Ch. 9: Presentation Slides
... lengthy as this requires additional generations of selfing (to identify the homozygous recessive) after every back-crossing • Some characters like complex disease resistance reaction or biotic stresses (QTLs) that show continuous variation and do not fit into Mendelian ratios are most difficult to d ...
... lengthy as this requires additional generations of selfing (to identify the homozygous recessive) after every back-crossing • Some characters like complex disease resistance reaction or biotic stresses (QTLs) that show continuous variation and do not fit into Mendelian ratios are most difficult to d ...
Activity-Sickle-Cell-Anemia-Instructor
... Q6: What does this comparison suggest about the ability of what seems like a deleterious mutation (HbS) to persist in human populations? How could you test this suggestion? Relate these ideas to assertion that "a gene's full meaning can never be known in advance”: what are two different “meanings” o ...
... Q6: What does this comparison suggest about the ability of what seems like a deleterious mutation (HbS) to persist in human populations? How could you test this suggestion? Relate these ideas to assertion that "a gene's full meaning can never be known in advance”: what are two different “meanings” o ...
Carbohydrates
... Oligomeric or polymeric carbohydrates are often covalently bound to lipids or proteins.eg.the glycolipids and glycoproteins in cell membranes . Glycoproteins also occur in the blood as plasma proteins . ...
... Oligomeric or polymeric carbohydrates are often covalently bound to lipids or proteins.eg.the glycolipids and glycoproteins in cell membranes . Glycoproteins also occur in the blood as plasma proteins . ...
Slide 1
... 4.Random Mutagenesisis is used to construct large &diverse clone libraries of mutated DNA ...
... 4.Random Mutagenesisis is used to construct large &diverse clone libraries of mutated DNA ...
Evolution of Man
... of genes. Even before the human genome was sequenced back in 2000, says biologist Sean Carroll of the University of Wisconsin, Madison, "it was estimated that humans had 100,000 genes. When we got the genome, the estimate dropped to 25,000. Now we know the overall number is about 22,000, and it migh ...
... of genes. Even before the human genome was sequenced back in 2000, says biologist Sean Carroll of the University of Wisconsin, Madison, "it was estimated that humans had 100,000 genes. When we got the genome, the estimate dropped to 25,000. Now we know the overall number is about 22,000, and it migh ...
DNA and Protein Synthesis Notes 2015
... • Mutations – heritable changes in genetic information (changes to the DNA sequence) • Two types - gene and chromosomal mutations • Mutations can be caused by chemical or physical agents (mutagens) – Chemical – pesticides, tobacco smoke, environmental pollutants – Physical – X-rays and ultraviolet l ...
... • Mutations – heritable changes in genetic information (changes to the DNA sequence) • Two types - gene and chromosomal mutations • Mutations can be caused by chemical or physical agents (mutagens) – Chemical – pesticides, tobacco smoke, environmental pollutants – Physical – X-rays and ultraviolet l ...
BITC1311 Intro to Biotechnology Name
... 2. The earliest recorded forms of biotechnology date from 2000 BC with the use of fermentations and selective breeding of domesticated livestock. Describe some applications of each of these forms of early biotechnology. 3. Antibiotics were discovered in 1928 by Alexander Fleming. How are antibiotics ...
... 2. The earliest recorded forms of biotechnology date from 2000 BC with the use of fermentations and selective breeding of domesticated livestock. Describe some applications of each of these forms of early biotechnology. 3. Antibiotics were discovered in 1928 by Alexander Fleming. How are antibiotics ...
File
... Meiosis I, which is preceded by a replication of chromosomes. Its stages are Prophase I: Each replicated chromosome pairs with its corresponding homologous chromosome forming a tetrad. During tetrad formation, alleles can be exchanged between chromatids, a process called crossing-over. Metaphase ...
... Meiosis I, which is preceded by a replication of chromosomes. Its stages are Prophase I: Each replicated chromosome pairs with its corresponding homologous chromosome forming a tetrad. During tetrad formation, alleles can be exchanged between chromatids, a process called crossing-over. Metaphase ...
Specter- DNA revolution- National Geographic
... tumor cells in the laboratory, then test various drugs to see which can stop them from growing. Soon doctors may be able to use CRISPR to treat some diseases directly. Stem cells taken from people with hemophilia, for example, could be edited outside of the body to correct the genetic flaw that cause ...
... tumor cells in the laboratory, then test various drugs to see which can stop them from growing. Soon doctors may be able to use CRISPR to treat some diseases directly. Stem cells taken from people with hemophilia, for example, could be edited outside of the body to correct the genetic flaw that cause ...
Data Mining in Ensembl with BioMart
... • BioMart is a search engine that can find multiple terms and put them into a table format. • Such as: mouse gene (IDs), chromosome and base pair position • No programming required! ...
... • BioMart is a search engine that can find multiple terms and put them into a table format. • Such as: mouse gene (IDs), chromosome and base pair position • No programming required! ...
slides - Botany
... percent of cases percent of cases wherewhere diploidsdiploids have higherhave rateshigher rates ...
... percent of cases percent of cases wherewhere diploidsdiploids have higherhave rateshigher rates ...
... To examine this, we applied the qPCR technique to mutants previously generated within this laboratory during the characterisation of mannitol metabolism in S. nodorum (Solomon et al., 2005; Solomon et al., 2006d). A series of deletion mutants lacking the mannitol dehydrogenase gene (Mdh1) and also t ...
Study Guide B
... polymerase strings together a complementary strand of RNA. The RNA strand detaches from the DNA as it is transcribed, and the DNA zips back together. mRNA: intermediate message that is translated to form a protein; rRNA: forms part of ribosomes; tRNA: brings amino acids from the cytoplasm to a ribos ...
... polymerase strings together a complementary strand of RNA. The RNA strand detaches from the DNA as it is transcribed, and the DNA zips back together. mRNA: intermediate message that is translated to form a protein; rRNA: forms part of ribosomes; tRNA: brings amino acids from the cytoplasm to a ribos ...
Morgan and Sex Linkage / Mutations
... 1 nucleotide is replaced by a different nucleotide, results in a new codon. It COULD affect one amino acid. - If substituted nucleotide does not change AA, no affect on organism - If substituted nucleotide does change AA, resulting protein will be altered, affecting the organism. ...
... 1 nucleotide is replaced by a different nucleotide, results in a new codon. It COULD affect one amino acid. - If substituted nucleotide does not change AA, no affect on organism - If substituted nucleotide does change AA, resulting protein will be altered, affecting the organism. ...
Chapter 6
... – The divergence between any pair of globin sequences is proportional to the time since they shared common ancestry. ...
... – The divergence between any pair of globin sequences is proportional to the time since they shared common ancestry. ...
Animal Cell Structure
... of DNA serves several functions. The overall negative charge of the DNA is neutralized by the positive charge of the histone molecules, the DNA takes up much less space, and inactive DNA can be folded into inaccessible locations until it is needed. There are two types of chromatin. Euchromatin is th ...
... of DNA serves several functions. The overall negative charge of the DNA is neutralized by the positive charge of the histone molecules, the DNA takes up much less space, and inactive DNA can be folded into inaccessible locations until it is needed. There are two types of chromatin. Euchromatin is th ...
Bacterial DNA Insert
... •All types and more are in the same transformation reaction. •We must distinguish bacteria that have taken up plasmid. •Later, we must distinguish the product of interest from other transformation products. ...
... •All types and more are in the same transformation reaction. •We must distinguish bacteria that have taken up plasmid. •Later, we must distinguish the product of interest from other transformation products. ...
Name per ______ date ______ Cell Respiration Introduction
... 2. How does the cell get glycolysis going? ...
... 2. How does the cell get glycolysis going? ...
Richard Dawkins on the nature of the gene
... “My unit of selection, whether I called it a gene or a replicator, never had any pretensions to unitariness ... unitariness is not an important consideration.” (TEP: 86) “If chromosomes were like bead necklaces... with crossing-over always breaking the necklace between beads and not within them, you ...
... “My unit of selection, whether I called it a gene or a replicator, never had any pretensions to unitariness ... unitariness is not an important consideration.” (TEP: 86) “If chromosomes were like bead necklaces... with crossing-over always breaking the necklace between beads and not within them, you ...
Review Questions
... activation? What do they phosphorylate once they are activated? 21. How is the Syk kinase activated and what, in turn, does it activate (and how)? 22. Describe the roles of BLNK and Btk in B cell signaling. 23. How is PLC-activated in B cells? 24. Be able to compare and contrast B cell and T cell ...
... activation? What do they phosphorylate once they are activated? 21. How is the Syk kinase activated and what, in turn, does it activate (and how)? 22. Describe the roles of BLNK and Btk in B cell signaling. 23. How is PLC-activated in B cells? 24. Be able to compare and contrast B cell and T cell ...
Suracell: My Test Results
... identical twins, which are 100% identical). However, that crucial variation of 0.5% is one of the factors that make us genetically unique. DNA can be thought of as a string of nucleotide sequences represented by the letters A (for adenine), T (for thymine), G (for guanine) and C ( for cytosine) - 3 ...
... identical twins, which are 100% identical). However, that crucial variation of 0.5% is one of the factors that make us genetically unique. DNA can be thought of as a string of nucleotide sequences represented by the letters A (for adenine), T (for thymine), G (for guanine) and C ( for cytosine) - 3 ...
Topic I Cells - JSH Elective Science with Ms. Barbanel
... Describe the structure and explain the function of various cellular structures for movement, including pseudopodia, flagella, and cilia. (DOK 1, 2) Explain the structure and function of microvilli, and explain the benefit of microvilli to rate of absorption. (DOK 1, 2, 3) Compare and contrast active ...
... Describe the structure and explain the function of various cellular structures for movement, including pseudopodia, flagella, and cilia. (DOK 1, 2) Explain the structure and function of microvilli, and explain the benefit of microvilli to rate of absorption. (DOK 1, 2, 3) Compare and contrast active ...
No Slide Title
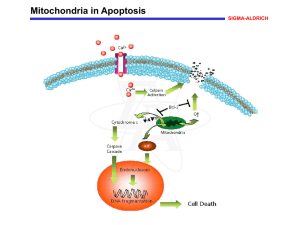
... Increases in cytosolic Ca2+ levels due to activation of ion channel-linked receptors, such as that for the excitatory amino acid neurotransmitter glutamic acid, can induce permeability transition (PT) of the mitochondrial membrane. PT constitutes the first rate-limiting event of the common pathway o ...
... Increases in cytosolic Ca2+ levels due to activation of ion channel-linked receptors, such as that for the excitatory amino acid neurotransmitter glutamic acid, can induce permeability transition (PT) of the mitochondrial membrane. PT constitutes the first rate-limiting event of the common pathway o ...
The rate of photosynthesis may vary with change that occur in
... c. Identify differences between transcription and translation. d. Describe structural changes that can occur in a protein after translation to make it function properly. Mitosis/Meiosis ...
... c. Identify differences between transcription and translation. d. Describe structural changes that can occur in a protein after translation to make it function properly. Mitosis/Meiosis ...