Absence of Inferior Gluteal Artery: A Rare Observation
... the superior gluteal artery constantly divides into two main branches, which are called the ascending and transverse branches. Of the ascending and transverse branches, one or both usually give off at least one well developed division running on the undersurface of the gluteus maximus muscle (98.2%) ...
... the superior gluteal artery constantly divides into two main branches, which are called the ascending and transverse branches. Of the ascending and transverse branches, one or both usually give off at least one well developed division running on the undersurface of the gluteus maximus muscle (98.2%) ...
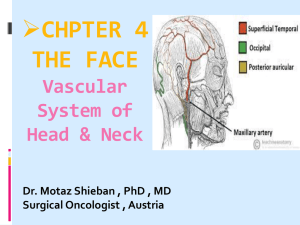
The Arterial System of the Head and Neck of the
... courses posteriorly, upwards and medially, passing between the styloglossus and stylopharyngeus muscles which it supplies. The vessel terminates on the lateral pharyngeal wall at the level of the palatine tonsil. The submandibular artery is an important vessel which arises from the facial artery whe ...
... courses posteriorly, upwards and medially, passing between the styloglossus and stylopharyngeus muscles which it supplies. The vessel terminates on the lateral pharyngeal wall at the level of the palatine tonsil. The submandibular artery is an important vessel which arises from the facial artery whe ...
I. Appendix of Specific Techniques
... Make sure you are in the very middle by checking in the coronal view that you are between the two hemispheres (Fig 5). Most Posterior Point: Again, go to the sagittal view. You must scroll through again because sometimes the head can be tilted to the left or right (which is visible in the axial view ...
... Make sure you are in the very middle by checking in the coronal view that you are between the two hemispheres (Fig 5). Most Posterior Point: Again, go to the sagittal view. You must scroll through again because sometimes the head can be tilted to the left or right (which is visible in the axial view ...
Vascular anatomy of the head and neck region, pictorial
... Common carotid artery (CC) CC runs behind sternocleidomastoid muscle paired with the internal jugular vein which is located laterally, c.n. X (vagus nerve) stays between them Fig.10. The structures are contained in a sheath known as the carotid sheath, which is derived from the deep cervical fascia ...
... Common carotid artery (CC) CC runs behind sternocleidomastoid muscle paired with the internal jugular vein which is located laterally, c.n. X (vagus nerve) stays between them Fig.10. The structures are contained in a sheath known as the carotid sheath, which is derived from the deep cervical fascia ...
The Cranial Nerves and Trigeminal Nerve Blocks
... The oculomotor, trochlear, and abducent nerves innervate the muscles that move the eyeball. The oculomotor nerve supplies all the orbital muscles except the superior oblique and the lateral rectus. It also supplies the levator palpebrae superioris and the smooth muscles concerned with accommodation— ...
... The oculomotor, trochlear, and abducent nerves innervate the muscles that move the eyeball. The oculomotor nerve supplies all the orbital muscles except the superior oblique and the lateral rectus. It also supplies the levator palpebrae superioris and the smooth muscles concerned with accommodation— ...
Gross Anatomical Classification of the Courses of the Human
... submental artery was first exposed and only the mandible was removed. The mylohyoid was then brought down laterally and the anatomical structures throughout the sublingual surface of the tongue to the sublingual region were then exposed from outside with special regard to the same structures as thos ...
... submental artery was first exposed and only the mandible was removed. The mylohyoid was then brought down laterally and the anatomical structures throughout the sublingual surface of the tongue to the sublingual region were then exposed from outside with special regard to the same structures as thos ...
study of arcuate foramen of atlas vertebrae
... Results: Arcuate foramen was found in 5 atlas vertebra (8.6%), one was bilateral and others were unilateral with equal incidence in right and left side. The mean length of the arcuate foramen was 6.09mm and the mean height of the arcuate foramen was 5.44mm. Ponticulus posterior was observed in 4 sid ...
... Results: Arcuate foramen was found in 5 atlas vertebra (8.6%), one was bilateral and others were unilateral with equal incidence in right and left side. The mean length of the arcuate foramen was 6.09mm and the mean height of the arcuate foramen was 5.44mm. Ponticulus posterior was observed in 4 sid ...
absence of superficial palmar arch with persistent
... median artery. The arterial supply to the palm is in the form of superficial and deep palmar arches. In the present case the median artery and ulnar artery supplies the palm without forming an arch on the left extremity. Awareness of variations in the vascular pattern of the palm is clinically impor ...
... median artery. The arterial supply to the palm is in the form of superficial and deep palmar arches. In the present case the median artery and ulnar artery supplies the palm without forming an arch on the left extremity. Awareness of variations in the vascular pattern of the palm is clinically impor ...
THE MUSCULATURE OF THE LABRUM, LABIUM AMD
... of the labral, labial, hypopharyngeal and pharyngeal muscles, it is necessary to remove the maxillae, mandibles and the corresponding muscles* The maxillary, mandibular and antennal muscles are not included in this study* This particular work evolved from an interest as to how chewing insects actual ...
... of the labral, labial, hypopharyngeal and pharyngeal muscles, it is necessary to remove the maxillae, mandibles and the corresponding muscles* The maxillary, mandibular and antennal muscles are not included in this study* This particular work evolved from an interest as to how chewing insects actual ...
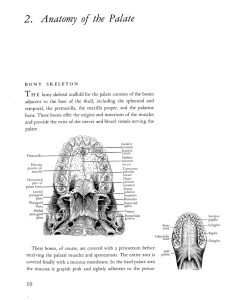
anatomy of the head and neck
... medial plate bends over to form a hook‐like process called the hamulus pterygoideus. The tendon of m. tensor palatini (one of the muscles of the soft palate), which arises here, passes around the hamulus pterygoideus. THE TEMPORAL BONE The temporal bone (os tempor ...
... medial plate bends over to form a hook‐like process called the hamulus pterygoideus. The tendon of m. tensor palatini (one of the muscles of the soft palate), which arises here, passes around the hamulus pterygoideus. THE TEMPORAL BONE The temporal bone (os tempor ...
Globa Lilian - Anatomia omului
... system, the brain and the sensory organs connected with it; moreover, it encloses the initial part of the digestive and respiratory tracts communicating with the external environment. In accordance with this, the skull of all vertebrates is divided into two parts: the cerebral cranium (neurocranium) ...
... system, the brain and the sensory organs connected with it; moreover, it encloses the initial part of the digestive and respiratory tracts communicating with the external environment. In accordance with this, the skull of all vertebrates is divided into two parts: the cerebral cranium (neurocranium) ...
Absence of Isthmus of Thyroid Gland - A Case Report
... Thyroid gland is first endocrine gland to develop in embryo . 1 It begins to form about 24 days after fertilization from a median endodermal thickening in the floor of the primitive pharynx near junction of first & second pharyngeal arches between tuberculum impar and copula respectively.1,2 This th ...
... Thyroid gland is first endocrine gland to develop in embryo . 1 It begins to form about 24 days after fertilization from a median endodermal thickening in the floor of the primitive pharynx near junction of first & second pharyngeal arches between tuberculum impar and copula respectively.1,2 This th ...
cross and radiological studies of the salivary gland in cattle
... between the buccal muscles , these glands are well developed and are arranged in three groups , dorsal ventral also middle buccal glands Fig (9) can be distinguished , the dorsal buccal glands extended from the angle of the mouth to the maxillary tuber , the ventral buccal gland reaches from the ang ...
... between the buccal muscles , these glands are well developed and are arranged in three groups , dorsal ventral also middle buccal glands Fig (9) can be distinguished , the dorsal buccal glands extended from the angle of the mouth to the maxillary tuber , the ventral buccal gland reaches from the ang ...
Acland`s DVD Atlas of Human Anatomy Transcript for Volume 4
... the intervertebral disks and the intervertebral joints. Then we’ll look at three ligaments that run the length of the cervical spine - the nuchal ligament, and the anterior and posterior longitudinal ligaments. Lastly we’ll look at the special ligaments around the odontoid process. ...
... the intervertebral disks and the intervertebral joints. Then we’ll look at three ligaments that run the length of the cervical spine - the nuchal ligament, and the anterior and posterior longitudinal ligaments. Lastly we’ll look at the special ligaments around the odontoid process. ...
2 Embryology and Surgical Anatomy of the Thyroid and Parathyroid
... In this case, a lingual thyroid is located at the junction of the oral and pharyngeal parts of the tongue (Fig. 2.1b). Ectopic thyroid tissue may occur at any point along the pathway of the descent of the thyroid. In rare conditions, the thyroid may descend into the thorax. There may also be remnant ...
... In this case, a lingual thyroid is located at the junction of the oral and pharyngeal parts of the tongue (Fig. 2.1b). Ectopic thyroid tissue may occur at any point along the pathway of the descent of the thyroid. In rare conditions, the thyroid may descend into the thorax. There may also be remnant ...
An autonomic pathway from the central nervous system to the
... All of the following statements about the posterior third of the tongue are correct EXCEPT A. it is located posterior to the sulcus terminalis. B. it receives general sensory supply via the glossopharyngeal nerve. C. it is located in the oropharynx. D. it is derived from the first branchial arch. E. ...
... All of the following statements about the posterior third of the tongue are correct EXCEPT A. it is located posterior to the sulcus terminalis. B. it receives general sensory supply via the glossopharyngeal nerve. C. it is located in the oropharynx. D. it is derived from the first branchial arch. E. ...
abberrant patterns of branching of external carotid artery
... (ECA) extends from the level of upper border of the lamina of thyroid cartilage to a point behind the neck of the mandible. During its course it gives altogether eight branches, of which the superficial temporal and maxillary arteries are its terminal branches (Dutta, 1994). The ascending pharyngeal ...
... (ECA) extends from the level of upper border of the lamina of thyroid cartilage to a point behind the neck of the mandible. During its course it gives altogether eight branches, of which the superficial temporal and maxillary arteries are its terminal branches (Dutta, 1994). The ascending pharyngeal ...
Title Morphologic characteristics of the superior pharyngeal
... articulation develop after birth, and as the superior pharyngeal constrictor muscle at the buccopharyngeal part and buccinator muscle act cooperatively, the morphology of the pterygomandibular raphe changes to suit particular functions. According to Casey [12], the superior pharyngeal constrictor m ...
... articulation develop after birth, and as the superior pharyngeal constrictor muscle at the buccopharyngeal part and buccinator muscle act cooperatively, the morphology of the pterygomandibular raphe changes to suit particular functions. According to Casey [12], the superior pharyngeal constrictor m ...
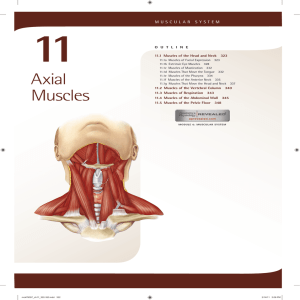
11. Axial Muscles
... Several muscles of facial expression are associated with the nose. The nasalis elevates the corners of the nostrils. When you “flare your nostrils,” you are using the nasalis muscles. If you wrinkle your nose in distaste after smelling a foul odor, you have used your procerus muscle. This muscle is ...
... Several muscles of facial expression are associated with the nose. The nasalis elevates the corners of the nostrils. When you “flare your nostrils,” you are using the nasalis muscles. If you wrinkle your nose in distaste after smelling a foul odor, you have used your procerus muscle. This muscle is ...
ent methods by associate professor dr. ayub ahmad khan
... Place the light source in the supermedial angle of the orbit and see light transmit through anterior wall of the sinus 9. EXAMINATION OF ASSOCIATED STRUCTURES a) Oral exam: tongue, buccal mucosa, palette, teeth (percus), gag reflex b) Posterior rhinoscopy: warm the curved mirror and bring it to the ...
... Place the light source in the supermedial angle of the orbit and see light transmit through anterior wall of the sinus 9. EXAMINATION OF ASSOCIATED STRUCTURES a) Oral exam: tongue, buccal mucosa, palette, teeth (percus), gag reflex b) Posterior rhinoscopy: warm the curved mirror and bring it to the ...
Cranial Nerves Organization of the Cranial Nerves The cranial
... that lies deep to the submandibular salivary gland and is attached to the lingual nerve by small nerves . Preganglionic parasympathetic fibersreach the ganglion from the facial nerve via the chorda tympani and the lingual nerves. Postganglionic secretomotor fibers pass to the submandibular and the s ...
... that lies deep to the submandibular salivary gland and is attached to the lingual nerve by small nerves . Preganglionic parasympathetic fibersreach the ganglion from the facial nerve via the chorda tympani and the lingual nerves. Postganglionic secretomotor fibers pass to the submandibular and the s ...
CHAPTER 7
... inferior horn (inferior cornu) of the thyroid cartilage - whose tip forms a true synovial joint with the more deeply placed cricoid cartilage. On the external surface of each lamina is a curvilinear ridge running downward and then a bit forward. This is called the oblique line and serves as the atta ...
... inferior horn (inferior cornu) of the thyroid cartilage - whose tip forms a true synovial joint with the more deeply placed cricoid cartilage. On the external surface of each lamina is a curvilinear ridge running downward and then a bit forward. This is called the oblique line and serves as the atta ...
middle meningeal artery
... • The second part of the maxillary artery also has five branches, but they differ from those of the first part is not entering bone. Muscular branches include deep temporal arteries (anterior, middle and posterior branches), pterygoid arteries and masseteric arteries . the deep temporal arteries pas ...
... • The second part of the maxillary artery also has five branches, but they differ from those of the first part is not entering bone. Muscular branches include deep temporal arteries (anterior, middle and posterior branches), pterygoid arteries and masseteric arteries . the deep temporal arteries pas ...
Tongue

The tongue is a muscular hydrostat on the floor of the mouth of most vertebrates which manipulates food for mastication. It is the primary organ of taste (gustation), as much of its upper surface is covered in taste buds. The tongue's upper surface is also covered in numerous lingual papillae. It is sensitive and kept moist by saliva, and is richly supplied with nerves and blood vessels. In humans a secondary function of the tongue is phonetic articulation. The tongue also serves as a natural means of cleaning one's teeth. The ability to perceive different tastes is not localised in different parts of the tongue, as is widely believed. This error arose because of misinterpretation of some 19th-century research (see tongue map).