflammation may be days to months, but typically have intermittent signs; normally resolves with time or after the first “heat” or “estrus” • Adult-onset vaginitis (inflammation of the vagina in the adult pet)— usually resolves after correction or removal of the underlying cause; antibi ...
Inflammation of the Vagina
... duration of inflammation may be days to months, but typically have intermittent signs; normally resolves with time or after the first ―heat‖ or ―estrus‖ • Adult-onset vaginitis (inflammation of the vagina in the adult pet)— usually resolves after correction or removal of the underlying cause; antibi ...
... duration of inflammation may be days to months, but typically have intermittent signs; normally resolves with time or after the first ―heat‖ or ―estrus‖ • Adult-onset vaginitis (inflammation of the vagina in the adult pet)— usually resolves after correction or removal of the underlying cause; antibi ...
Catheter-Related Infections - Its All About Biofilm
... transient and resident micro-organisms exist on the surface of the skin. About 80% of resident micro-organisms inhabit the first 5 cell layers of the stratum corneum. The remaining 20% survive in biofilms within the underlying epidermal layers, sebaceous glands, and hair follicles.[5,9,10] The micro ...
... transient and resident micro-organisms exist on the surface of the skin. About 80% of resident micro-organisms inhabit the first 5 cell layers of the stratum corneum. The remaining 20% survive in biofilms within the underlying epidermal layers, sebaceous glands, and hair follicles.[5,9,10] The micro ...
LOWER RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS
... • More common at the extremes of age • Twice as common in winter months • A General Practitioner is likely to see up to 10 cases per yr • Represent <10% of all respiratory infection cases prescribed antibiotics • Most will be managed in the community ...
... • More common at the extremes of age • Twice as common in winter months • A General Practitioner is likely to see up to 10 cases per yr • Represent <10% of all respiratory infection cases prescribed antibiotics • Most will be managed in the community ...
The Growing Problem of Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
... hand rubs are comparatively more effective against MRSA than hand-washing, easier to accomplish, and lead to greater compliance; they do not work well for Clostridium difficile, the organism responsible for antibiotic-related diarrhea (and discussed in Pop-Vicas’s companion article),14 resulting in ...
... hand rubs are comparatively more effective against MRSA than hand-washing, easier to accomplish, and lead to greater compliance; they do not work well for Clostridium difficile, the organism responsible for antibiotic-related diarrhea (and discussed in Pop-Vicas’s companion article),14 resulting in ...
Let`s Talk About...Meningitis
... Just what are the symptoms of the viral and bacterial kind? Are they the same? The signs and symptoms of viral and bacterial meningitis can be the same but the symptoms are not necessarily the same for everyone. Common symptoms for any meningitis are high fever, severe headache, stiff neck, nausea, ...
... Just what are the symptoms of the viral and bacterial kind? Are they the same? The signs and symptoms of viral and bacterial meningitis can be the same but the symptoms are not necessarily the same for everyone. Common symptoms for any meningitis are high fever, severe headache, stiff neck, nausea, ...
DART German Antimicrobial Resistance Strategy
... For a long time, it was commonly believed that the discovery of penicillin and the use of antibiotics meant that bacterial infections had been conquered for all time. In recent years, however, we have been observing an increase in antimicrobially resistant infective agents in both human and veterina ...
... For a long time, it was commonly believed that the discovery of penicillin and the use of antibiotics meant that bacterial infections had been conquered for all time. In recent years, however, we have been observing an increase in antimicrobially resistant infective agents in both human and veterina ...
ABM Clinical Protocol #4: Mastitis, Revised March 2014
... Cephalexin is usually safe in women with suspected penicillin allergy, but clindamycin is suggested for cases of severe penicillin hypersensitivity.16 (III) Dicloxacillin appears to have a lower rate of adverse hepatic events than flucloxacillin.17 Many authorities recommend a 10–14-day course of an ...
... Cephalexin is usually safe in women with suspected penicillin allergy, but clindamycin is suggested for cases of severe penicillin hypersensitivity.16 (III) Dicloxacillin appears to have a lower rate of adverse hepatic events than flucloxacillin.17 Many authorities recommend a 10–14-day course of an ...
Evaluation of the penetration ofciprofloxacin and
... shows, bronchial tissue concentrations of ciprofloxacin had reached a steady state after four days of treatment as there was no correlation between the antibiotic concentration and the interval since the last dose of antibiotic. Several studies have shown greater success in eradicating organisms cau ...
... shows, bronchial tissue concentrations of ciprofloxacin had reached a steady state after four days of treatment as there was no correlation between the antibiotic concentration and the interval since the last dose of antibiotic. Several studies have shown greater success in eradicating organisms cau ...
Therapy for Bacterial Infections Following Ionizing Radiation Injury
... weapons could be synergistic, so that injury severity would be much greater than from either weapons or infectious agents alone. Irradiation diminishes innate immune responses, particularly the inflammatory response, without which systemic infections among large numbers of casualties may become diff ...
... weapons could be synergistic, so that injury severity would be much greater than from either weapons or infectious agents alone. Irradiation diminishes innate immune responses, particularly the inflammatory response, without which systemic infections among large numbers of casualties may become diff ...
Antibiotic Guidelines - NHS Antibiotic Guidelines App
... function. In severe or recurrent cases consider a larger dose or longer course. 3. Lower threshold for antibiotics in immunocompromised or those with multiple morbidities; consider culture and seek advice. 4. Prescribe an antibiotic only when there is likely to be a clear clinical benefit. 5. Consid ...
... function. In severe or recurrent cases consider a larger dose or longer course. 3. Lower threshold for antibiotics in immunocompromised or those with multiple morbidities; consider culture and seek advice. 4. Prescribe an antibiotic only when there is likely to be a clear clinical benefit. 5. Consid ...
Acinetobacter For Clinicians Important Facts
... How are Acinetobacter infections treated? Infections with Acinetobacter are treated with antibiotics and with other supportive care using all available clinical and laboratory information and expertise. Surgeon General’s Advisors for infectious diseases and laboratory medicine as well as preventive ...
... How are Acinetobacter infections treated? Infections with Acinetobacter are treated with antibiotics and with other supportive care using all available clinical and laboratory information and expertise. Surgeon General’s Advisors for infectious diseases and laboratory medicine as well as preventive ...
Vol. 2. No. 1 - Infection Control Resource
... treatment and systemic antibiotics, and antibiotic-resistant bacteria such as methicillinresistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE). The literature reveals that increased length of stay and costs are associated with SSIs. 3 Deep SSIs involving organs or spaces ...
... treatment and systemic antibiotics, and antibiotic-resistant bacteria such as methicillinresistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE). The literature reveals that increased length of stay and costs are associated with SSIs. 3 Deep SSIs involving organs or spaces ...
Antimicrobial resistance
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is when microbes are less treatable with one or more medication used to treat or prevent infection. This makes these medications less effective in both treating and preventing infection. Resistant microbes may require other medications or higher doses – often with more side effects, some of which may be life threatening on their own. Some infections become completely untreatable due to resistance. All classes of microbes develop resistance: fungi – antifungal resistance, viruses – antiviral resistance, protozoans – antiprotozoal resistance, and bacteria – antibiotic resistance. Microbes which are resistant to multiple antimicrobials are termed multidrug resistant (MDR) (or, sometimes in the lay press, superbugs). Antimicrobial resistance is a growing problem in the world, and causes millions of deaths every year.Antibiotics should only be used when needed and only when prescribed. Health care providers should try to minimize spread of resistant infections by using proper sanitations techniques including handwashing or disinfecting between each patient. Prescribing the correct antibiotic is important and doses should not be skipped. The shortest duration needed should be used. Narrow-spectrum antibiotics should be used rather than broad-spectrum antibiotics when possible. Cultures should be taken before treatment when indicated and treatment potentially changed based on the susceptibility report.Some organisms are naturally resistant but the term most often refers to acquired resistance, which can be a result of either new mutations or transfer of resistance genes between organisms. The increasing rates of antibiotic resistant infections are caused by antibiotic use from human and veterinary medicine. Any use of antibiotics can increase selective pressure in a population of bacteria, promoting resistant bacteria and causing vulnerable bacteria to die. As resistance to antibiotics becomes more common there is greater need for alternative treatments. Call for new antibiotic therapies have been issues, but there is continuing decline in the number of approved drugs. Infection by resistant microbes may occur outside of a healthcare institution or within a healthcare institution. Common types of drug-resistant bacteria include: methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), vancomycin-resistant S. aureus (VRSA), extended spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL), vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus (VRE), multidrug-resistant A. baumannii (MRAB).Antibiotic resistance is a serious and growing global problem: a World Health Organization (WHO) report released April 2014 stated, ""this serious threat is no longer a prediction for the future, it is happening right now in every region of the world and has the potential to affect anyone, of any age, in any country. Antibiotic resistance—when bacteria change so antibiotics no longer work in people who need them to treat infections—is now a major threat to public health."" There have been increasing public calls for global collective action to address the threat, including a proposal for an international treaty on antimicrobial resistance. Antibiotic resistance is not properly mapped across the world, but the countries that are affected the most are poorer countries with already weaker healthcare systems.