STAR FORMATION (Ch. 19) - University of Texas Astronomy Home
... gaseous pillars to the right and lower left of the cluster. These pillars are sculptured by the same physical processes as the famous pillars Hubble photographed in the M16 Eagle Nebula. Dark clouds at the upper right are so-called Bok globules, which are probably in an earlier stage of star formati ...
... gaseous pillars to the right and lower left of the cluster. These pillars are sculptured by the same physical processes as the famous pillars Hubble photographed in the M16 Eagle Nebula. Dark clouds at the upper right are so-called Bok globules, which are probably in an earlier stage of star formati ...
Lecture6
... molecular clouds (cool clouds with CO and H2 molecules). Bursts of protostar formation takes place when these dense regions are hit by high speed (`supersonic’, meaning speed faster than the sound speed) winds from a near-by supernova explosion or UV light and winds from near-by hot O and B stars ...
... molecular clouds (cool clouds with CO and H2 molecules). Bursts of protostar formation takes place when these dense regions are hit by high speed (`supersonic’, meaning speed faster than the sound speed) winds from a near-by supernova explosion or UV light and winds from near-by hot O and B stars ...
Chapter 10 Measuring the Stars: Giants, Dwarfs, and the Main
... • Hotter, more massive blue stars (top left) to cooler, less massive red stars (lower right) ...
... • Hotter, more massive blue stars (top left) to cooler, less massive red stars (lower right) ...
OUR COSMIC NEIGHBORS Story of the Stars
... its principal stars there is the suggestion of a chair, and it is easy to imagine it as being occupied by the Queen. This constellation is found directly across the Pole from Ursa Major. Both are circumpolar constellations, so when one is high in the sky, the other is low over the northern point. Ca ...
... its principal stars there is the suggestion of a chair, and it is easy to imagine it as being occupied by the Queen. This constellation is found directly across the Pole from Ursa Major. Both are circumpolar constellations, so when one is high in the sky, the other is low over the northern point. Ca ...
Stars
... A blue giant is very bright. Like a light house, they shine across a great distance. Even though blue giant stars are rare, they make up many of the stars we see at night. Blue giant stars die in a spectacular way. They grow larger just like the Sun sized stars, but then instead of shrinking and for ...
... A blue giant is very bright. Like a light house, they shine across a great distance. Even though blue giant stars are rare, they make up many of the stars we see at night. Blue giant stars die in a spectacular way. They grow larger just like the Sun sized stars, but then instead of shrinking and for ...
Define the following terms in the space provided
... 13) If you could see stars during the day, the drawing above shows what the sky would look like at noon on a given day. Which of the constellations shown would be highest in the sky six hours later than the time pictured above? A) Leo D) Taurus B) Cancer E) Pisces C) Gemini 14) If you could see star ...
... 13) If you could see stars during the day, the drawing above shows what the sky would look like at noon on a given day. Which of the constellations shown would be highest in the sky six hours later than the time pictured above? A) Leo D) Taurus B) Cancer E) Pisces C) Gemini 14) If you could see star ...
Stars
... • Overall spectrum is strongly related to the surface temperature of the star • Stars are categorized into classes by: 1. Strength of the spectral lines 2. Shape ...
... • Overall spectrum is strongly related to the surface temperature of the star • Stars are categorized into classes by: 1. Strength of the spectral lines 2. Shape ...
31-2 - Fremont Peak Observatory
... one should consider this tour to be through the back roads of Scorpius. One can begin this tour of Scorpius at the “Cat’s Eyes.” The Cat’s Eyes, λ and υ-Scorpii, are located at the Scorpion’s stinger on the tail of the scorpion. Lambda-Scorpii, Shaula, is the second brightest star in Scorpius (magni ...
... one should consider this tour to be through the back roads of Scorpius. One can begin this tour of Scorpius at the “Cat’s Eyes.” The Cat’s Eyes, λ and υ-Scorpii, are located at the Scorpion’s stinger on the tail of the scorpion. Lambda-Scorpii, Shaula, is the second brightest star in Scorpius (magni ...
SMMP_BISANA - Infinity and Beyond
... • At the time of Homer, however, most of the constellations were not associated with any particular myth, hero, or god. They were instead known simply as the objects or animals which they represented--the Lyre, for instance, or the Ram. By the 5th century B.C., however, most of the constellations h ...
... • At the time of Homer, however, most of the constellations were not associated with any particular myth, hero, or god. They were instead known simply as the objects or animals which they represented--the Lyre, for instance, or the Ram. By the 5th century B.C., however, most of the constellations h ...
same
... is in the state of New York, we specify for example that Betelgeuse is in Orion. However, there are also reasons why we use right ascension and declination (i.e., exact coordinates) as you will find out. Actually, professional astronomers only use the exact coordinates. The stars that make up the co ...
... is in the state of New York, we specify for example that Betelgeuse is in Orion. However, there are also reasons why we use right ascension and declination (i.e., exact coordinates) as you will find out. Actually, professional astronomers only use the exact coordinates. The stars that make up the co ...
IB_Op_F_04 - Effectsmeister
... become smaller) and if a star is moving radially away from the earth, the light spectrum will be redshifted (all wavelengths become larger). Use the four positions in the figure under part 2 to predict which star(s) that are blue/redshifted if a shift appears. A simulation might make the various cas ...
... become smaller) and if a star is moving radially away from the earth, the light spectrum will be redshifted (all wavelengths become larger). Use the four positions in the figure under part 2 to predict which star(s) that are blue/redshifted if a shift appears. A simulation might make the various cas ...
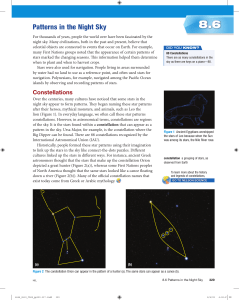
Patterns in the Night Sky
... 4. The North Celestial Pole is very close to the star shown in Figure 9. What is its name? K/U 5. Explain why it might be beneficial to use the geocentric model when describing the positions and motions of the stars in the night sky. T/I 6. Name two ways that ancient cultures recognized the importan ...
... 4. The North Celestial Pole is very close to the star shown in Figure 9. What is its name? K/U 5. Explain why it might be beneficial to use the geocentric model when describing the positions and motions of the stars in the night sky. T/I 6. Name two ways that ancient cultures recognized the importan ...
Properties of Stars - Mr. Carter`s Earth
... The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is actually a graph that illustrates the relationship that exists between the average surface temperature of stars and their absolute magnitude, which is how bright they would appear to be if they were all the same distance away. Rather than speak of the brightness of ...
... The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is actually a graph that illustrates the relationship that exists between the average surface temperature of stars and their absolute magnitude, which is how bright they would appear to be if they were all the same distance away. Rather than speak of the brightness of ...
Microsoft Power Point version
... temperature dictates the energy states of electrons in atoms temperature dictates the types of ions or molecules which exist this, in turn, determines the number and relative strengths of absorption lines in the star’s spectrum this fact was discovered by Cecilia Payne-Gaposchkin in 1925 ...
... temperature dictates the energy states of electrons in atoms temperature dictates the types of ions or molecules which exist this, in turn, determines the number and relative strengths of absorption lines in the star’s spectrum this fact was discovered by Cecilia Payne-Gaposchkin in 1925 ...
HR Diagram Activity - Mr. Alster`s Science Classes
... Credit: Activity adapted from sir-ray.com ...
... Credit: Activity adapted from sir-ray.com ...
Legends Night Sky Orion
... - The little dog is indeed ‘little’, only two stars. - The brighter one of these is Procyon. - It can be found by following an imaginary line through Orion’s shoulders and approximately straight up from Sirius. ...
... - The little dog is indeed ‘little’, only two stars. - The brighter one of these is Procyon. - It can be found by following an imaginary line through Orion’s shoulders and approximately straight up from Sirius. ...
Introduction to Basic Stargazing Part I - Naples Free-Net
... Earth. It is interesting to note that the magnitude of some stars can vary also, but once again that is an article for another time. Notice how bright stars, particularly Sirius, sparkle and flash different colors while near the horizon. This is caused by our atmosphere being thicker and rather unst ...
... Earth. It is interesting to note that the magnitude of some stars can vary also, but once again that is an article for another time. Notice how bright stars, particularly Sirius, sparkle and flash different colors while near the horizon. This is caused by our atmosphere being thicker and rather unst ...
Educator`s Guide
... - The little dog is indeed ‘little’, only two stars. - The brighter one of these is Procyon. - It can be found by following an imaginary line through Orion’s shoulders and approximately straight up from Sirius. ...
... - The little dog is indeed ‘little’, only two stars. - The brighter one of these is Procyon. - It can be found by following an imaginary line through Orion’s shoulders and approximately straight up from Sirius. ...
JWST_eye - University of Arizona
... second, one picture every 0.1 second. Instruments on JWST, like NIRCam, can take much longer time exposures to collect even more light and record much fainter objects. How much more light would be collected if your eye could take a one hour exposure instead of its normal 0.1 second? ____ (minutes pe ...
... second, one picture every 0.1 second. Instruments on JWST, like NIRCam, can take much longer time exposures to collect even more light and record much fainter objects. How much more light would be collected if your eye could take a one hour exposure instead of its normal 0.1 second? ____ (minutes pe ...
Highlights of the Month - Bridgend Astronomical Society
... Between Beta and Gamma Lyra lies a beautiful object called the Ring Nebula. It is the 57th object in the Messier Catalogue and so is also called M57. Such objects are called planetary nebulae as in a telescope they show a disc, rather like a planet. But in fact they are the remnants of stars, simila ...
... Between Beta and Gamma Lyra lies a beautiful object called the Ring Nebula. It is the 57th object in the Messier Catalogue and so is also called M57. Such objects are called planetary nebulae as in a telescope they show a disc, rather like a planet. But in fact they are the remnants of stars, simila ...
The Ursa Major Moving Cluster, Collinder 285
... at 10 km/sec, and its spatial velocity relative to our Sun is about 46 km/s. This cluster is centered at a distance of about 75 light years from us (i.e., our solar system). As it is spread over a volume of 30 light years length and 18 light years width, it covers an enourmous portion of the sky, an ...
... at 10 km/sec, and its spatial velocity relative to our Sun is about 46 km/s. This cluster is centered at a distance of about 75 light years from us (i.e., our solar system). As it is spread over a volume of 30 light years length and 18 light years width, it covers an enourmous portion of the sky, an ...
How Bright is that Star?
... A 1st magnitude star is 100x brighter than a “6th ” Each order of magnitude is therefore 2.15 times brighter than the one below it. Magnitude is now given in decimal form. Deneb now rates a 1.26, and Betelgeuse rates .87. Hipparchus underestimated how bright the brightest were, so now we even use ne ...
... A 1st magnitude star is 100x brighter than a “6th ” Each order of magnitude is therefore 2.15 times brighter than the one below it. Magnitude is now given in decimal form. Deneb now rates a 1.26, and Betelgeuse rates .87. Hipparchus underestimated how bright the brightest were, so now we even use ne ...
Characteristics of Stars (Ph)
... Astronomers classify stars according to their physical characteristics. The main characteristics used to classify stars are size, temperature, and brightness. Sizes of Stars When you look at stars in the sky, they all appear to be the same size. Many stars are actually about the size of the sun, whi ...
... Astronomers classify stars according to their physical characteristics. The main characteristics used to classify stars are size, temperature, and brightness. Sizes of Stars When you look at stars in the sky, they all appear to be the same size. Many stars are actually about the size of the sun, whi ...
Trapezium Fracture
... begin to understand the ultimate of their own world? Perhaps these beings will not have evolved on the Orion home worlds at all, but travelled to them from another distant place, and when they peer curiously at our own long dead region of space, it will not be in order to understand their ultimate f ...
... begin to understand the ultimate of their own world? Perhaps these beings will not have evolved on the Orion home worlds at all, but travelled to them from another distant place, and when they peer curiously at our own long dead region of space, it will not be in order to understand their ultimate f ...
Images from the Las Cumbres Observatory Global Telescope
... This map shows the constellations seen in the South during the early evening, including the prominent constellation of Orion. Moving up and to the right - following the line of the 3 stars of Orion's belt - brings one to Taurus; the head of the bull being outlined by the V-shaped cluster called the ...
... This map shows the constellations seen in the South during the early evening, including the prominent constellation of Orion. Moving up and to the right - following the line of the 3 stars of Orion's belt - brings one to Taurus; the head of the bull being outlined by the V-shaped cluster called the ...
Orion (constellation)

Orion is a prominent constellation located on the celestial equator and visible throughout the world. It is one of the most conspicuous and recognizable constellations in the night sky. It was named after Orion, a hunter in Greek mythology. Its brightest stars are Rigel (Beta Orionis) and Betelgeuse (Alpha Orionis), a blue-white and a red supergiant, respectively.