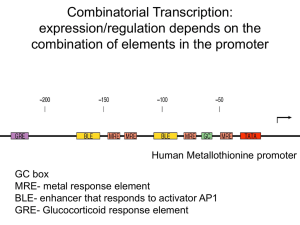
Combinatorial Transcription: expression/regulation depends on the
... Figure 3 Mechanism of insulator effect on enhancer function. (a) Diagram of two genes, X and Y, located within a chromosomal domain defined by two insulator sequences (ins) and their associated proteins (ibp). Enhancers located between the two genes (en1and en2) can activate transcription from the ...
... Figure 3 Mechanism of insulator effect on enhancer function. (a) Diagram of two genes, X and Y, located within a chromosomal domain defined by two insulator sequences (ins) and their associated proteins (ibp). Enhancers located between the two genes (en1and en2) can activate transcription from the ...
Dichotomy in the definition of prescriptive information suggests both
... logical base 4 system. (To be fully correct, we would have to include cytosine methylation as the source of an additional configurable switch-setting option, and other nonbiological bases, including non-right-handed sugar nucleotides, in the alphabet of possible tokens that could theoretically polym ...
... logical base 4 system. (To be fully correct, we would have to include cytosine methylation as the source of an additional configurable switch-setting option, and other nonbiological bases, including non-right-handed sugar nucleotides, in the alphabet of possible tokens that could theoretically polym ...
RNA or DNA Extractions: Where can I get my samples extracted
... microarray staff for successful RNA recovery from cells sorted using flow cytometry. Several key points are highlighted below: Preparing the flow cytometry is not a small task as it must be completely free of RNases from the sheath tank to the sorting nozzle. This decontamination procedure will take ...
... microarray staff for successful RNA recovery from cells sorted using flow cytometry. Several key points are highlighted below: Preparing the flow cytometry is not a small task as it must be completely free of RNases from the sheath tank to the sorting nozzle. This decontamination procedure will take ...
Meiosis pre test
... B. DNA > mRNA > Protein > tRNA C. DNA > mRNA > tRNA > amino acids > protein ...
... B. DNA > mRNA > Protein > tRNA C. DNA > mRNA > tRNA > amino acids > protein ...
Chapters 16-17 (DNA and protein synthesis)
... - There are 64 different codons, which each code for one of the 20 amino acids The base triples along the template strand of a gene of DNA are transcribed into mRNA codons. The same strand of a DNA molecule can be the template strand for one gene and the complementary strand for another. The mRNA is ...
... - There are 64 different codons, which each code for one of the 20 amino acids The base triples along the template strand of a gene of DNA are transcribed into mRNA codons. The same strand of a DNA molecule can be the template strand for one gene and the complementary strand for another. The mRNA is ...
Notes - Haiku Learning
... b) Different sections of a gene act as introns at different times which increases the number of proteins that can be made by one gene ...
... b) Different sections of a gene act as introns at different times which increases the number of proteins that can be made by one gene ...
Ribosome Display: In Vitro Selection of Protein
... To perform ribosome display, one needs a highquality library in the appropriate format. This section does not explain how to generate this library, as this depends entirely on the experimental goal, but rather how to convert an existing one into a format suitable for ribosome disp lay. A ribosome-di ...
... To perform ribosome display, one needs a highquality library in the appropriate format. This section does not explain how to generate this library, as this depends entirely on the experimental goal, but rather how to convert an existing one into a format suitable for ribosome disp lay. A ribosome-di ...
From Genes to Proteins
... on the gene being expressed. When a cell needs a particular protein, it is messenger RNA that is made. Messenger RNA (mRNA) is a form of RNA that carries the instructions for making a protein from a gene and delivers it to the site of translation. The information is translated from the language of R ...
... on the gene being expressed. When a cell needs a particular protein, it is messenger RNA that is made. Messenger RNA (mRNA) is a form of RNA that carries the instructions for making a protein from a gene and delivers it to the site of translation. The information is translated from the language of R ...
SURVEY AND SUMMARY Origins of tmRNA: the
... as the elimination of the related incomplete proteins and mRNA. A particular RNA performs this process: tmRNA associated with Small protein B (SmpB). tmRNA is a hybrid molecule carrying out both transfer and messenger RNA activities, and its total length varies between about 260 and 430 nucleotides, ...
... as the elimination of the related incomplete proteins and mRNA. A particular RNA performs this process: tmRNA associated with Small protein B (SmpB). tmRNA is a hybrid molecule carrying out both transfer and messenger RNA activities, and its total length varies between about 260 and 430 nucleotides, ...
Use of Cellular Decapping Activators by Positive
... The (+)RNA viruses have developed a myriad of strategies to shield their RNA from degradation by Xrn1, often by directly suppressing or degrading the cellular decay machinery. For example, picornaviruses use an aggressive mechanism to combat decay by inducing the rapid degradation of Xrn1 and Dcp1 [ ...
... The (+)RNA viruses have developed a myriad of strategies to shield their RNA from degradation by Xrn1, often by directly suppressing or degrading the cellular decay machinery. For example, picornaviruses use an aggressive mechanism to combat decay by inducing the rapid degradation of Xrn1 and Dcp1 [ ...
Giant DNA Lab Manual.
... will be much easier to keep your DNA strands lined up. This lab must be your own work. Your lab report will be worth 20 points and must consist of answers to the following questions: Make up a protein that is 5 amino acids long. You will then design a gene from the hypothetical organism used in this ...
... will be much easier to keep your DNA strands lined up. This lab must be your own work. Your lab report will be worth 20 points and must consist of answers to the following questions: Make up a protein that is 5 amino acids long. You will then design a gene from the hypothetical organism used in this ...
Complex Degradation Processes Lead to Non
... extent by endonucleolytic degradation than prokaryotic mRNAs [5]. In eukaryotic cells, the most common mechanisms of degradation are those that lead to decapping. This mechanism requires deadenylation at the 39 region and the destabilization of the 59 cap structure before degradation occurs in the 5 ...
... extent by endonucleolytic degradation than prokaryotic mRNAs [5]. In eukaryotic cells, the most common mechanisms of degradation are those that lead to decapping. This mechanism requires deadenylation at the 39 region and the destabilization of the 59 cap structure before degradation occurs in the 5 ...
Modeling Transcription and Translation
... Students will discuss their initial responses with a table partner, then make a final response as group. Students will be given a chance to revise or leave answers. The teacher will discuss and reveal the correct answers for the APK activities with the class. The teacher will provide feedback to stu ...
... Students will discuss their initial responses with a table partner, then make a final response as group. Students will be given a chance to revise or leave answers. The teacher will discuss and reveal the correct answers for the APK activities with the class. The teacher will provide feedback to stu ...
here - IMSS Biology 2014
... changes make no difference to the organism, whereas others can change cells and organisms.” ...
... changes make no difference to the organism, whereas others can change cells and organisms.” ...
INTRODUCTION
... • Transcription literally means the act or process of making a copy • In genetics, the term refer to the copying of a DNA sequence into an RNA sequence • The structure of DNA is not altered as a result of this process – It can continue to store information Copyright ©The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. ...
... • Transcription literally means the act or process of making a copy • In genetics, the term refer to the copying of a DNA sequence into an RNA sequence • The structure of DNA is not altered as a result of this process – It can continue to store information Copyright ©The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. ...
Messenger RNA reprogramming by spliceosome-mediated
... leading to the production of the expected 1•2•3 mRNA is shown (i). Three targeted SMaRT reactions are shown. PTM[A] contains a functional 5′ splice site that can trans-splice to the 3′ splice site adjacent to exon 2 in the pre-mRNA target (ii). This trans-splicing produces a chimeric A•2•3 mRNA. PTM ...
... leading to the production of the expected 1•2•3 mRNA is shown (i). Three targeted SMaRT reactions are shown. PTM[A] contains a functional 5′ splice site that can trans-splice to the 3′ splice site adjacent to exon 2 in the pre-mRNA target (ii). This trans-splicing produces a chimeric A•2•3 mRNA. PTM ...
Biochemistry
... helix unwinds, and the bases on the two strands are exposed. RNA nucleotides (ribonucleotides) line up in the proper order by hydrogen-bonding to their complementary bases on DNA, the nucleotides are joined together by a DNA dependent RNA polymerase enzyme, and mRNA results. UNLIKE what happens in D ...
... helix unwinds, and the bases on the two strands are exposed. RNA nucleotides (ribonucleotides) line up in the proper order by hydrogen-bonding to their complementary bases on DNA, the nucleotides are joined together by a DNA dependent RNA polymerase enzyme, and mRNA results. UNLIKE what happens in D ...
Document
... directly, shutting themselves down in response to particular chemical clues. • Breaker, Nudler, Yura and Cossart laboratories report that specific RNA sequences can act as environmental sensors of vitamin cofactors (including vitamins B1, B2 and B12) and temperature, which allow them to directly reg ...
... directly, shutting themselves down in response to particular chemical clues. • Breaker, Nudler, Yura and Cossart laboratories report that specific RNA sequences can act as environmental sensors of vitamin cofactors (including vitamins B1, B2 and B12) and temperature, which allow them to directly reg ...
Document
... • Proteins with quaternary structure may display cooperative binding • Cooperativity is caused by conformational changes in the first protein subunit which lead to conformational and binding rate changes in neighboring subunits • Regulatory molecules usually change conformation and therefore propert ...
... • Proteins with quaternary structure may display cooperative binding • Cooperativity is caused by conformational changes in the first protein subunit which lead to conformational and binding rate changes in neighboring subunits • Regulatory molecules usually change conformation and therefore propert ...
DNA and Proteins - Furman University
... the muscle proteins in muscle cells that contract) or involve in transport (membrane proteins). That is what we will look at in this lecture. Basically, DNA is a recipe for proteins. By making these proteins, a cell can make anything else it needs from what it absorbs from the environment. So, it is ...
... the muscle proteins in muscle cells that contract) or involve in transport (membrane proteins). That is what we will look at in this lecture. Basically, DNA is a recipe for proteins. By making these proteins, a cell can make anything else it needs from what it absorbs from the environment. So, it is ...
Bio-201-chapter-5-MEC
... • Many herbivores, from cows to termites, have symbiotic relationships with these microbes ...
... • Many herbivores, from cows to termites, have symbiotic relationships with these microbes ...
Cell Division Mitosis vs. Meiosis - kromko
... ribosome. The initiator tRNA fits into one of the two tRNA-binding sites on the ribosome. This site, called the P site, will hold the growing polypeptide. The other tRNA-binding site, called the A site, is vacant and ready for the next amino-acidbearing tRNA molecule. Important Note: Each amino acid ...
... ribosome. The initiator tRNA fits into one of the two tRNA-binding sites on the ribosome. This site, called the P site, will hold the growing polypeptide. The other tRNA-binding site, called the A site, is vacant and ready for the next amino-acidbearing tRNA molecule. Important Note: Each amino acid ...
Dynamics of protein noise can distinguish between alternate
... illustrated in Figure 2, which plots the function f ðgm ; gp ; Zm ; tÞ for different values of Zm, and hence different relative contributions of mRNA birth/death and promoter fluctuations to expression noise. More specifically, as we increase Zm, the initial rise in the protein-noise level becomes mor ...
... illustrated in Figure 2, which plots the function f ðgm ; gp ; Zm ; tÞ for different values of Zm, and hence different relative contributions of mRNA birth/death and promoter fluctuations to expression noise. More specifically, as we increase Zm, the initial rise in the protein-noise level becomes mor ...
Messenger RNA

Messenger RNA (mRNA) is a large family of RNA molecules that convey genetic information from DNA to the ribosome, where they specify the amino acid sequence of the protein products of gene expression. Following transcription of primary transcript mRNA (known as pre-mRNA) by RNA polymerase, processed, mature mRNA is translated into a polymer of amino acids: a protein, as summarized in the central dogma of molecular biology.As in DNA, mRNA genetic information is in the sequence of nucleotides, which are arranged into codons consisting of three bases each. Each codon encodes for a specific amino acid, except the stop codons, which terminate protein synthesis. This process of translation of codons into amino acids requires two other types of RNA: Transfer RNA (tRNA), that mediates recognition of the codon and provides the corresponding amino acid, and ribosomal RNA (rRNA), that is the central component of the ribosome's protein-manufacturing machinery.The existence of mRNA was first suggested by Jacques Monod and François Jacob, and subsequently discovered by Jacob, Sydney Brenner and Matthew Meselson at the California Institute of Technology in 1961.























