What we can measure
... the sun – since we have the planets orbiting the sun. We are only now being able to “see” other planets orbit other stars since those stars are so far away. However, we notice that there are lots of stars that orbit each other – and we can use that to get the mass of the bigger (central) star. ...
... the sun – since we have the planets orbiting the sun. We are only now being able to “see” other planets orbit other stars since those stars are so far away. However, we notice that there are lots of stars that orbit each other – and we can use that to get the mass of the bigger (central) star. ...
The Solar Neighborhood
... Estimating the Ages of Star Clusters - Massive stars burn their nuclear fuel faster than lower mass stars and leave the main sequence sooner. In a cluster in which all the stars formed at the same time, the stars “peel off” the main sequence from the top, leaving only progressively less and less mas ...
... Estimating the Ages of Star Clusters - Massive stars burn their nuclear fuel faster than lower mass stars and leave the main sequence sooner. In a cluster in which all the stars formed at the same time, the stars “peel off” the main sequence from the top, leaving only progressively less and less mas ...
ASTRO-114--Lecture 37-
... is. If you look with your two eyes and you notice that — well, you don’t even think about it, but your eyes notice that there’s a slightly different perspective. You have a different background behind an object you’re looking at and so you can tell how far away an object is by how much parallax you ...
... is. If you look with your two eyes and you notice that — well, you don’t even think about it, but your eyes notice that there’s a slightly different perspective. You have a different background behind an object you’re looking at and so you can tell how far away an object is by how much parallax you ...
Stars (Ch. 13)
... bound are called binary stars. • Binary stars provide a means of determining the masses of stars. • Other properties can also sometimes be determined from binary stars. ...
... bound are called binary stars. • Binary stars provide a means of determining the masses of stars. • Other properties can also sometimes be determined from binary stars. ...
Picture: Alnitak is the left-hand star in Orion`s Belt. Image: NASA
... survive long enough to move far from the place where they were formed. Their brief main sequence careers, measured in tens of millions of years, probably allows too little time for even the most primitive forms of life to develop on any worlds that circle around them (assuming that life could exist ...
... survive long enough to move far from the place where they were formed. Their brief main sequence careers, measured in tens of millions of years, probably allows too little time for even the most primitive forms of life to develop on any worlds that circle around them (assuming that life could exist ...
Constellation Catalog
... Constellation was first cataloged by Ptolemy in 2nd century B.C. The constellation is named after Andromeda who, in Greek Mythology, was the daughter of Cassiopeia and Cepheus. Cassiopeia bragged that her daughter was prettier than the sea nymphs. The Sea Nymphs heard this and were angered so they t ...
... Constellation was first cataloged by Ptolemy in 2nd century B.C. The constellation is named after Andromeda who, in Greek Mythology, was the daughter of Cassiopeia and Cepheus. Cassiopeia bragged that her daughter was prettier than the sea nymphs. The Sea Nymphs heard this and were angered so they t ...
HR Diagram Explorer Worksheet
... Uncheck show luminosity classes and check show instability strip. Note that this region of the HR Diagram indicates where pulsating stars are found such as RR Lyrae stars and Cepheid variable stars. These stars vary in brightness because they are pulsating – alternately growing bigger and smaller – ...
... Uncheck show luminosity classes and check show instability strip. Note that this region of the HR Diagram indicates where pulsating stars are found such as RR Lyrae stars and Cepheid variable stars. These stars vary in brightness because they are pulsating – alternately growing bigger and smaller – ...
The Sky
... defined groupings called asterisms. – The Big Dipper, for example, is a well-known asterism that is part of the constellation Ursa Major (Great Bear). – Another asterism is the Great Square of Pegasus, which includes three stars from Pegasus and one (Alpheratz) from Andromeda. ...
... defined groupings called asterisms. – The Big Dipper, for example, is a well-known asterism that is part of the constellation Ursa Major (Great Bear). – Another asterism is the Great Square of Pegasus, which includes three stars from Pegasus and one (Alpheratz) from Andromeda. ...
Lecture 10 Spectra of Stars and Binaries
... • O B A F G K M L T Subdivide each class into numbered subclasses: ...
... • O B A F G K M L T Subdivide each class into numbered subclasses: ...
star
... The Lives of Stars Stars live for a very long time, up to 100 million years or more No humans can possibly observe a star this long! How can we learn about the stages in a star’s life? We can take a celestial census, getting a snapshot of many stars at different stages of their life We can then try ...
... The Lives of Stars Stars live for a very long time, up to 100 million years or more No humans can possibly observe a star this long! How can we learn about the stages in a star’s life? We can take a celestial census, getting a snapshot of many stars at different stages of their life We can then try ...
Rotation in the ZAMS: Be and Bn stars
... predicted (τo = 1) with the actually observed number of Be stars around the Sun is shown in Fig. 1d. This shows that the apparently bi-modal distribution of Be stars around the Sun against the spectral type is entirely explained by the interplay of the probability of detecting Be stars (EHα ), the s ...
... predicted (τo = 1) with the actually observed number of Be stars around the Sun is shown in Fig. 1d. This shows that the apparently bi-modal distribution of Be stars around the Sun against the spectral type is entirely explained by the interplay of the probability of detecting Be stars (EHα ), the s ...
Astronomy Report Southern Cross Authors Maria Constanza Pavez
... The Southern Cross has not been visible from the Northern Hemisphere for 20 centuries but it has been well observable form the South for many centuries, as it has been demonstrated through ancient cultures that worshiped this constellation. III. Today’s sky. If Ptolemy lived at this time, he would n ...
... The Southern Cross has not been visible from the Northern Hemisphere for 20 centuries but it has been well observable form the South for many centuries, as it has been demonstrated through ancient cultures that worshiped this constellation. III. Today’s sky. If Ptolemy lived at this time, he would n ...
Night Sky Course Stars and Star Clusters within the
... cluster was close enough, like the Hyades, astronomers would measure proper motions.The proper motions appear to converge toward a point in the sky, which indicates the direction of travel for the cluster. From the Doppler shift (using spectral data) we find the component of V away from us. From thi ...
... cluster was close enough, like the Hyades, astronomers would measure proper motions.The proper motions appear to converge toward a point in the sky, which indicates the direction of travel for the cluster. From the Doppler shift (using spectral data) we find the component of V away from us. From thi ...
The Celestial Sphere
... Building a Celestial Sphere 1. Prepare the two star charts by cutting along the outside lines with the scissors. The star chart will look like a black flower with eight petals. The white line that crosses four of the petals is the ECLIPTIC. This line represents the apparent path of the Sun against t ...
... Building a Celestial Sphere 1. Prepare the two star charts by cutting along the outside lines with the scissors. The star chart will look like a black flower with eight petals. The white line that crosses four of the petals is the ECLIPTIC. This line represents the apparent path of the Sun against t ...
The Sky This Month
... • Bright diffuse nebula with brightest central region about 1° across. • 100 ly away and ~60 ly across. • The closest known star forming region – filled with lots of young stars (Trapezium cluster). • Galileo discovered the Trapezium cluster (4/2/1617) but missed the nebula… ...
... • Bright diffuse nebula with brightest central region about 1° across. • 100 ly away and ~60 ly across. • The closest known star forming region – filled with lots of young stars (Trapezium cluster). • Galileo discovered the Trapezium cluster (4/2/1617) but missed the nebula… ...
Astronomy Activity: The Life-Line of the Stars
... brightness . Stars which are very bright are called magnitude 1 stars . The next brightest are magnitude 2 stars. Then comes magnitude 3, 4, 5, and down to the very faintest stars visible with the naked eye, magnitude 6 stars*. All stars are not the same distance away. Obviously, a star which is far ...
... brightness . Stars which are very bright are called magnitude 1 stars . The next brightest are magnitude 2 stars. Then comes magnitude 3, 4, 5, and down to the very faintest stars visible with the naked eye, magnitude 6 stars*. All stars are not the same distance away. Obviously, a star which is far ...
Stellarium01 Starter Part A B Doc - ASTR101
... galaxies, nebulae, star clusters, and much more! The last three objects are called Deep Sky Objects. Each of these is a distant object much bigger than a single star and (almost) permanently located at a certain spot in the sky, in a particular constellation. There are many catalogs of Deep Sky Obje ...
... galaxies, nebulae, star clusters, and much more! The last three objects are called Deep Sky Objects. Each of these is a distant object much bigger than a single star and (almost) permanently located at a certain spot in the sky, in a particular constellation. There are many catalogs of Deep Sky Obje ...
The Milky Way - Houston Community College System
... difficult. To discover the properties of stars, astronomers have used their telescopes and spectrographs in clever ways to learn the secrets hidden in starlight. The result is a family portrait of the stars. In this chapter you will find answers to five important questions about stars: • How far awa ...
... difficult. To discover the properties of stars, astronomers have used their telescopes and spectrographs in clever ways to learn the secrets hidden in starlight. The result is a family portrait of the stars. In this chapter you will find answers to five important questions about stars: • How far awa ...
uniview glossary - DMNS Galaxy Guide Portal
... composed of highly dense gaseous hydrogen and helium, with a metal hydrogen mantle, but a very small inner core, hence the phrase “Gas Giant.” The average distance from the Sun is 4.9 AU. Saturn: (Greek-Cronus); also the father of Jupiter in mythology) The day, Saturday, is named after the planet ...
... composed of highly dense gaseous hydrogen and helium, with a metal hydrogen mantle, but a very small inner core, hence the phrase “Gas Giant.” The average distance from the Sun is 4.9 AU. Saturn: (Greek-Cronus); also the father of Jupiter in mythology) The day, Saturday, is named after the planet ...
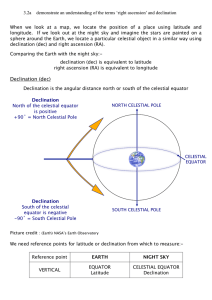
3.2a Right Ascension and Declination
... If a person was able to see the night sky shown above for a full day, the full band of stars would pass in front of them, moving steadily towards the right. The longitude reference point was more difficult. Many countries have laid claim to the Prime Meridian – the Chinese once used a gate from the ...
... If a person was able to see the night sky shown above for a full day, the full band of stars would pass in front of them, moving steadily towards the right. The longitude reference point was more difficult. Many countries have laid claim to the Prime Meridian – the Chinese once used a gate from the ...
Bright versus Nearby Stars
... • 95% of the brightest stars are more luminous than the Sun. • The average absolute magnitude of a bright star is –1.2, equivalent to 300 solar luminosities. ...
... • 95% of the brightest stars are more luminous than the Sun. • The average absolute magnitude of a bright star is –1.2, equivalent to 300 solar luminosities. ...
THE LIFE CYCLES OF STARS (3)
... Illust Fraunhofer spectrum Fraunhofer found dark lines crossing the sun's spectrum. He was not the first to see them but was the first to catalogue them. He named them A,B,C,D,……. He did not know what caused them. These dark lines mean something. We now know each one is caused by some element in the ...
... Illust Fraunhofer spectrum Fraunhofer found dark lines crossing the sun's spectrum. He was not the first to see them but was the first to catalogue them. He named them A,B,C,D,……. He did not know what caused them. These dark lines mean something. We now know each one is caused by some element in the ...
Unit 1
... • a. Because this is the only phase that is common to all stars • b. because most stars die at the end of main sequence phase • c. because most stars in the sky are created at about the same time • d. because this is the longest lasting phase in each star life ...
... • a. Because this is the only phase that is common to all stars • b. because most stars die at the end of main sequence phase • c. because most stars in the sky are created at about the same time • d. because this is the longest lasting phase in each star life ...
Orion (constellation)

Orion is a prominent constellation located on the celestial equator and visible throughout the world. It is one of the most conspicuous and recognizable constellations in the night sky. It was named after Orion, a hunter in Greek mythology. Its brightest stars are Rigel (Beta Orionis) and Betelgeuse (Alpha Orionis), a blue-white and a red supergiant, respectively.